Question 1
Kerryn Brown, aged 42 years, is rushed into your rural emergency department because she has suddenly felt unwell. Her heart is racing rapidly, her chest feels tight and she feels short of breath. On examination, her temperature is 36.2 °C, heart rate is 153/min, blood pressure is 100/70 mmHg (lying down), respiratory rate is 20/min and oxygen saturation is 95% on room air. An electrocardiogram is performed (see image). Initial non-pharmacological management is ineffective.
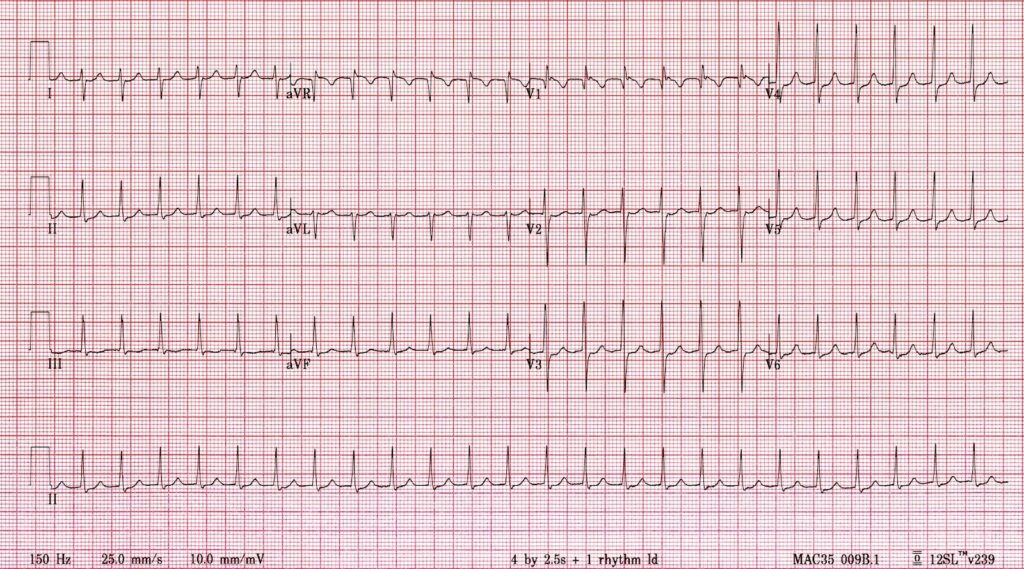
What is the MOST appropriate pharmacological treatment?
A. Adenosine 6 mg intravenously stat
B. Amiodarone 300 mg intravenously stat
C. Apixaban 5 mg orally twice daily
D. Aspirin 300 mg orally stat
E. Metoprolol 50 mg orally stat
Correct Answer: A. Adenosine 6 mg intravenously stat
Question 2
Yvonne Hartley, aged 52 years, returns for blood test results. Twelve weeks earlier, she completed a course of sofosbuvir and velpatasvir for chronic hepatitis C infection. She contracted hepatitis C via a blood transfusion when she was travelling overseas in her 30s. Prior to treatment, she had a normal aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index score of < 1, and a FibroScan score of 0–1 kPa (normal range: < 5.3).
Further results are as follows:
| Test | Result | Normal range |
| Total protein | 71 g/L | 60 – 82 |
| Albumin | 38 g/L | 35 – 50 |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 65 umol/L | 30 – 120 |
| Bilirubin | 16 umol/L | < 25 |
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase | 21 U/L | < 51 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase | 18 U/L | < 41 |
| Alanine aminotransferase | 11 U/L | < 41 |
| Hepatitis C antibodies | Positive* | |
| Hepatitis C RNA | Negative | |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise that the hepatitis C treatment was not successful and refer to hepatologist
B. Liver ultrasound
C. Reassure her that the hepatitis C infection has been successfully treated
D. Recommend lifelong hepatocellular carcinoma screening
E. Repeat hepatitis C RNA in six months’ time
Correct Answer: C. Reassure her that the hepatitis C infection has been successfully treated
Question 3
Hermione Rogers, aged 5 years, presents with her mother, Mary, who has noticed some skin lesions on Hermione’s trunk that have been present for the past few weeks (see image). Hermione does not appear to be bothered by them.
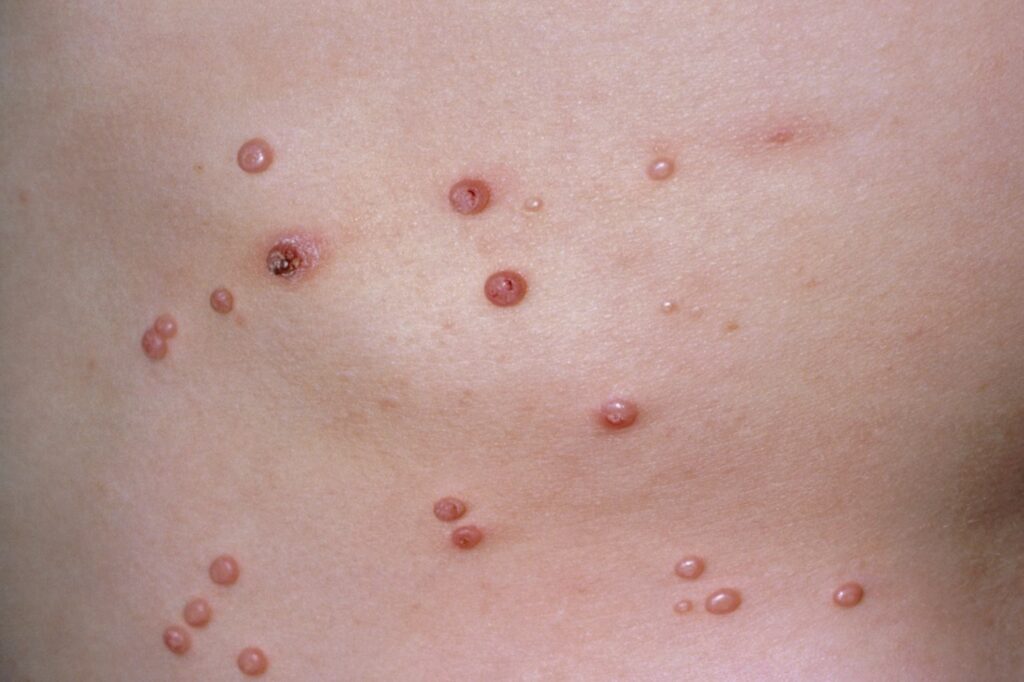
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Hydrocortisone 1% cream topically twice daily for two weeks
B. Imiquimod 5% cream topically daily for two weeks
C. Liquid nitrogen therapy applied to each lesion for 30 seconds
D. Reassure that no active management is required and let condition self-resolve
E. Salicylic acid 0.5% patches topically daily for four weeks
Correct Answer: D. Reassure that no active management is required and let condition self-resolve
Question 4
Selina Lopez, aged 34 years, presents for antenatal care following a positive home pregnancy test result five days earlier. She has been married for three years and this is her first pregnancy. Her last normal menstrual period was five weeks ago, and she has a 32-day cycle. Selina has polycystic ovarian syndrome and type 2 diabetes. She takes metformin 500 mg orally twice daily and a pregnancy multivitamin supplement daily. Her cervical screening test is up to date.
On examination, her heart rate is 70/min and blood pressure is 132/89 mmHg. Her body mass index is 28 kg/m2. Her abdomen is soft and non-tender.
You arrange appropriate antenatal blood and urine tests for Selina.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Aspirin 100 mg orally daily
B. Cease metformin and commence basal-bolus insulin regime
C. Enalapril 5 mg orally daily
D. Folic acid 5 mg orally daily
E. High vaginal swab for group B streptococcus
F. Iron polymaltose 100 mg orally daily
G. Nifedipine extended release 30 mg orally daily
H. Transvaginal ultrasound pelvis
Correct Answer: D. Folic acid 5 mg orally daily
Question 5
Thomas Maxwell, aged 55 years, had his random cholesterol checked at a community pharmacy and was advised the result was 7.8 mmol/L. He had a fasting lipid profile performed at your practice last year, which was normal. On examination, his heart rate is 70/min, blood pressure is 140/95 mmHg and body mass index is 27.8 kg/m2. You arrange a fasting blood test, and his investigation results are shown below.
| Test | Result | Normal range |
| Sodium | 142 mmol/L | 135 – 145 |
| Potassium | 4.7 mmol/L | 3.5 – 5.2 |
| Creatinine | 120 μmol/L | 40 – 120 |
| Estimated glomerular filtration rate | 80 mL/min/1.73m2 | > 90 |
| Total cholesterol | 7.5* mmol/L | 3.5 – 5.5 |
| Triglycerides | 1.2 mmol/L | 0.5 – 2.0 |
| High-density lipoprotein cholesterol | 0.6* mmol/L | > 1.0 |
| Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol | 5.5* mmol/L | < 3.5 |
| Blood glucose | 5.4 mmol/L | 4.0 – 5.4 |
Which investigation is MOST appropriate to evaluate for a secondary cause of his hypercholesterolaemia?
A. Early morning cortisol
B. Human leukocyte antigen B27
C. Liver function tests
D. Serum electrophoresis
E. Thyroid function test
Correct Answer: C. Liver function tests and E. Thyroid function test
Question 6
Millie West, aged 18 years, has had a painful right ear for three days. She had a new ear piercing two weeks earlier and has been applying antiseptic spray daily. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 37.6°C and the pinna is warm and tender to touch (see image). You advise removal of the piercing.
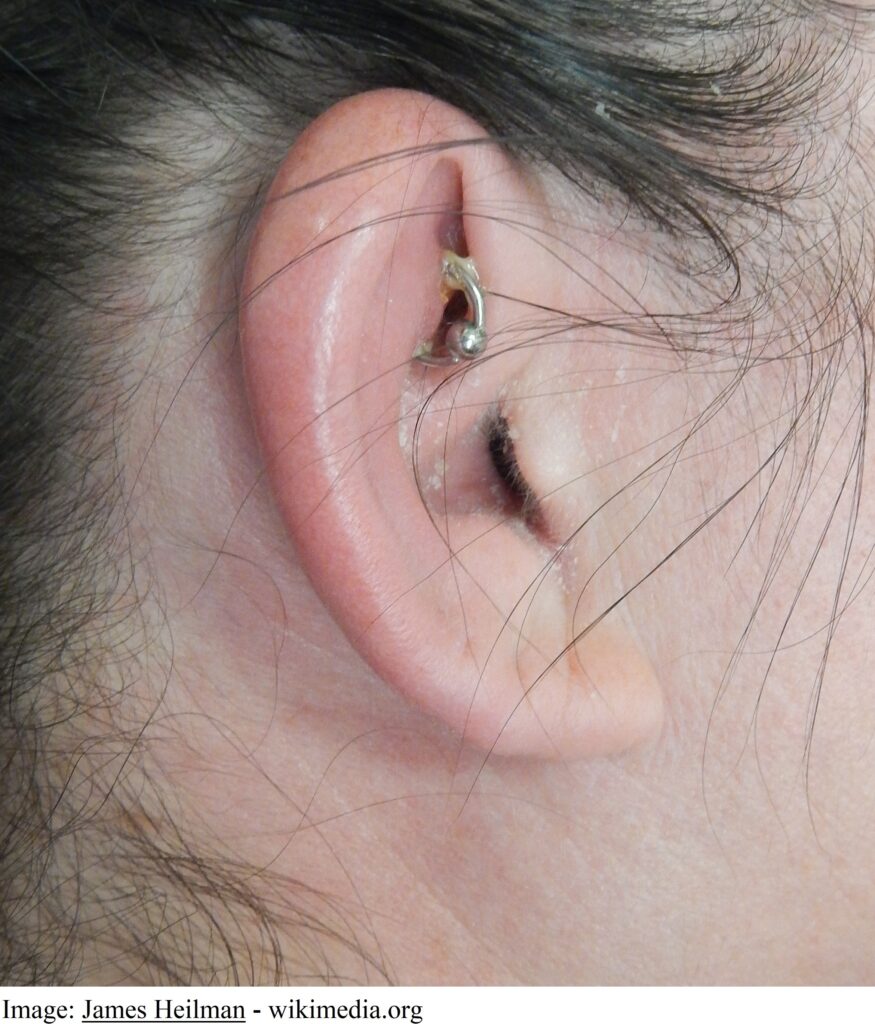
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Cetirizine 10 mg orally daily for three days
B. Ciprofloxacin 500 mg orally twice daily for seven days
C. Computed tomography scan head
D. Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for seven days
E. Magnetic resonance imaging head
F. Normal saline 0.9% soaked compresses applied twice daily
G. Prednisolone 50 mg orally daily for five days
H. Promethazine 50 mg orally at night for three days
Correct Answer: B. Ciprofloxacin 500 mg orally twice daily for seven days
Question 7
Adele Chan, aged 54 years, had three days of heavy vaginal bleeding last week, which has now stopped. Before this, she had amenorrhoea and hot flushes for the past 18 months. Adele was divorced three years ago and has had a new male partner for the past six months. On examination, there is vaginal atrophy. Bimanual pelvic examination is normal. You perform a co-test and take a cervical swab for chlamydia polymerase chain reaction, the results of which are all normal. Adele’s full blood count and thyroid stimulating hormone levels are within normal limits.
Transvaginal pelvic ultrasound result is as follows: The uterus is enlarged. The endometrium is not visualised due to the presence of a submucosal fibroid measuring 44 × 40 mm. A posterior intramural fibroid measuring 22 × 20 mm is also seen. Both ovaries appear normal.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise no further action required unless bleeding recurs
B. Arrange insertion of levonorgestrel 52 mg intrauterine device
C. Cervical swab for gonorrhoea polymerase chain reaction
D. Cervical swab for Mycoplasma genitalium polymerase chain reaction
E. Oestradiol 10 mcg intravaginally daily for two weeks, then twice per week
F. Oestradiol–dydrogesterone 1 mg/5 mg orally daily
G. Refer to gynaecologist for hysteroscopy and endometrial sampling
H. Serum oestradiol, progesterone, follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinising hormone
Correct Answer: G. Refer to gynaecologist for hysteroscopy and endometrial sampling
Question 8
Mary Rasheed, aged 7 years, is brought in by her father, James, as she has been vomiting for two days. She describes central abdominal pain, which is worse with urination. She has been off her food for the past few days. On examination, she appears tired and her tympanic temperature is 39.8°C, heart rate is 130/min and blood pressure is 110/60 mmHg. Abdominal examination reveals guarding and rebound tenderness in the right iliac fossa. Urine dipstick result is positive for ketones.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Arrange urgent transfer to paediatric emergency department for surgical assessment
B. Cefalexin 25 mg/kg (max 500 mg) orally four times daily for five days
C. Full blood count, C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate
D. Urgent computed tomography scan abdomen
E. Urgent ultrasound abdomen
Correct Answer: A. Arrange urgent transfer to paediatric emergency department for surgical assessment
Question 9
Donald Lynam, aged 54 years, has been struggling with alcohol misuse since his divorce five years earlier. He started drinking again four months ago, which ended in an acute crisis and inpatient alcohol detoxification last week. You see him today, three days after discharge, and he has not had any alcohol in seven days. He is receiving counselling and attends Alcoholics Anonymous. His discharge summary shows normal liver and renal function.
Donald is motivated to continue life without drinking alcohol and would like to try a medication to help. He tried acamprosate in the past, but it caused nausea and diarrhoea so he stopped. He is worried that he may drink, even while on medication, despite his best intentions.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in pharmacological management?
A. Amitriptyline 10 mg orally at night
B. Baclofen 5 mg orally twice daily
C. Disulfiram 100 mg orally daily
D. Diazepam 5–10mg orally twice daily
E. Naloxone 5 mg orally daily
F. Naltrexone 50 mg orally daily
G. Quetiapine 50 mg orally at night
H. Topiramate 25 mg orally at night
I. Venlafaxine 75 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: F. Naltrexone 50 mg orally daily
Question 10
Bill Douglas aged 32 years, an Aboriginal man, presents to your rural clinic requesting a ‘kidney health check’ after hearing about renal disease in a public health campaign. He does not have any personal or family history of kidney disease. On examination, his body mass index is 21 kg/m2, blood pressure is 138/85 mmHg and the remainder of his examination is unremarkable. His urine dipstick result is positive for protein and you arrange urinary albumin:creatinine ratio testing, with results as follows:
| Test | Result | Normal range |
| Albumin | 121* mg/L | 0 – 30 |
| Creatinine | 6.0 mmol/L | |
| Albumin:creatinine ratio | 20* mg/mmol | 0 – 3.5 |
His estimated glomerular filtration rate is normal.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Perindopril 5 mg orally daily
B. Prostate-specific antigen
C. Repeat urinary albumin:creatinine ratio testing on first morning void sample within three months
D. Ultrasound kidneys, ureters and bladder
E. Urine microscopy, culture and sensitivity
Correct Answer: C. Repeat urinary albumin:creatinine ratio testing on first morning void sample within three months
Question 11
Genny Gomes, aged 29 years, is new to your practice, having relocated from interstate. She presents for an antenatal visit at 30 weeks’ gestation. This is her first pregnancy. She informs you that she takes famciclovir 1 g orally twice daily episodically for recurrences of genital herpes. She was diagnosed six years earlier and has recurrences about once per year. She asks if herpes will impact her delivery.
What is the MOST appropriate advice?
A. She can consider a normal vaginal delivery, as her baby’s risk of neonatal herpes is low
B. She has an increased risk of preterm labour and prelabour rupture of membranes
C. She should have an elective caesarian section at 38 weeks’ gestation
D. She should have sequential genital cultures for herpes polymerase chain reaction during late gestation to identify if she is shedding herpes virus
E. She will be commenced on intravenous acyclovir once labour starts
Correct Answer: A. She can consider a normal vaginal delivery, as her baby’s risk of neonatal herpes is low
Question 12
Gabriel Pesaturo, aged 5 years, has woken with a cough three nights a week for the last two months. His cough often settles after two inhalations of salbutamol 100 mcg via spacer. He has asthma that is triggered by upper respiratory infections, and is then treated with salbutamol 100 mcg two to six inhalations if required via spacer. On examination, his heart rate is 94/min regular, respiratory rate 28/min and weight 20 kg, following the 50th percentile. Auscultation of his chest is normal. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Add ciclesonide 160 mcg inhaler one puff daily via spacer
B. Add fluticasone proprionate 50 mcg inhaler two puffs twice daily via spacer
C. Add prednisolone 20 mg orally daily for three days
D. Chest X-ray
E. Recommend salbutamol 100 mcg two inhalations via spacer before bed
F. Refer for a bronchial provocation test
G. Refer to paediatrician to further assess the cough
H. Spirometry both pre and post salbutamol
Correct Answer: B. Add fluticasone proprionate 50 mcg inhaler two puffs twice daily via spacer
Question 13
Jayne Trott, aged 27 years, is 29 weeks’ pregnant. This is her first pregnancy. Her partner left her when he found out that she was pregnant, and for the past three months she has been feeling sad all the time. She is tired, finding it hard to sleep and not enjoying things like she used to. She has been seeing a psychologist, but she cannot concentrate during the sessions, and they are becoming less helpful for her. Her recent antenatal blood tests were normal. Jayne wants to know what she can take to help manage her symptoms during pregnancy and while breastfeeding.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Agomelatine 25 mg orally at night
B. Temazepam 10 mg orally at night
C. Explain antidepressants are not safe in pregnancy
D. Fluoxetine 20 mg orally daily
E. Melatonin extended release 2 mg orally at night
F. Paroxetine 20 mg orally daily
G. Sertraline 50 mg orally daily
H. St John’s wart (Hypericum perforatum) 300 mg orally three times daily
Correct Answer: G. Sertraline 50 mg orally daily
Question 14
Rowan Bridges, aged 20 years, is brought to your rural emergency department by his father, Stephen, with increasing confusion and muscle pain for the past 24 hours. Rowan has a history of schizophrenia. He received his second dose of paliperidone 100 mg intramuscular injection one week earlier. His psychiatrist changed his therapy, as Rowan had difficulty remembering to take his medication. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 39.5°C, heart rate is 100/min and blood pressure is 165/100 mmHg. He is not orientated to his location and does not recognise his father. He has widespread rigidity of his muscles. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Acute alcohol overdose
B. Acute opiate intoxication
C. Bacterial endocarditis
D. Bacterial meningitis
E. Carcinoid syndrome
F. Dermatomyositis
G. Fulminant pancreatitis
H. Injection-site infection
I. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
J. Septicaemia
Correct Answer: I. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
Question 15
Benjamin Turner, aged 38 years, has had moderately severe, constant, non-radiating central chest pain for two days. The pain is worse when he breathes in and out. If he sits forward, the pain improves. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 37.1°C, heart rate 95/min regular, blood pressure 128/82 mmHg, respiratory rate 14/min and oxygen saturation 99% on room air. Cardiac auscultation reveals a squeaking sound with each contraction. The rest of his examination is unremarkable.
The practice nurse has performed an electrocardiogram (see image).
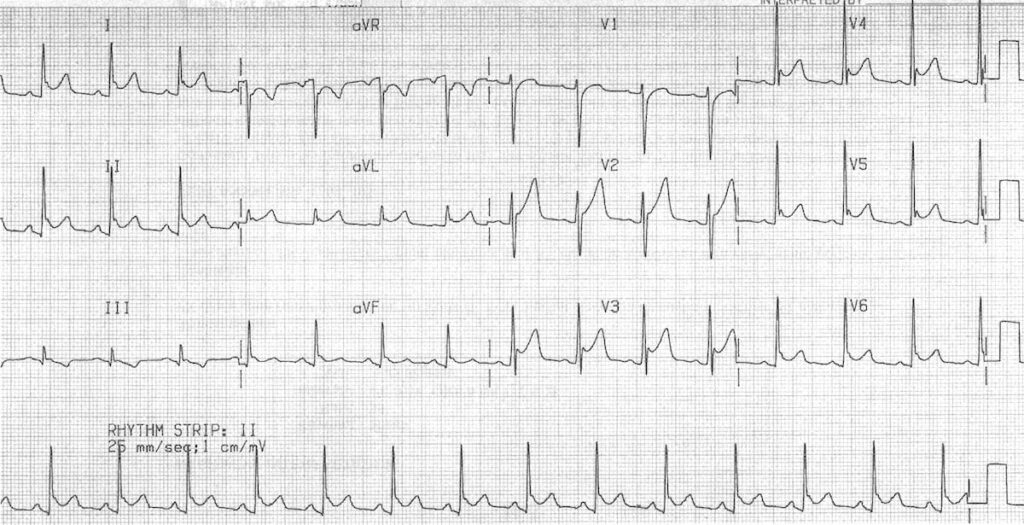
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Costochondritis
B. Ischaemic cardiomyopathy
C. Myocarditis
D. Pericarditis
E. Pleural effusion
F. Pneumonia
G. Pneumothorax
H. Pulmonary embolism
I. Rheumatic heart disease
Correct Answer: D. Pericarditis
Question 16
Hayden Gallagher, aged 10 years, is brought in by his mother, Samantha, due to right knee pain. He has had pain for the past month and it is becoming progressively worse when playing soccer. The pain settles with rest. On examination, he has significant tenderness below his right patella. An X-ray is performed (see image).
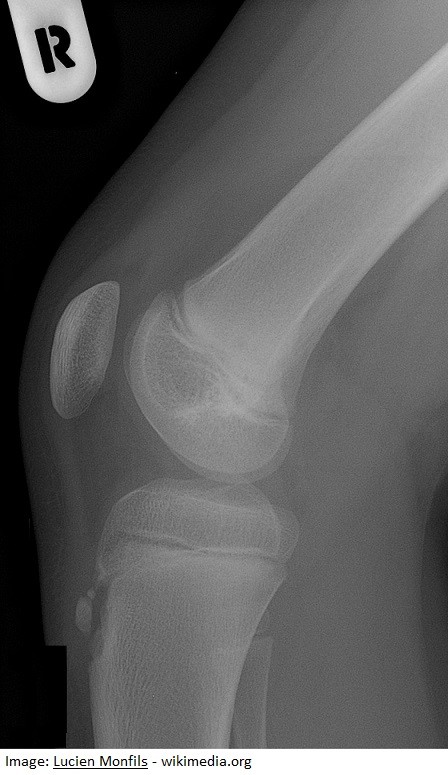
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Cortisone injection into pre-patellar bursa
B. Crutches with touch weight bearing on right leg for six weeks
C. Immobilise right knee with range of motion brace
D. Magnetic resonance imaging right knee
E. Modification of sporting activities
F. Nuclear bone scan right knee
G. Refer to orthopaedic surgeon for arthroscopy
H. Ultrasound right knee
Correct Answer: E. Modification of sporting activities
Question: 17
Savannah Rydges, aged 13 years, has had a rash on her upper arms for the past five months (see image). She is becoming increasingly self-conscious about the appearance. Savannah had eczema as an infant and is using a soap-free cleanser. She has also been applying 10% urea cream topically daily, with only slight improvement.
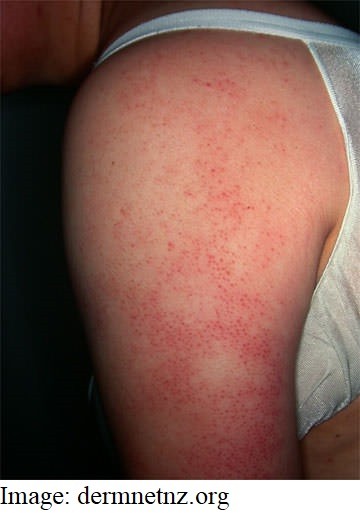
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Calcipotriol–betamethasone dipropionate 50 mcg/500 mcg ointment topically daily
B. Ethinylestradiol–levonorgestrel 20 mcg/100 mcg orally daily
C. Hydrocortisone 1% cream topically daily for 14 days
D. Terbinafine 1% cream topically twice daily for 14 days
E. Tretinoin 0.025% cream topically daily at night
Correct Answer: E. Tretinoin 0.025% cream topically daily at night
Question 18
Katherine Marsden, aged 18 years, has been feeling dizzy when exercising over the past two weeks. She hates how she looks and has been trying hard to lose weight. She has lost 5 kg over the past two months and her current weight is 50 kg. She tells you about her strict diet and an exercise regimen of long distance running. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 35.5°C, heart rate is 50/min (sitting) and 82/min (standing), blood pressure is 95/71 mmHg (sitting) and 90/65 mmHg (standing) and body mass index is 17 kg/m2.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Arrange a follow-up visit with her parents
B. Fluoxetine 20 mg orally daily
C. Inpatient admission to a specialist eating disorder clinic
D. Recommend increasing total daily protein consumption
E. Referral to a psychologist for family therapy sessions
Correct Answer: C. Inpatient admission to a specialist eating disorder clinic
Question 19
Dakota Williams, aged 24 years, would like to quit smoking. She has smoked 25 cigarettes per day for the past six years. She has a history of migraine and takes amitriptyline 50 mg orally at night for prophylaxis. Over the past six months, she has tried numerous methods to quit, including nicotine replacement therapy, psychological therapy, multiple books and ceasing without assistance. No method has worked successfully.
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Advise Dakota that pharmacological methods are contraindicated due to her migraine history
B. Bupropion 150 mg orally daily
C. Nortriptyline 25 mg orally daily
D. Refer for hypnotherapy
E. Varenicline 0.5 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: E. Varenicline 0.5 mg orally daily
Question 20
Abdul Bajwa, aged 72 years, has experienced chest tightness with exertion over the past three weeks, which is associated with shortness of breath and light-headedness. His symptoms all quickly settle when he rests. However, in the past week, his symptoms have worsened. On examination, his heart rate is 76/min, with a low volume pulse, and blood pressure is 110/95 mmHg. On chest auscultation, he has a soft systolic murmur at the right upper sternum and occasional soft crackles at the lung bases. His electrocardiogram today is normal.
What is the MOST appropriate investigation to confirm your provisional diagnosis?
A. Cardiac catheterization and angiography
B. Chest X-ray
C. Echocardiogram
D. Exercise stress test
E. Myocardial perfusion scan
Correct Answer: C. Echocardiogram
Question 21
Wil Sterling, aged 15 months, is brought in by his mother, Radhika. Earlier today, he slipped while walking down a flight of stairs while holding Radhika’s hand. She managed to pull him back onto his feet to prevent him falling, but since then he has been reluctant to use his left arm. Examination is consistent with your suspected provisional diagnosis.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Apply below-elbow volar backslab
B. Arrange urgent orthopaedic review
C. Place arm in a collar and cuff and arrange review tomorrow
D. Refer to physiotherapy for range of motion exercises
E. Strap the wrist and apply ice regularly for the first 48 hours
F. Ultrasound left shoulder
G. While applying pressure over the radial head, fully pronate the left forearm and flex the elbow
H. X-ray left wrist and elbow
Correct Answer: G. While applying pressure over the radial head, fully pronate the left forearm and flex the elbow
Question 22
Simone Basquet, aged 47 years, wishes to discuss lung cancer screening. Her father died four weeks earlier from small-cell lung cancer at 72 years of age. Simone has smoked five cigarettes per day for the past 10 years. She feels well and has no specific symptoms. On examination, chest auscultation is clear with equal air entry. You counsel her regarding smoking cessation.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise Simone to return if she develops symptoms of lung cancer
B. Annual clinical examination
C. Annual low-dose computed tomography scan chest
D. Chest X-ray every two years
E. Immediate high-resolution computed tomography scan chest
F. Positron emission tomography–computed tomography scan chest every two years
G. Referral to thoracic physician for screening bronchoscopy
H. Sputum for cytology collected on three consecutive mornings
Correct Answer: A. Advise Simone to return if she develops symptoms of lung cancer
Question 23
Craig Stevens, aged 68 years, has had a sore, swollen lump on his right thigh for the past three days. He is administered a goserelin 10.8 mg implant subcutaneously into his abdomen every three months for management of metastatic prostate cancer. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 37.2°C and there is a firm, erythematous, tender linear mass on his medial right thigh. You arrange a duplex Doppler ultrasound, which demonstrates a 6 cm thrombus in the greater saphenous vein, 4 cm from the saphenofemoral junction.
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Aspirin 100 mg orally daily
B. Cefalexin 500 mg orally four times daily
C. Diclofenac 1% gel topically three times daily
D. Diclofenac 50 mg orally three times daily
E. Enoxaparin 40 mg subcutaneously daily
F. Flucloxacillin 500 mg orally four times daily
G. Reassurance that no active management is required
H. Warfarin orally daily, with dose adjusted according to international normalised ratio
Correct Answer: E. Enoxaparin 40 mg subcutaneously daily
Question 24
Aruj Singh, aged 78 years, returns for review after a recent hospital admission for an infective exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. He has now fully recovered, but you note that this is his second exacerbation in the past six months that required hospitalisation. He was diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 10 years earlier. He had a computed tomography scan of his chest 18 months earlier that reported emphysematous changes and hyperinflation of the lungs. He currently uses vilanterol–umeclidinium 25 mcg/62.5 mcg inhaled once daily and salbutamol 100 mcg two inhalations as required. His oxygen saturation is 94% on room air.
Spirometry performed today is as follows:
| Test | Predicted value | Actual (pre-bronchodilator) value | % Predicted (pre- bronchodilator) | Actual (post-bronchodilator) value | % Change (post- bronchodilator) |
| Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1)(L) | 3.03 | 1.31 | 43 | 1.44 | 10 |
| Forced vital capacity (FVC)(L) | 3.79 | 2.18 | 57 | 2.35 | 8 |
| FEV1/FVC (%) | 77 | 60 | 78 | 66 | 10 |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Add fluticasone 100 mcg inhaled daily
B. Ambulatory oxygen
C. Change vilanterol–umeclidinium inhaler to formoterol–aclidinium 12 mcg/340 mcg inhaled twice daily
D. Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for seven days
E. Repeat high-resolution computed tomography scan chest
Correct Answer: A. Add fluticasone 100 mcg inhaled daily
Question 25
Steven Fine, aged 32 years, is brought to the surgery after collapsing outside your clinic. You ask your receptionist to call an ambulance. The nurse advises you that she has found some white powder in Steven’s jeans pocket. On examination, his arms and legs are twitching and he is making gurgling noises. There is a slight movement to painful stimulus but his eyes remain closed with some groaning, Glasgow coma scale 8. His tympanic temperature is 36 °C, heart rate 50/min regular, respiratory rate 12/min, oxygen saturation 94% on room air and blood pressure 90/50 mmHg. His pupils appear very small but reactive. There are no signs of external injury. You gain intravenous access and administer a 500 mL saline bolus.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Adrenaline 1 mg intravenously
B. Atropine 600 mcg intravenously
C. Isoprenaline 2 mcg via intravenous infusion
D. Naloxone hydrochloride 40 mcg intravenously slow push over one minute
E. Re-warming measures
Correct Answer: D. Naloxone hydrochloride 40 mcg intravenously slow push over one minute
Question 26
Ishmael Martujara, aged 22 years, is an inmate at a local prison that you visit weekly. He complains of ‘white spot’ disease, which has worsened over the summer (see image). It is not itchy or sore but he does not like the way it looks.
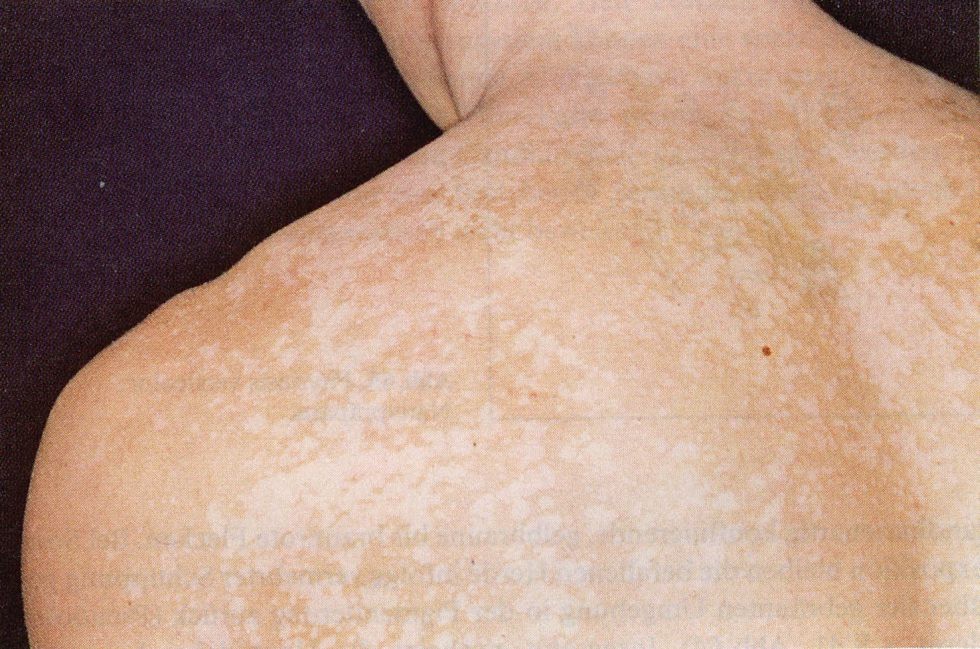
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Cephalexin 500 mg orally four times daily for five days
B. Hydrocortisone 1% topically to affected area three times daily for two weeks
C. Ketoconazole shampoo 2% topically to affected area daily for two weeks
D. Send skin biopsy for histopathology
E. Terbinafine 250 mg orally daily for four weeks
Correct Answer: C. Ketoconazole shampoo 2% topically to affected area daily for two weeks
Question 27
Thomas Jones, aged 74 years, an Aboriginal man, is a new patient to your practice. He has had a gradual reduction in his ability to complete his regular round of golf due to increasing fatigue over the past six weeks. He has a history of hypertension and rheumatic heart disease. Thomas is prescribed perindopril 4 mg orally daily and atenolol 50 mg orally daily.
On examination, his heart rate is 90/min irregular and blood pressure is 136/88 mmHg. He has a low- pitched diastolic murmur best heard at the cardiac apex. An electrocardiogram is performed (see image). You arrange appropriate investigations.
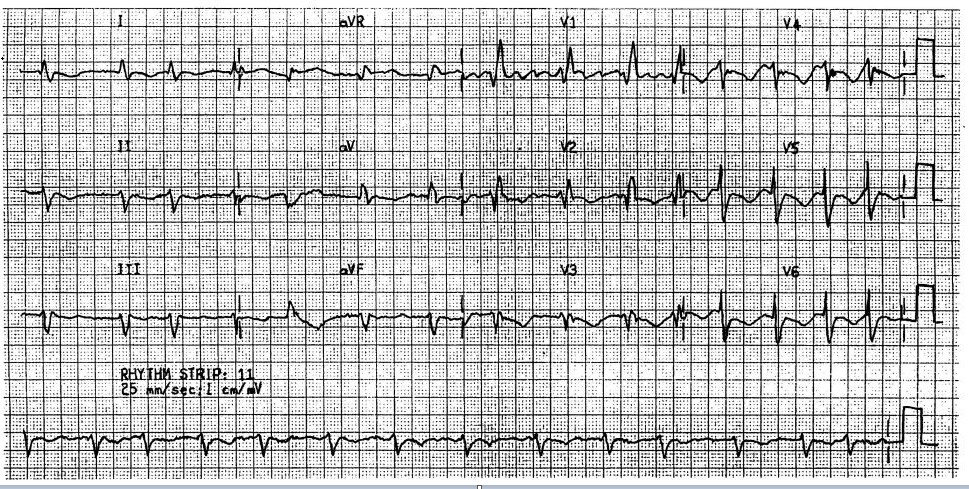
What is the MOST appropriate pharmacological management?
A. Aspirin 100 mg orally daily
B. Change atenolol to bisoprolol 1.25 mg orally
C. Clopidogrel 75 mg orally daily
D. Dipyridamole extended release–aspirin 200 mg/25 mg orally twice daily
E. Indapamide 1.25 mg orally daily
F. Rivaroxaban 20 mg orally daily
G. Spironolactone 25 mg orally daily
H. Warfarin orally daily, dose as per international normalised ratio
Correct Answer: H. Warfarin orally daily, dose as per international normalised ratio
Question 28
Samantha Burgell, aged 48 years, presents because her face has appeared different over the last 24 hours (see image). One week ago, Samantha presented with burning pain and then developed a mild herpes zoster rash in the C4 dermatome. She was treated with acyclovir 800 mg orally five times daily for seven days and appropriate analgesia. Her pain has now resolved. Samantha takes methotrexate 10 mg orally once weekly and prednisolone 15 mg orally daily for a mixed connective tissue disorder.

What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Amitriptyline 10 mg orally at night increasing up to 75 mg orally daily
B. Carbamazepine 100 mg orally twice daily for seven days before reviewing dosage
C. Increase total prednisolone dose to 1 mg/kg (up to 75 mg) orally daily for five days
D. Pregabalin 75 mg orally at night for seven days
E. Urgent referral to neurologist for nerve conduction studies
Correct Answer: C. Increase total prednisolone dose to 1 mg/kg (up to 75 mg) orally daily for five days
Question 29
Aiden Edwards, aged 18 years, asks about post-exposure prophylaxis, as he had potential exposure to human immunodeficiency virus. Aiden had anal sex with several men at a party two days earlier. He is unsure whether condoms were used. Aiden had a negative human immunodeficiency virus test two months earlier. You arrange baseline sexual health screening.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise that it is too late to take post-exposure prophylaxis
B. Commence pre-exposure prophylaxis
C. Explain that post-exposure prophylaxis is not recommended, as the sexual exposure is uncertain
D. Recommend that Aiden attends counselling to discuss safe sexual practices
E. Refer Aiden to a sexual health clinic or emergency department for consideration of post-exposure prophylaxis
Correct Answer: E. Refer Aiden to a sexual health clinic or emergency department for consideration of post-exposure prophylaxis
Question 30
James Kennedy, aged 73 years, presents with a one-month history of a persistently painful ulcer approximately 2 cm × 1 cm in size on his left foot (see image). It has failed to heal, despite dressings and a course of oral antibiotics. He was started on dipyridamole–aspirin 200 mg/25 mg orally twice daily after a recent stroke. He also takes enalapril 10 mg orally daily for hypertension and atorvastatin 40 mg orally daily for dyslipidaemia, and has diet-controlled type 2 diabetes. He is active and mobile and ceased smoking nine years earlier. His ankle-brachial pressure index is 0.40* (normal range: 1.0–1.4).
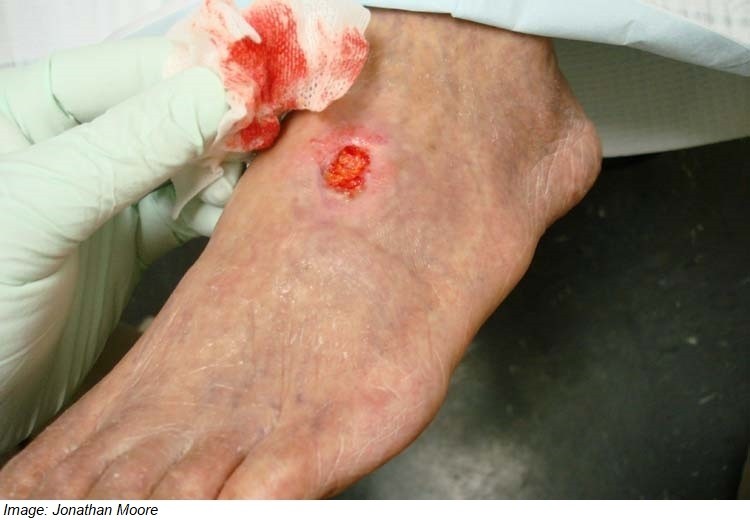
What is the MOST appropriate diagnosis?
A. Ischaemic ulcer
B. Lymphoma
C. Neuropathic ulcer
D. Pressure ulcer
E. Syphilitic gumma
F. Ulcerated basal cell carcinoma
G. Ulcerated squamous cell carcinoma
H. Venous ulcer
Correct Answer: A. Ischaemic ulcer
Question 31
Brady Robinson, aged 68 years, has returned today for results. You arranged investigations, as he has had chest pain when walking during the past six months. The pain occurs after walking for 15 minutes and settles within five minutes of resting. He has hypertension and hyperlipidaemia, for which he takes ramipril 5 mg orally daily and atorvastatin 40 mg orally daily. On examination, his heart rate is 75/min and blood pressure is 158/104 mmHg. An electrocardiogram is performed (see image).
Brady’s full blood count, urea and electrolytes and lipid profile are within the normal range. Chest X-ray showed increased cardiopulmonary ratio. A myocardial perfusion scan demonstrated an area of reversible ischaemia and his echocardiography showed left ventricular hypertrophy and an ejection fraction of 35% with no valvular lesions.
You initiate aspirin 100 mg orally daily and glyceryl trinitrate spray 400 mcg sublingually, as required, for episodes of chest pain.
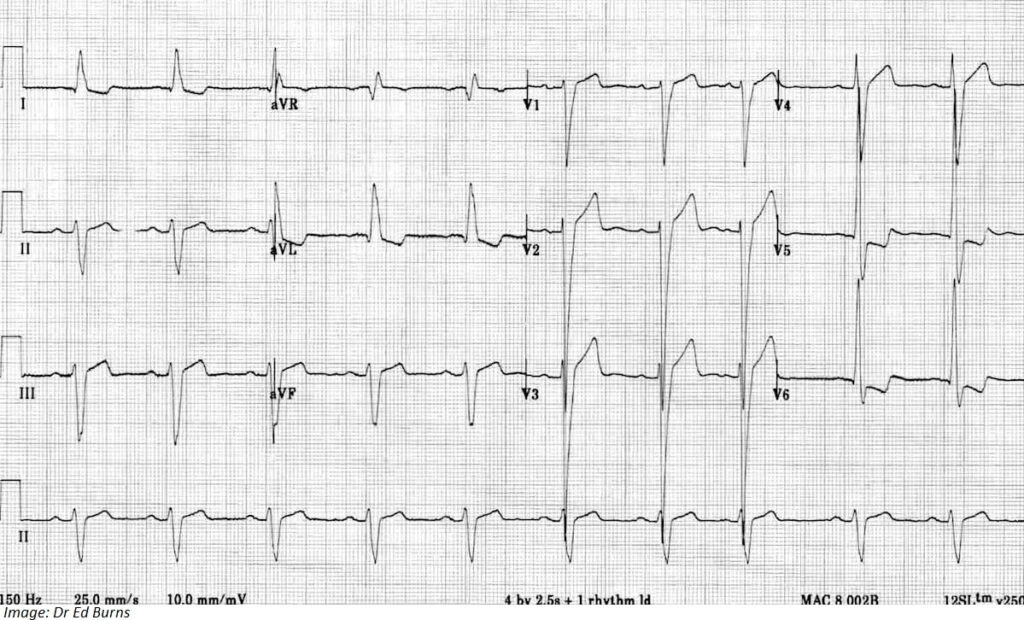
What is the MOST appropriate additional medication to initiate today?
A. Bisoprolol 1.25 mg orally daily
B. Clopidogrel 75 mg orally daily
C. Diltiazem extended release 180 mg orally daily
D. Nicorandil 5 mg orally twice daily
E. Verapamil extended release 120 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: A. Bisoprolol 1.25 mg orally daily
Question 32
Jordan Breakwater, aged 21 years, is concerned that he might have tonsillitis, as he has noticed a white patch on his left tonsil (see image). He first noticed it two weeks ago. When he swallows, he feels an irritation on that side, and his girlfriend is complaining that his breath smells bad.
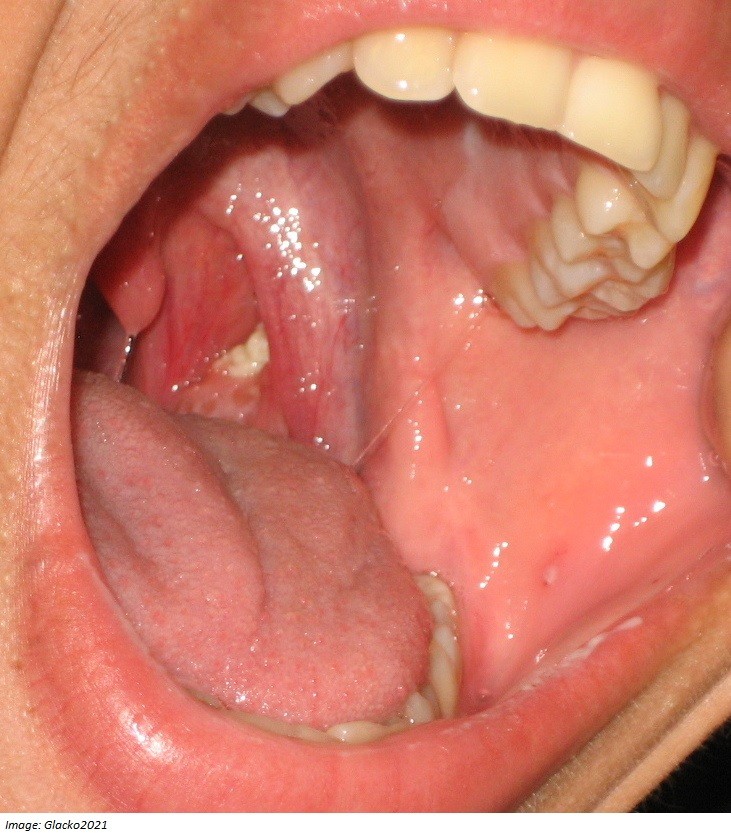
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Cefalexin 1 g orally twice daily for 10 days
B. Phenoxymethylpenicillin 500 mg orally twice daily for 10 days
C. Regular salt water gargles
D. Throat swab for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
E. Urgent referral to ear, nose and throat surgeon for biopsy
Correct Answer: C. Regular salt water gargles
Question 33
Prisha Singh, aged 6 months, is brought in by her concerned grandmother who is looking after her today while her parents are at work. She noticed marks on Prisha’s buttocks while changing her nappy earlier today (see image). On examination, her tympanic temperature is 36.8°C. She is interactive and developmentally appropriate for her age.
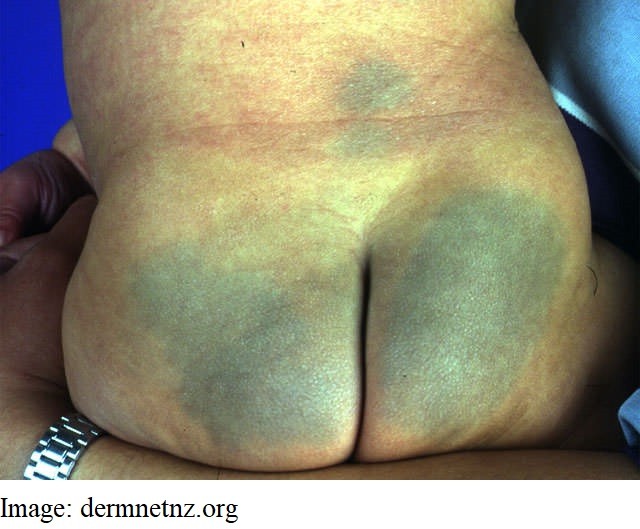
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Benzylpenicillin 60 mg/kg (max 1 g) stat dose intramuscularly
B. Full blood count and coagulation profile
C. Mandatory notification to child safety services
D. Provide reassurance the lesions are benign and will likely fade with time
E. Review in one week to monitor progress of the lesions
F. Ultrasound sacrum
G. Transfer to emergency department
H. X-ray pelvis
Correct Answer: D. Provide reassurance the lesions are benign and will likely fade with time
Question 34
John Walters, aged 65 years, has had a painful right ankle for the past week. He has recently retired and lives a sedentary lifestyle. He does not recall any injury. He has been resting his ankle and taking paracetamol 1 g orally four times daily, without improvement. He has a history of bronchiectasis and
takes indacaterol 150 mcg inhaled daily. He had an episode of pneumonia recently and finished a course of ciprofloxacin last week. On examination, he has an antalgic gait and is not able to place his heel on the ground when walking. There is limited active flexion and extension at the ankle due to pain. There is tenderness over his Achilles tendon, and the overlying skin is erythematous.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Acute Charcot foot
B. Calcaneal apophysitis
C. Fluoroquinolone-induced Achilles tendonitis
D. Gout
E. Retrocalcaneal bursitis
F. Rheumatoid arthritis
G. Ruptured Achilles tendon
H. Septic arthritis
Correct Answer: C. Fluoroquinolone-induced Achilles tendonitis
Question 35
Edith Stapleton, aged 53 years, has developed a widespread rash today and is feeling fatigued. The rash is not itchy. She finished chemotherapy for acute lymphoid leukaemia one week ago. On examination, the rash does not blanch (see image). Her tympanic temperature is 37.2°C, heart rate is 96/min, blood pressure is 110/84 mmHg and respiratory rate is 18/min. You arrange transfer to the local emergency department and Edith asks what treatment will be initiated.
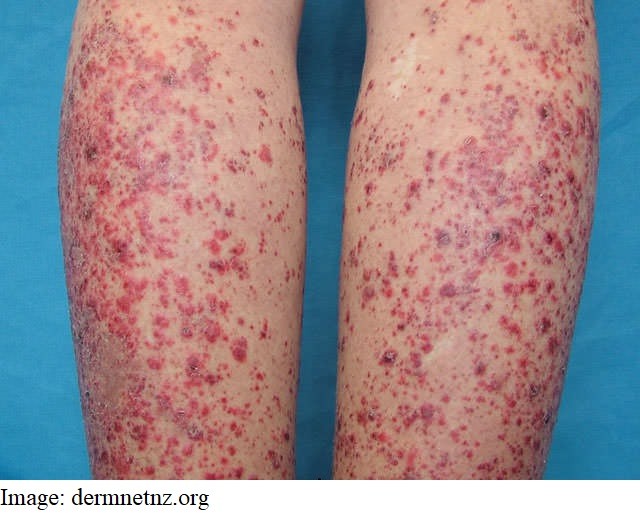
What is the MOST appropriate treatment?
A. Ceftriaxone 2 g intravenously every 12 hours
B. Intravenous fluid replacement
C. Recommencement of chemotherapy
D. Transfusion of platelets
E. Unfractionated heparin 80 units/kg via intravenous infusion
Correct Answer: D. Transfusion of platelets
Question 36
Manuel Tyre, aged 4 years, is brought in by his mother, Marion, as he has had an ongoing moist cough at night. Ten days earlier, Manuel had experienced an upper respiratory tract infection. His initial rhinorrhoea and fever have resolved; however, he has an ongoing cough, which is waking him up at night.
Manuel is usually well and his vaccinations are up to date. On examination, he is alert and appears well, but does have an occasional cough. His chest auscultation is clear. The rest of his clinical examination is unremarkable. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
What is the MOST appropriate management of Manuel’s cough?
A. Amoxicillin 25 mg/kg (max 1 g) orally three times daily for five days
B. Bromhexine 8 mg orally three times daily, as required
C. One teaspoon of honey in warm water before bed
D. Promethazine 0.5 mg/kg (max 50 mg) orally at night
E. Recommend humidifier in the bedroom overnight
Correct Answer: C. One teaspoon of honey in warm water before bed
Question 37
Viki Barnes, aged 54 years, presents to your rural general practice with a painful right hand. She was gardening yesterday when she slipped and fell, landing on her right hand, which was in a fist position. She works as a typist, but was unable to work today. On examination, there is mild swelling of the dorsum of her hand and she is tender over the medial aspect of her palm. She has full range of motion in her hand with no deformity. An X-ray is performed (see image). You arrange an orthopaedic referral; her appointment is in one week.
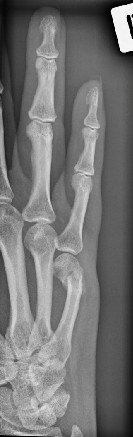
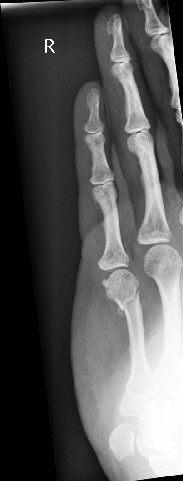
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Apply backslab to keep hand in full extension at metacarpophalangeal joint
B. Buddy strap right fifth finger to fourth finger
C. Elevate hand with broad arm sling
D. Physiotherapy to maintain range of motion
E. Splint hand at 90 degrees of flexion at metacarpophalangeal joint
Correct Answer: E. Splint hand at 90 degrees of flexion at metacarpophalangeal joint
Question 38
Peter Stevenson, aged 34 years, has a lesion on his left eyelid (see image). It has been growing slowly over
three days and causing some discomfort. His visual acuity is normal.
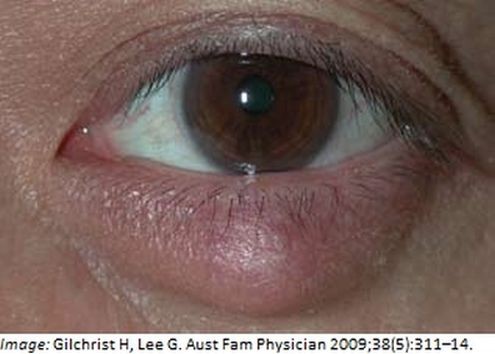
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Amoxicillin 500 mg orally three times daily
B. Apply warm compresses three times daily
C. Cefalexin 500 mg orally four times daily
D. Chloramphenicol 1% ointment topically four times daily
E. Refer to ophthalmologist for incision and curettage
Correct Answer: B. Apply warm compresses three times daily
Question 39
Jane Owens, aged 25 years, presents for routine antenatal care. She is 12 weeks pregnant and this is her first pregnancy. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated and she has no significant medical history. She advises you that she is due for cervical screening.
What is the MOST appropriate recommendation regarding cervical screening
A. Cervical screening should be delayed until six weeks after delivery
B. Organise cervical screening now by self-collection
C. Perform cervical screening now using cyto-broom
D. Perform cervical screening now using endocervical brush
E. Refer for cervical screening to be performed under colposcopic guidance
Correct Answer: B. Organise cervical screening now by self-collection and C. Perform cervical screening now using cyto-broom
Question 40
Derifa Khaled, aged 6 years, is a refugee from Syria who has just arrived in Australia. She has had itchy lesions on her back, palms and soles (see image) that have been slowly worsening over several weeks. The itch is particularly troublesome at night.
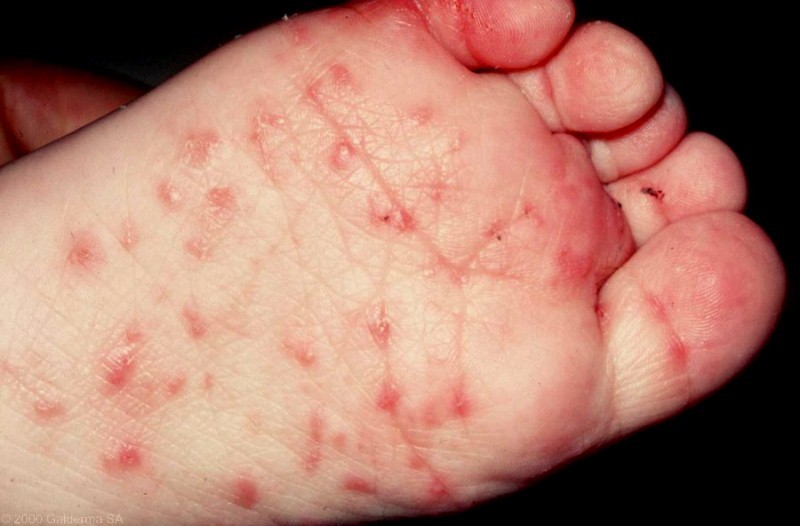
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Cephalexin 50 mg/kg (max 1 g) orally twice daily for 10 days
B. Hydrocortisone 1% cream topically nocte
C. Permethrin 5% cream topically from the neck down and leave for eight hours
D. Prednisone 1 mg/kg (max 50 mg) orally daily for seven days
E. Reassurance that no treatment is needed and rash will resolve spontaneously
Correct Answer: C. Permethrin 5% cream topically from the neck down and leave for eight hours
Question 41
Charlene James, aged 14 years, is brought in by her father, Simon. For the past two weeks, Charlene has been lethargic and appears to have lost weight. The family recently moved from interstate and Simon is concerned about how Charlene is settling into her new school. She has already been reprimanded on several occasions for asking to use the bathroom during class. On examination, Charlene is quiet and has dry mucous membranes. Her tympanic temperature is 36.4 °C, heart rate 99/min regular and blood pressure 100/74 mmHg. Cardiovascular, respiratory and abdominal examination is normal. She can not give a urine sample as she has ‘just been’.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Fingerprick blood glucose test
B. Offer to speak to Charlene on her own
C. Recommend appointment with school counsellor
D. Request mid-stream urine for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
E. Serum ferritin
Correct Answer: A. Fingerprick blood glucose test and B. Offer to speak to Charlene on her own
Question 42
Sandra Jenkins, aged 58 years, presents with her brother, Jack, who is concerned that Sandra’s behaviour has changed. Sandra has Down syndrome and lives in supported accommodation. Over the past eight months, she has required increasing levels of assistance with dressing and has been incontinent of urine once or twice a week. She still has a good appetite, but now needs to have her food cut up for her. She continues to sleep well and seems to have good energy levels. She used to love going out for lunch with Jack every Saturday but now often refuses to go. Jack says that Sandra used to be a happy and ‘chatty’ person but is now much quieter.
Sandra has been previously well. She takes omeprazole 20 mg orally daily for oesophageal reflux, and macrogol 3350 one sachet orally daily for constipation.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Alzheimer’s disease
B. Brain tumour
C. Cataracts
D. Depression
E. Epilepsy
F. Hypothyroidism
G. Medication side effect
H. Menopause
I. Multiple sclerosis
J. Normal pressure hydrocephalus
K. Osteoarthritis
L. Schizophrenia
Correct Answer: A. Alzheimer’s disease
Question 43
Philip Windsor, aged 19 years, injured his knee last week while playing soccer. He had a sudden onset of pain when he slipped sideways and fell. The knee became swollen as the day progressed, but he has managed the pain with over-the-counter analgesics. Examination today shows a small effusion with
maximal tenderness over the medial joint line. Valgus stress testing of the knee elicits pain. Thessaly’s test is negative.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Anterior cruciate ligament tear
B. Iliotibial band syndrome
C. Lateral collateral ligament strain
D. Medial collateral ligament strain
E. Medial meniscal tear
F. Osteochondritis dissecans
G. Patellar tendonitis
H. Patello-femoral syndrome
I. Prepatellar bursitis
J. Quadriceps tendon tear
Correct Answer: D. Medial collateral ligament strain
Question 44
Joseph Czechowicz, aged 65 years, has come for review of his recent blood test results. He has type 2 diabetes and ischaemic heart disease. He is prescribed metformin extended-release 2 g orally daily, atenolol 25 mg orally daily, ramipril 5 mg orally daily, atorvastatin 40 mg orally daily and aspirin 100 mg orally daily. He did not tolerate gliclazide due to hypoglycaemia. His last two HbA1c readings, three and six months ago, were 8% (64 mmol/mol) and 7.6% (60 mmol/mol) respectively, with estimated glomerular filtration rate 68* mL/min/1.73m2 (normal range > 90). His body mass index is 23 kg/m2.
He is working very hard on modifying his lifestyle, including diet and exercise. You discuss introducing another medication to help control his diabetes.
What is the MOST appropriate additional medication?
A. Empagliflozin 10 mg orally daily
B. Glibenclamide 2.5 mg orally daily
C. Glimepiride 1 mg orally daily
D. Insulin glargine 10 units subcutaneous injection nocte
E. Liraglutide 0.6 mg subcutaneous injection daily; increase to 1.2 mg daily after one week
F. Lispro 100 units/mL insulin 4 units subcutaneous injection 15 mins prior to meals
G. Pioglitazone 30 mg orally daily
H. Sitagliptin 100 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: A. Empagliflozin 10 mg orally daily
Question 45
Bazza Newman, aged 72 years, is a retired physical education teacher who asks you to freeze a few sunspots on his hands and forearms. He has a 10 × 10 mm, dry, well-defined lesion on his left forearm that appears different to the rest (see image).
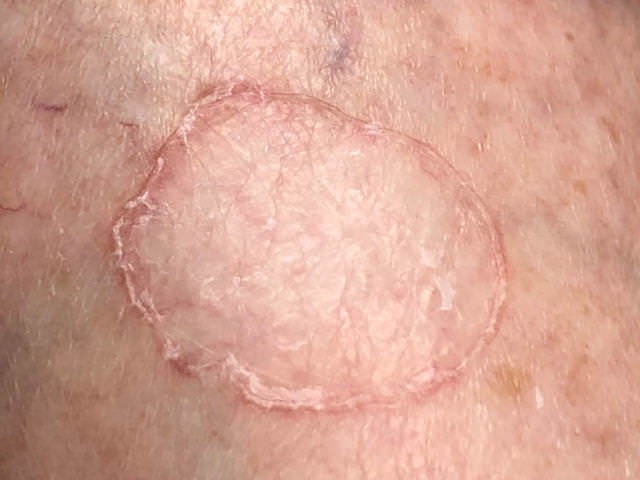
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Actinic keratosis
B. Bowen’s disease
C. Dysplastic naevus
D. Granuloma annulare
E. Melanoma
F. Porokeratosis
G. Scar tissue
H. Squamous cell carcinoma
Correct Answer: F. Porokeratosis
Question 46
Bruno Petrelli, aged 47 years, has had two months of gradually worsening right shoulder pain. Bruno enjoys gardening and is right hand dominant. The pain is worsened when pruning trees, and when he lies on his right side in bed. He gets some relief with paracetamol slow release tablets 665 mg two tablets orally at night. On examination, there is pain with active abduction of the shoulder greater than 60 degrees and the empty can test is positive.
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Advise to see physiotherapist for provision of a focused exercise program
B. Refer to orthopaedic surgeon for consideration of surgery
C. Rest in a broad-arm sling for two weeks then review
D. Shoulder hydrodilatation
E. Ultrasound guided steroid injection to the subacromial bursa
Correct Answer: A. Advise to see physiotherapist for provision of a focused exercise program
Question 47
Bruce Bennett, aged 86 years, visits you before scheduled dental therapy. Bruce had a total hip replacement three months ago, a prosthetic mitral valve repair five months ago, and is being treated for rheumatoid arthritis with prednisolone 5 mg orally daily. His dentist has suggested asking you whether
Bruce requires antibiotics before upcoming root canal treatment.
What is the MOST appropriate reason to provide Bruce with prophylactic antibiotics?
A. Bruce’s current age
B. Prednisolone use
C. Prosthetic mitral valve
D. Recent orthopaedic surgery
E. Rheumatoid arthritis
Correct Answer: C. Prosthetic mitral valve
Question 48
Daniel Warnock, aged 18 years, developed sudden onset of vomiting, lower abdominal and scrotal pain approximately four hours ago. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 36.5 °C and heart rate 80/min regular. Abdominal examination reveals diffuse, lower abdominal tenderness. Scrotal examination reveals a tender left scrotum. The pain is not relieved by elevation of the scrotum.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Arrange urgent ultrasound of abdomen and scrotum
B. Ceftriaxone 500 mg in 2 mL of 1% lidocaine intramuscularly stat dose
C. First stream urine for chlamydia polymerase chain reaction
D. Trimethoprim 300 mg orally daily for two weeks
E. Urgent surgical referral for immediate scrotal exploration
Correct Answer: E. Urgent surgical referral for immediate scrotal exploration
Question 49
Sharon Edwards, aged 51 years, is concerned about her risk of developing heart disease. Her father recently died from a myocardial infarction at age 73 years. Sharon is a non-smoker, non-drinker and jogs for 40 minutes four times per week. On examination, her heart rate is 72/min regular, blood pressure
138/89 mmHg, heart sounds dual and body mass index 23 kg/m2. An electrocardiogram shows normal sinus rhythm 75/min.
Full blood examination, liver and renal function tests are within normal limits. Lipid results are as follows:
Fastinglipidstudies | Result | Desirablerange(fasting) |
| Total cholesterol | 5.5 mmol/L | < 5.6 |
| Triglycerides | 1.6*mmol/L | < 1.5 |
| Low-density lipoprotein | 3.0*mmol/L | < 2.5 |
| High-density lipoprotein (HDL) | 0.9*mmol/L | > 1.0 |
| Cholesterol:HDL ratio | 6.1* | < 0.45 |
Sharon’s cardiovascular risk using the Australian absolute cardiovascular disease risk calculator = 2% risk of cardiovascular disease event in the next five years.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Aspirin 100 mg orally daily
B. Computed tomography coronary angiogram
C. Docosahexaenoic acid 120 mg orally daily
D. Exercise stress echocardiogram
E. Myocardial perfusion scan
F. Olmesartan 20 mg orally daily
G. Provide specific advice about diet
H. Rosuvastatin 5 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: G. Provide specific advice about diet
Question 50
Jayden Branson, aged 6 years, an Aboriginal boy, presents with his mother, Leticia, as he has had a cough for seven days. Initially, he had a runny nose and a sore throat for two days, but then developed the cough. Leticia says he has had difficulty catching his breath at times. His immunisations are up to date.
On examination, his tympanic temperature is 38.6°C, heart rate is 150/min, respiratory rate is 32/min and oxygen saturation is 96% on room air. Ear, nose and throat examination reveals clear rhinorrhoea and an erythematous pharynx. There are crackles and bronchial breath sounds bilaterally on chest auscultation with intercostal retraction. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Acute rheumatic fever
B. Asthma
C. Bronchiolitis
D. Community-acquired pneumonia
E. Laryngotracheobronchitis
F. Lung abscess
G. Pertussis
H. Protracted bacterial bronchitis
I. Q fever
J. Tuberculosis
