Question 1
Andrew Lane, aged 44 years, attends for review of a bloodborne virus screen you performed at his request last week. Andrew has recently experienced a major depressive episode and has been injecting ice (crystal methamphetamine) most weekends over the past 12 months. He was diagnosed with hepatitis C 10 years ago, which was successfully treated. His results are shown below.
| Human immunodeficiency virus antigen/antibody | Negative |
| Hepatitis B surface antibody | Positive* |
| Hepatitis B core antibody | Positive* |
| Hepatitis B surface antigen | Negative |
| Hepatitis C antibody (immunoglobulin G) | Positive* |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Hepatitis
B. Hepatitis B virus DNA
C. Hepatitis C genotype
D. Hepatitis C RNA polymerase chain reaction
E. Ultrasound elastography liver
Correct Answer: D. Hepatitis C RNA polymerase chain reaction
Question 2
Jayden Jones, aged 10 years, is brought in by his mother for an itchy red rash in his groin that you confirm is mild tinea. While completing your examination, you note that the left testicle is in the scrotum and the right testicle is in the inguinal canal. His mother tells you that he had all
his usual childhood health checks as an infant and she was always told that Jayden’s testicles were normal.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise that Jayden requires no further management
B. Alpha-fetoprotein level
C. Karyotype
D. Refer to a paediatric surgeon for right orchidopexy
E. Refer to a paediatric surgeon for right orchidectomy
F. Refer to a paediatrician for consideration of gonadotropin-releasing hormone
G. Serum testosterone
H. Ultrasound testes
Correct Answer: D. Refer to a paediatric surgeon for right orchidopexy
Question 3
Sarah Baker, aged 25 years, would like your opinion about her recent blood test results. She is six weeks pregnant. Her antenatal bloods were ordered by her usual general practitioner. She was recalled to discuss the results, but has since moved to your area and asks you to take over her care. She is asymptomatic and her physical examination is normal.
| Test | Result | Normal range |
| Thyroid-stimulating hormone | 3.2 mIU/L* | First trimester pregnancy: 0.4– 2.4 |
| Free T3 | 4.9 pmol/L | 3.5–6.5 |
| Free T4 | 8.2 pmol/L* | 9–25 |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Carbimazole 15 mg orally twice daily
B. Levothyroxine 1.6 mcg/kg orally daily
C. Repeat thyroid function test in three months
D. Thyroid peroxidase antibody test
E. Ultrasound thyroid
Correct Answer: B. Levothyroxine 1.6 mcg/kg orally daily
Question 4
Donna Hart, aged 28 years, has experienced recurrent episodes of chest tightness, palpitations and dizziness. She says that when the symptoms start, she often panics, as she worries she will have a heart attack. These episodes last for a few minutes and she has not been able to identify what triggers them. Her physical examination today is normal. You arrange an electrocardiogram (see image).
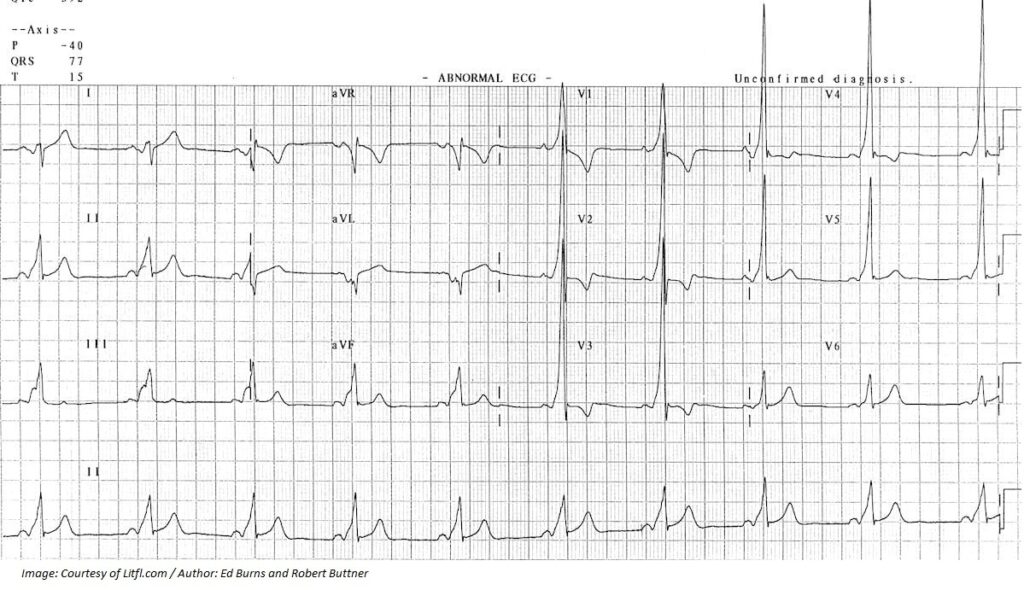
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Amiodarone 200 mg orally daily
B. Amiodarone 200 mg orally daily
C. Digoxin 250 mcg orally daily
D. Refer for computed tomography cardiac angiogram
E. Refer to a cardiologist for catheter ablation
F. Refer to a psychologist for cognitive behavioural therapy
G. Sertraline 50 mg orally daily
H. Verapamil modified release 180 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: E. Refer to a cardiologist for catheter ablation
Question 5
Henry Abel, aged 65 years, has come to your clinic to ask about several new odd dark shapes in his left vision that he notices when he moves his eye. The symptoms began a few days ago and he has had some streaks of light in the extremes of his vision. His visual acuity has otherwise remained normal, and he has had no pain. Physical examination is normal.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Atypical migraine
B. Cataract
C. Central retinal vein occlusion
D. Cerebrovascular accident
E. Iritis
F. Macular degeneration
G. Optic neuritis
H. Posterior vitreous detachment
I. Presbyopia
J. Primary angle closure glaucoma
K. Retinal detachment
Correct Answer: H. Posterior vitreous detachment
Question 6
Carol Reid, aged 35 years, has been feeling fatigued for the past two weeks. She has also noticed numbness and weakness of her left foot. She mentions an episode that occurred 18 months ago when she was pregnant with her first child. At that time, she experienced feeling unstable while walking, and blurred vision, but it all seemed to go away on its own. On examination, there is reduced sensation to fine touch on the left big toe and brisk tendon
reflex of the left ankle with a power of 3/5.
What is the MOST appropriate investigation to confirm the provisional diagnosis?
A. Acetylcholine receptor antibodies
B. Lumbar puncture
C. Magnetic resonance imaging brain and spinal cord
D. Nerve conduction studies left leg
E. Serum vitamin B12 level
Correct Answer: C. Magnetic resonance imaging brain and spinal cord
Question 7
Lisa Tungston, aged 18 years, attends with her father, who is concerned about her eating habits. Over the past few months, Lisa has become fearful of becoming fat and dislikes her appearance. She usually does not eat until after 3.00 pm and will only have a few mouthfuls at a time. Every two weeks, she will eat a packet of chips or half a tub of ice cream, and then try, unsuccessfully, to vomit. She has never used laxatives. She has lost 2 kg in the past four
months. She has had a delayed period twice, previously being regular. She enjoys school and is still performing well academically. She performs 30 minutes of exercise most days. Her physical examination is normal, with a body mass index of 20.1 kg/m2.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Body dysmorphic disorder
B. Bulimia nervosa
C. Generalised anxiety disorder
D. Major depressive disorder
E. Unspecified eating disorder
Correct Answer: E. Unspecified eating disorder
Question 8
Darcy Childers, aged 12 days, is brought in by his mother Maryanne, aged 18 years, with red, sticky eyes for the past two days. Maryanne’s pregnancy was unplanned, but progressed normally. Darcy was born by normal vaginal delivery at term. On examination, Darcy looks well; temperature is 36.5°C, and there is mild bilateral conjunctival injection and a copious amount of purulent discharge from both eyes.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Aenovirus conjunctivitis
B. Adenovirus conjunctivitis
C. Blocked tear ducts
D. Chlamydia trachomatis conjunctivitis
E. Congenital glaucoma
F. Congenital glaucoma
G. Herpes simplex keratitis
H. Kawasaki disease
I. Staphylococcus aureus conjunctivitis
Correct Answer: D. Chlamydia trachomatis conjunctivitis
Question 9
Melissa Loh, aged 42 years, requests an antibiotic. She was diagnosed with bronchiectasis and mild immunoglobulin A deficiency six months ago. She has regular chest physiotherapy. Melissa has noticed her sputum has turned yellow, rather than the usual white colour, for the past four days. She has not noticed any increase in her sputum volume or frequency of coughing. On examination, her temperature is 37.2°C, blood pressure 120/70 mmHg, respiratory rate 20/min and oxygen saturation 98% on room air. Her chest is clear to auscultation.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Amoxicillin–clavulanate 875 mg/125 mg orally twice daily for 14 days
B. Ciprofloxacin 750 mg orally twice daily for 14 days
C. Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for seven days
D. Nebulised saline three times daily
E. Refer for bronchoscopy
F. Salbutamol 100 mcg inhaler two puffs, as required
G. Sputum microscopy, culture and sensitivities
H. X-ray chest
Correct Answer: G. Sputum microscopy, culture and sensitivities
Question 10
Stella Douglas, aged 49 years, is bothered by perimenopausal symptoms. For the past three months, she has had her period about every two weeks, with bleeding that lasts from five to 10 days. Her periods have become very heavy, requiring her to wear a pad and a tampon at the same time. She often experiences flooding and passes clots. She has also had frequent hot flushes, which wake her at night. She has hypothyroidism and takes thyroxine 100 mcg orally daily. Thyroid-stimulating hormone level last week was 1.1 mIU/L (normal range: 0.35–5.5). Cervical screening test two months ago was normal. Stella’s husband has had a vasectomy and she has had no other sexual partners. Her body mass index is 30 kg/m2.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Clonidine 25 mcg orally twice daily
B. Ethinyloestradiol–levonorgestrel 20 mcg/100 mcg orally daily
C. Follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinising hormone and oestradiol levels
D. Levonorgestrel 52 mg intrauterine device
E. Norethisterone 10 mg orally twice daily while bleeding
F. Oestradiol 1 mg orally daily and dydrogesterone 10 mg orally daily for first 14 days of menstrual cycle
G. Oestradiol–dydrogesterone 1 mg/5 mg orally daily
H. Ultrasound pelvis
Correct Answer: H. Ultrasound pelvis
Question 11
Kaine Phipps, aged 23 years, is a soccer player who comes to see you on Monday morning after having collapsed on the soccer field while playing two days earlier. He was running on the field when he suddenly collapsed, but was only momentarily unconscious. He had had no associated contact with another player. The paramedic stretchered him off the field, checked him over and said he was fit to go home but to see his general practitioner. His physical examination today is normal.
What is the MOST appropriate investigation to confirm the provisional diagnosis?
A. Computed tomography brain
B. Duplex Doppler ultrasound carotid arteries
C. Echocardiogram
D. Magnetic resonance imaging brain
E. Urea, electrolytes and creatinine
Correct Answer: C. Echocardiogram
Question 12
Geoffrey Jones, aged 56 years, has been feeling unwell for the past three days with fever, headache, cough, shortness of breath and stomach pain. He tells you he returned two weeks ago from volunteering in the clean-up after recent flooding in North Queensland and sustained a superficial laceration on his left lower leg while there. He has diet-controlled type 2 diabetes. On examination, he is alert and orientated, but looks tired. His temperature is 38.9°C, heart rate 100/min regular, respiratory rate 26/min and oxygen saturation 95% room air. He has increased work of breathing and crepitations at the left lung base. The lower leg wound is warm and tender on palpation with surrounding cellulitis. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Astrovirus
B. Congestive heart failure
C. Dengue fever
D. Entamoeba histolytica
E. Melioidosis
F. Moraxella catarrhalis
G. Pulmonary embolism
H. Tuberculosis
Correct Answer: E. Melioidosis
Question 13
Jasinta Weaver, aged 26 years, an Aboriginal woman, has attended for her baby’s newborn check. Jasinta’s daughter, Samara, is 2 weeks old and was born via spontaneous vaginal delivery at the local hospital following an uncomplicated pregnancy. Samara is bottle fed and her neonatal examination is unremarkable; however, Jasinta appears dishevelled in her appearance and speaks loudly and quickly. Jasinta tells you she thinks her aunt is poisoning the baby. Jasinta has been staying up all night to make sure her aunt is not feeding the baby while she sleeps. Jasinta has had no thoughts of harming herself or her baby. You attempt to ask further questions, but she becomes angry and suspicious of you.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Arrange for an Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander health practitioner to perform a home visit within the next 24 hours
B. Diazepam 5 mg orally three times daily, as required
C. Escitalopram 10 mg orally daily
D. Quetiapine 25 mg orally at night
E. Refer to a psychologist for cognitive behavioural therapy
F. Report Jasinta’s aunt to child protection services
G. Sertraline 50 mg orally daily
H. Urgent referral for psychiatric admission to mother–baby unit
Correct Answer: H. Urgent referral for psychiatric admission to mother–baby unit
Question 14
Matthew Bryson, aged 10 days, is brought in by his mother, Samantha, for review of jaundice. Matthew was born at term via normal vaginal delivery with no immediate complications. The jaundice was first noted by Samantha when he was 4 days old. He is fully breastfed and has eight to 10 wet nappies per day. He has three nappies with mustard-coloured stool each day. On examination, Matthew’s skin is yellow on his face, torso and abdomen. His height, weight and head circumference are all tracking on the 50th centile. The results of blood tests performed today are as follows:
Full blood examination, liver function test and thyroid function test are normal.
| Test | Result | Normal range |
| Total serum bilirubin | 180 μmol/L* | <20 |
| Conjugated (direct) bilirubin | 5 μmol/L | <7 |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise Samantha to stop breastfeeding and commence formula feeding
B. Arrange bag specimen urine
C. Ask Samantha to top up with formula or expressed breast milk following every breastfeed
D. Close observation and follow up with early review if worsening
E. Gentle sun exposure for 30 minutes per day
Correct Answer: D. Close observation and follow up with early review if worsening
Question 15
Jim Selby, aged 65 years, has had a sore right first toe for the past two days. He does not recall any trauma to the toe, although he did have a night of heavy drinking the day prior to his symptoms starting. He has a history of hypertension that is currently well controlled with candesartan hydrochlorothiazide 32 mg/12.5 mg orally daily. On examination, his temperature is 37.3°C, and the right first toe is swollen, erythematous, tender and warm (see image).
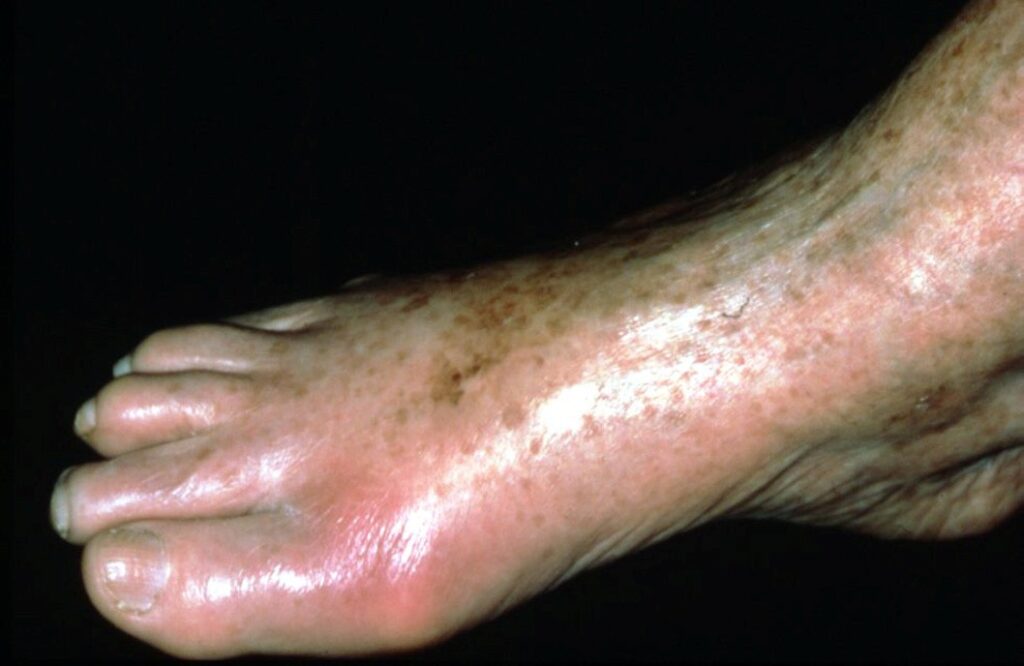
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Allopurinol 50 mg orally daily
B. Cephalexin 500 mg orally four times daily for five days
C. Diclofenac 50 mg orally three times daily for three days
D. Indomethacin 100 mg suppository rectally twice daily
E. Prednisone 15 mg orally daily for three days
Correct Answer: E. Prednisone 15 mg orally daily for three days
Question 16
Jenna Martin, aged 28 years, has had a rash on her face that has become increasingly prominent over the past four months (see image). She believes that it appeared after starting the oral contraceptive pill, and has stopped taking it for this reason. Since stopping the pill, she has been very careful with photoprotection, but the rash has not changed.
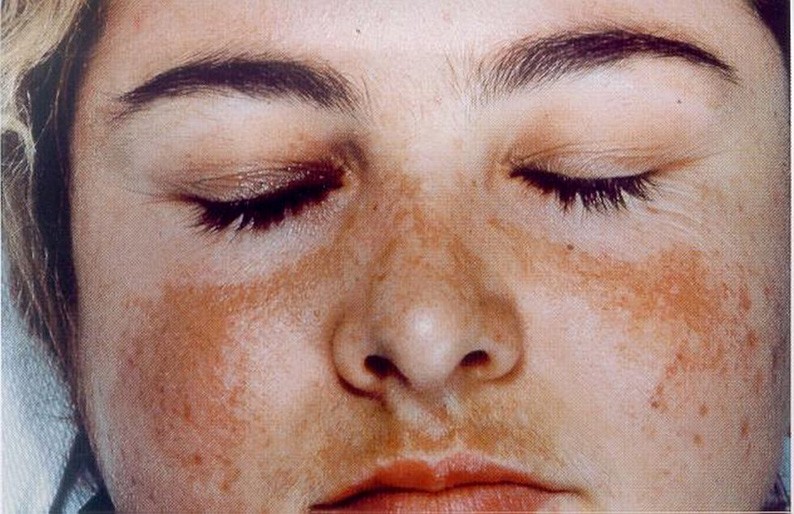
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Antinuclear antibodies
B. Clotrimazole 1% cream topically twice daily
C. Extractable nuclear antigen antibodies
D. Hydroquinone 2% cream topically twice daily
E. Metronidazole 0.75% cream topically twice daily
F. Pimecrolimus 1% cream topically twice daily
G. Salicylic acid 2% cream topically daily
H. Urea 10% cream topically twice daily
Correct Answer: D. Hydroquinone 2% cream topically twice daily
Question 17
Joshua Smith, aged 10 years, presents with left wrist pain after falling from his skateboard earlier today. On examination, there is tenderness and swelling of his left wrist. An X-ray is performed (see images).
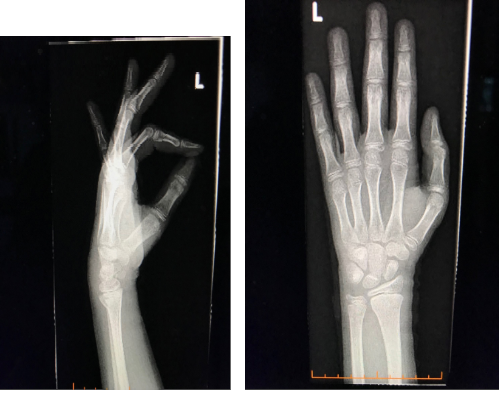
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Below-elbow wrist splint for three weeks
B. Closed reduction and above-elbow cast for six weeks
C. Open reduction and below-elbow cast for six weeks
D. Manipulation under general anaesthetic and below-elbow cast for six weeks
E. Soft tissue compression bandage
Correct Answer: A. Below-elbow wrist splint for three weeks
Question 18
James Miller, aged 25 years, has cramping abdominal pain and diarrhoea. He had unprotected anal intercourse with a casual male partner two days earlier. This morning he awoke with fevers, chills and bloody diarrhoea. On examination, his temperature is 38.5°C, heart rate 120/min regular and blood pressure 105/80 mmHg. Abdominal palpation reveals generalised tenderness and no guarding. The perianal area appears normal.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Chlamydia trachomatis infection
B. Crohn’s disease
C. Giardiasis
D. Hepatitis A infection
E. Shigellosis
Correct Answer: E. Shigellosis
Question 19
Fiona Kaufmann, aged 38 years, is concerned about her facial rash (see image). It is not itchy or painful, but she is unhappy with the appearance. The rash has been a long-term problem since puberty, but has recently become worse after she increased her alcohol consumption. It improves with a zinc-based barrier cream, but then eventually returns.
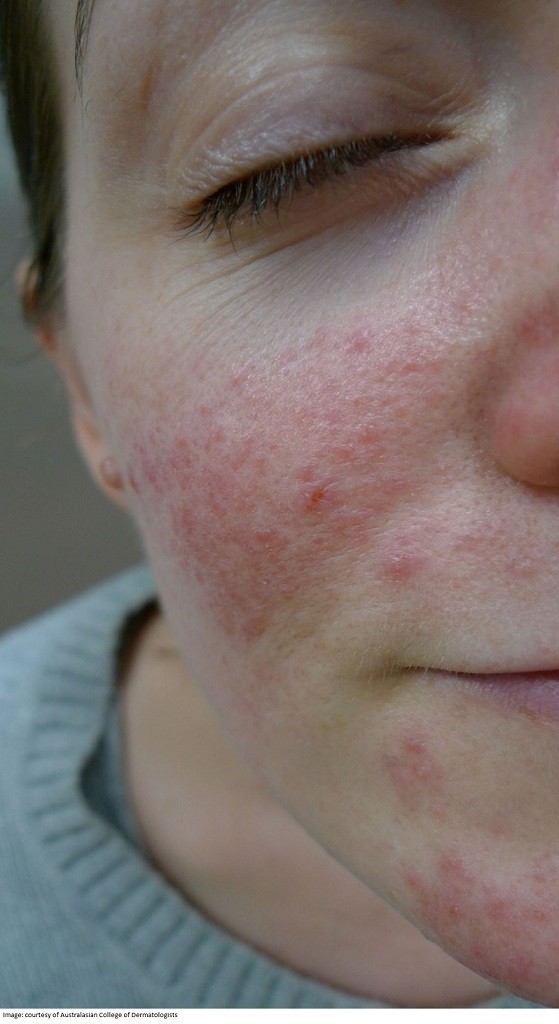
What is the MOST appropriate initial treatment?
A. Benzoyl peroxide 5% lotion topically daily for four weeks
B. Doxycycline 100 mg orally daily for eight weeks
C. Hydrocortisone 1% cream topically twice daily for two weeks
D. Metronidazole 0.75% gel topically twice daily for 12 weeks
E. Refer to a dermatologist for vascular laser therapy
Correct Answer: D. Metronidazole 0.75% gel topically twice daily for 12 weeks
Question 20
George Parker, aged 63 years, returns for review of his recently diagnosed type 2 diabetes. You review his immunisation history. He is up to date with his annual influenza immunisation and COVID-19 immunisations. He last received a diphtheria–tetanus–pertussis immunisation four years ago before the birth of his granddaughter.
What is the MOST appropriate immunisation recommendation?
A. 13-Valent pneumococcal conjugate today
B. 23-Valent pneumococcal polysaccharide at 65 years old
C. Diphtheria–tetanus–pertussis today
D. Haemophilus influenzae type B today
E. No immunisations are required, as he is up to date
Correct Answer: A. 13-Valent pneumococcal conjugate today
Question 21
Caoimhe O’Malley, aged 43 years, has had a spontaneous discharge from her right breast for the past two weeks. She stopped breastfeeding her youngest child three years ago. She takes ethinyloestradiol–norethisterone 35 mcg/500 mcg orally daily for contraception. On examination, there is a serous discharge from a single duct in her right breast. She has no palpable breast lumps or axillary lymphadenopathy. You arrange a mammogram, breast ultrasound and cytology of breast fluid, all of which are normal.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Arrange review after next menstrual period
B. Cease oral contraceptive
C. Reassurance that the discharge is physiological
D. Refer to a breast surgeon for further investigation
E. Serum prolactin
Correct Answer: D. Refer to a breast surgeon for further investigation
Question 22
Eugene Nolan, aged 70 years, has been experiencing intermittent chest pain for the past 12 months. Over the past six months, he has had worsening mental fogginess and fatigue. He has lost 3 kg without trying to. On examination, he is tender over the right third rib. Abnormal blood test results are as follows:
| Test | Results | Normal range |
| Red blood cells | 3.0 × 1012/L* | 3.6–5.2 |
| Haemoglobin | 97 g/L* | 115–160 |
| Urea | 20 mmol/L* | 2–7 |
| Creatinine | 180 μmol/L* | 40–110 |
| Estimated glomerular filtration rate | 40 mL/min/1.73 m2* | >90 |
| Calcium | 2.68 mmol/L* | 2.15–2.60 |
What is the MOST appropriate investigation to support the provisional diagnosis?
A. Angiotensin-converting enzyme
B. Bone marrow aspiration
C. Computed tomography chest
D. Prostate-specific antigen
E. Serum electrophoresis
Correct Answer: E. Serum electrophoresis
Question 23
Debra Daniels, aged 59 years, returns for results of recent blood tests ordered to investigate fatigue. She is known to be heterozygous for the haemochromatosis gene. Her medical history includes hypertension, hypercholesterolaemia and impaired fasting glycaemia. She drinks two
standard drinks of alcohol per day on weekends only. On examination, her heart rate is 88/min regular, blood pressure 142/86 mmHg and body mass index 33 kg/m2.
| Cumulative iron studies – Fasting | |||
| Test | Result: Two years ago | Result: Last week | Normal range |
| Iron | 12 µmol/L | 12 µmol/L | 10–33 |
| Total iron-binding capacity | 52 µmol/L | 55 µmol/L | 45–70 |
| Saturation | 23% | 22% | 16–50 |
| Ferritin | 573 µg/L* | 666 µg/L* | 30–320 |
| Cumulative liver function tests | |||
| Test | Result: Two years ago | Result: Last week | Normal range |
| Total bilirubin | 5 µmol/L | 8 µmol/L | 2-20 |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 68 U/L | 75 U/L | 30-115 |
| Gamma glutamyl transferase | 26 U/L | 59 U/L* | 0–45 |
| Alanine transaminase | 36 | 50* | 0–45 U/L |
| Aspartate aminotransferase | 36 | 43* | 0–41 U/L |
| Lactate dehydrogenase | 195 | 183 | 80–250 U/L |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Arrange therapeutic venesection
B. Haematologist review
C. Magnetic resonance imaging liver
D. Repeat iron studies in three months
E. Ultrasound liver
Correct Answer: E. Ultrasound liver
Question 24
Marie Robinson, age 41 years, has had a dry, non-productive cough for more than a year. She has also experienced shortness of breath with activity and is very tired. She has had swelling and pain of her ankles, elbows and wrists. On examination, there is swelling and tenderness of her ankles, elbows and wrists. You note a tender, erythematous, nodular rash on her shins bilaterally. Chest X-ray shows bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy.
What is the MOST likely investigation finding which supports the provisional diagnosis?
A. Elevated angiotensin-converting enzyme level
B. Pancoast tumour on computed tomography chest
C. Positive antinuclear antibodies
D. Positive anticyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies
E. Serum hypocalcaemia
Correct Answer: A. Elevated angiotensin-converting enzyme level
Question 25
Winifred Brannon, aged 38 years, is concerned about her risk of bowel cancer. Her brother has recently been diagnosed with bowel cancer at age 52 years. Her mother was diagnosed with bowel cancer at age 56 years, and her maternal uncle at age 61 years. You refer her to the familial cancer clinic for genetic risk assessment.
What is the MOST appropriate initial screening to recommend?
A. Colonoscopy every five years from age 42 years
B. Colonoscopy every two years from age 45 years
C. Faecal occult blood test every two years from age 45 years
D. Faecal occult blood test every two years plus colonoscopy every five years starting immediately
E. Faecal occult blood test every two years starting immediately until age 40 years, then colonoscopy every five years.
Correct Answer: A. Colonoscopy every five years from age 42 years
Question 26
Barry van Dyke, aged 70 years, is becoming increasingly short of breath with his daily walk around the block. He was diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease three years ago and takes tiotropium 18 mcg inhaled once daily and salbutamol inhaler 100 mcg two puffs, as required. He stopped smoking when he was diagnosed and has a history of 17 pack-years.
You organise spirometry today. The results are as follows:
| Test | Actual (prebronchodilator | Predicted | % Predicted (prebronchodilator) | % Change (postbronchodilator |
| Forced expiratory volume in one second (L) | 1.23 | 2.43 | 51 | 9 |
| Forced vital capacity (L) | 2.03 | 3.19 | 63 | 8 |
| Forced expiratory volume in one second/forced vital capacity (%) | 60 | 75 | 2 |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Add fluticasone 250 mcg inhaled twice daily
B. Amoxicillin–clavulanate 875 mg/125 mg orally twice daily
C. Azathioprine 25 mg orally daily
D. Cease tiotropium
E. Change tiotropium to budesonide–eformoterol 200 mcg/6 mcg two inhalations twice daily
F. Change tiotropium to glycopyrronium 50 mcg inhaled once daily
G. Change tiotropium to olodaterol–tiotropium 2.5 mcg/2.5 mcg two inhalations once daily
H. Prednisolone 50 mg orally daily for five days
Correct Answer: G. Change tiotropium to olodaterol–tiotropium 2.5 mcg/2.5 mcg two inhalations once daily
Question 27
Vanessa Ford, aged 39 years, returns to discuss results. She is currently 13 weeks into her first pregnancy. Her combined first trimester screening identified a high risk for Down syndrome. She had non-invasive prenatal testing with results as follows:
Chromosome 21 – Risk score = 99/100 – High risk*
You arrange formal genetic counselling, and Vanessa asks what they are likely to recommend.
What is the MOST appropriate recommendation?
A. Amniocentesis
B. Chorionic villus sampling
C. Extended carrier screening for father
D. Reproductive carrier screening for Vanessa
E. Termination of pregnancy
Correct Answer: A. Amniocentesis and B. Chorionic villus sampling
Question 28
Angela Graham, aged 46 years, reports intermittent tingling around her lips and cramps in her hands and feet for the past two weeks. She also describes a sensation of her throat ‘closing up’ and making it difficult to swallow at times. She has had some trouble concentrating and has felt tired.
Angela had a total thyroidectomy for papillary thyroid cancer four months ago. Her current medication is thyroxine 150 mcg orally daily.
On examination, her heart rate is 58/min regular and blood pressure 122/78 mmHg.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Hypercalcaemia
B. Hyperthyroidism
C. Hyperventilation
D. Hypocalcaemia
E. Hypothyroidism
Correct Answer: D. Hypocalcaemia
Question 29
Thomas Kent, aged 19 years, has had lesions on his penis for approximately three months (see image). He has seen another doctor for cryotherapy, with minimal effect. A recent sexually transmissible infection screen was negative.
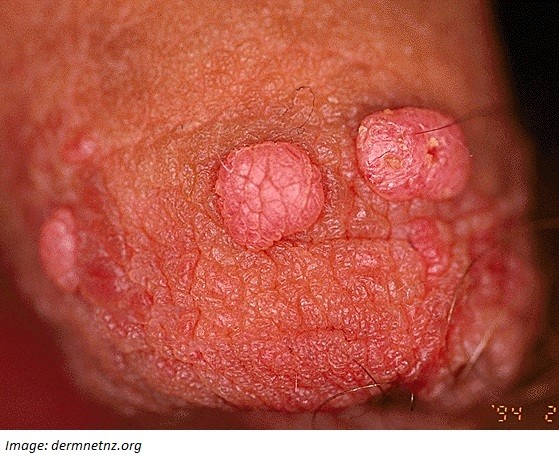
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Betamethasone valerate 0.05% ointment topically daily for 14 days
B. Imiquimod 5% cream topically three times per week for eight to 16 weeks
C. Punch biopsy of lesion
D. Refer to urologist for surgical excision
E. Salicylic acid 20% ointment topically daily until resolved
Correct Answer: B. Imiquimod 5% cream topically three times per week for eight to 16 weeks
Question 30
Lauren Campbell, aged 25 years, presents with one month of waking from sleep with numbness, and pins and needles through her fourth and fifth fingers and the medial side of her right hand. On examination, she has mildly reduced sensation in her fifth finger and on the medial side of her fourth finger in her right hand. Power is equal in both hands.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Magnetic resonance imaging cervical spine
B. Night-time elbow extension splinting
C. Refer for ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection to the carpal tunnel
D. Serum B12
E. X-ray right wrist
Correct Answer: B. Night-time elbow extension splinting
Question 31
David Jennings, aged 50 years, limps into the clinic. He had dropped a dresser drawer on his left great toe two days earlier. His immunisations are up to date. On examination, there is a subungual haematoma involving approximately 20% of the distal nail of the left great toe with tenderness over the distal phalanx; however, his nail bed is clinically intact. There is full range of movement of the interphalangeal joint. You arrange an X-ray (see images).
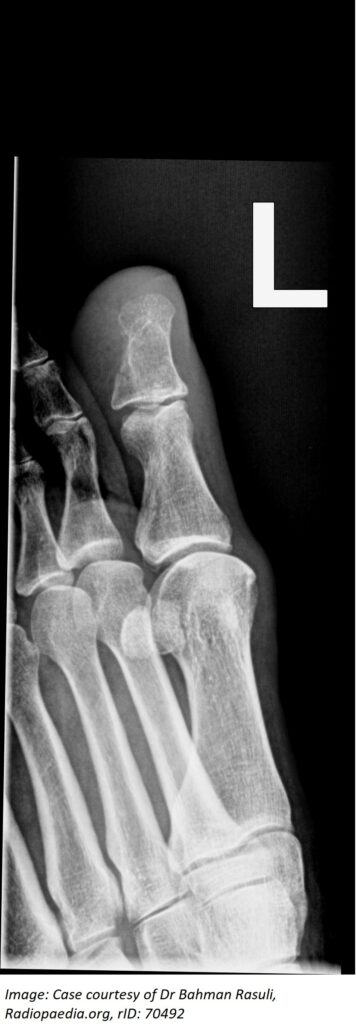
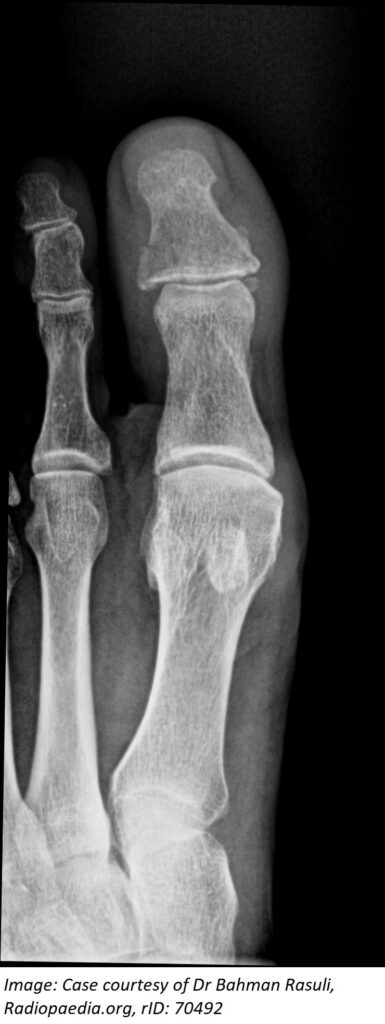
What is the MOST appropriate initial treatment?
A. Buddy strap great toe to second toe
B. Refer to physiotherapy for rehabilitation exercises
C. Short-leg walking cast with toe plate
D. Subungual haematoma drainage
E. Urgent review by orthopaedic surgeon for consideration of K-wire insertion
Correct Answer: C. Short-leg walking cast with toe plate
Question 32
Margaret Parer, aged 69 years, returns for results. She requested bone mineral densitometry testing after she sustained wrist and rib fractures recently in a motor vehicle accident. After discussion about her usual diet, you calculate her daily calcium intake to be around 1400 mg per day. Her vitamin D level is 55 nmol/L (normal range: >50). The results of her bone mineral densitometry are as follows:
| Location | Result | T-score normal range |
| Lumbar spine | T score = –1.2* | >–1.0: Normal –1.0 to –2.5: Osteopenia |
| Femoral neck | T score = –1.4* | <–2.5: Osteoporosis |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Alendronate 70 mg orally weekly
B. Calcium 500 mg orally daily
C. Encourage balance training and regular resistance exercise
D. Oestradiol–norethisterone acetate 50 mcg/140 mcg transdermal patch twice weekly
E. Vitamin D3 1000 IU orally daily
Correct Answer: C. Encourage balance training and regular resistance exercise
Question 33
Vicki O’Gorman, aged 36 years, developed a painful left breast two days earlier. She has been applying heat packs and gently massaging the breast. She is currently exclusively breast feeding her three-week-old baby. She has a history of type 1 diabetes and has an insulin pump. On examination, her temperature is 39.0°C, blood pressure 88/65 mmHg and heart rate 110/min regular. She has localised breast erythema and tenderness in the lateral left breast (see image).
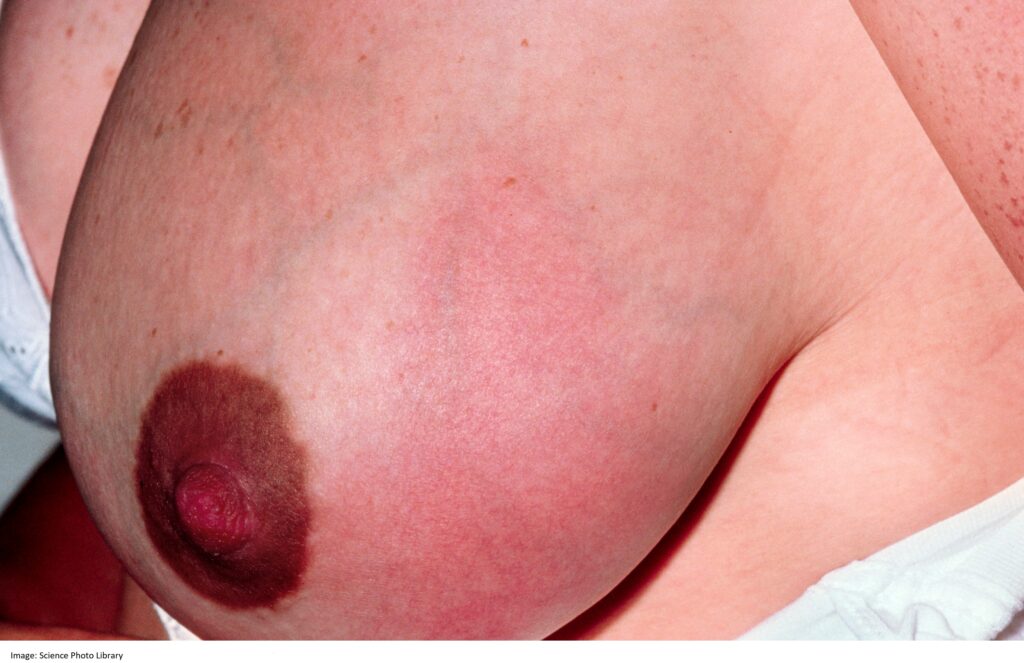
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Breast ultrasound
B. Cefalexin 500 mg orally four times daily for five days
C. Continue current management and review in 24 hours
D. Dicloxacillin 500 mg orally four times daily for seven days
E. Transfer to emergency department for intravenous antibiotics
Correct Answer: E. Transfer to emergency department for intravenous antibiotics
Question 34
Buckley Jones, aged 21 years, is concerned about the appearance and odour of his armpits. He has recently moved to North Queensland to attend university and feels that his body odour has become much worse. He is having difficulty masking the odour with an antiperspirant deodorant. He has also noticed a rash in his axillae. On examination, there are small dark yellow spots around the bases of the hair follicles, and you note the rash (see image).
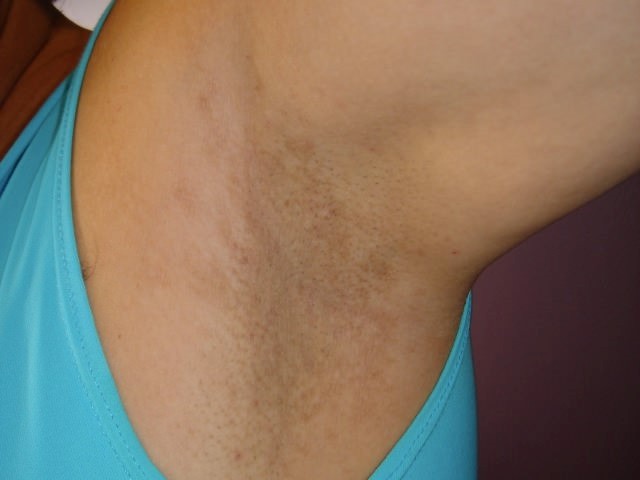
What is the MOST appropriate diagnosis?
A. Atopic dermatitis
B. Contact dermatitis
C. Erythrasma
D. Pityriasis versicolor
E. Tinea axillaris
Correct Answer: C. Erythrasma
Question 35
Siyuan Han, aged 40 years, reports blurring of her vision in the past two months. As a result, she had a car accident where she ‘just didn’t see the car coming.’ Her periods have also been less regular in the past six months.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
B. Cushing syndrome
C. Hemiplegic migraine
D. Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
E. Meningioma
F. Myasthenia gravis
G. Optic neuritis
H. Pituitary macroadenoma
Correct Answer: H. Pituitary macroadenoma
Question 36
Ajay Kandera, aged 51 years, and of Indian heritage, presents for blood test results. Over the past three months, he has been checking his blood pressure readings, and the average reading is 160/100 mmHg. He has already instituted some diet and lifestyle interventions to improve his cardiovascular risk. His fasting cholesterol results are shown below.
| Lipid study | Result | Desirable range (fasting) |
| Total cholesterol | 5.8 mmol/L* | <5.6 |
| High-density lipoprotein | 1.0 mmol/L* | >1.0 |
| Low-density lipoprotein | 2.3 mmol/L | <2.5 |
| Triglyceride | 1.3 mmol/L | <1.5 |
| Cholesterol/high-density lipoprotein ratio | 5.8* | <4.5 |
You calculate his absolute risk of cardiovascular disease within the next five years as high risk.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Aspirin 100 mg orally daily
B. Atenolol 50 mg orally daily
C. Candesartan 8 mg orally daily
D. Ezetimibe 10 mg orally daily
E. Reassess in 12 months after further dietary and lifestyle changes
Correct Answer: C. Candesartan 8 mg orally daily
Question 37
Melissa Gallagher, aged 28 years, returns for results. She initially presented two days earlier with painless, light vaginal spotting that lasted for three hours. She had recently had a positive home pregnancy test, and although her cycles are very irregular, it is estimated that she is seven weeks pregnant, according to her last menstrual period. At her initial visit, her heart rate was 75/min regular and blood pressure 120/70 mmHg. You performed a speculum examination and identified a closed cervix with a small amount of blood in the vagina. You arranged blood tests and an obstetric ultrasound. Her results are as follows:
| Test | Result from two days ago | Result from today | Normal range |
| Serum beta human chorionic gonadotropin | 220 mIU/L* | 450 mIU/L* | <5 |
| Blood group | A negative | – | – |
| Antibody screen | Negative | – | – |
| Haemoglobin | 128 g/L | – | 115–165 |
Ultrasound report: Uterus is mobile, volume 34 cc. Myometrium and endometrium normal. No gestational sac visible. Right ovary 3 cc, left 2 cc. No ovarian cystic or solid mass. No adnexal mass. Kidneys unremarkable.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Administer Rh(D) immunoglobulin 250 IU intramuscularly stat
B. Advise that she has had a miscarriage
C. Methotrexate 50 mg/m2 intramuscular injection
D. Refer to a gynaecologist for suction curettage
E. Repeat transvaginal ultrasound in seven days
F. Serum progesterone
G. Ulipristal 30 mg orally stat
H. Urgent transfer to emergency department
Correct Answer: E. Repeat transvaginal ultrasound in seven days
Question 38
Sarah Williams, aged 55 years, presents with a sudden onset of sharp, right-sided chest pain that is worse with breathing. She had a total laparoscopic hysterectomy three weeks ago, without any complications. Her temperature is 37.5°C, heart rate 120/min regular, blood pressure 135/78 mmHg, respiratory rate 24/min, oxygen saturation 96% on room air and her chest is clear to auscultation. You perform an electrocardiogram (see image). Her chest X-ray is normal.
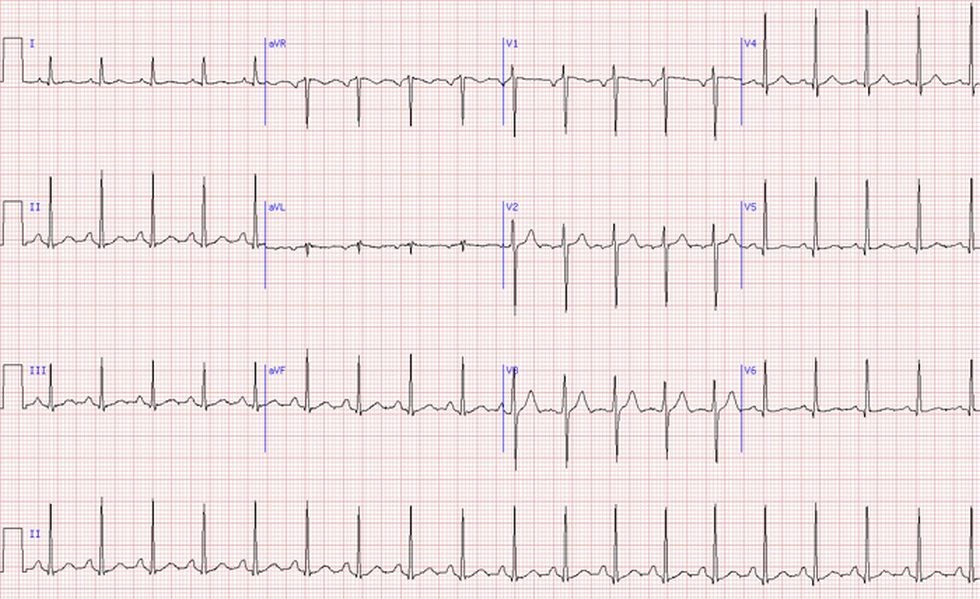
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Computed tomography chest
B. Computed tomography pulmonary angiography
C. D-dimer
D. Troponin assays
E. Ventilation–perfusion scan
Correct Answer: B. Computed tomography pulmonary angiography
Question 39
Erin Carson, aged 21 years, is an Aboriginal woman who is 10 weeks pregnant. She attends your remote health clinic for review of her routine antenatal investigations. Her only past medical history is of syphilis, which was fully treated 12 months ago; however, you are aware of an ongoing outbreak in her community. Erin’s antenatal tests show the following:
| Test | Result |
| Treponema pallidum enzyme immunoassay | Immunoglobulin G positive* |
| Treponema pallidum haemagglutination assay | Reactive* |
| Rapid plasma reagin | Negative |
| Fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test | Reactive* |
All other antenatal test results are normal.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Arrange chorionic villus sampling as soon as possible
B. Benzathine penicillin 1.8 g single dose by intramuscular injection
C. Provide reassurance that no further treatment or investigation is required
D. Recommend repeat syphilis serology at 28 weeks’ gestation
E. Repeat rapid plasma reagin in two weeks
Correct Answer: D. Recommend repeat syphilis serology at 28 weeks’ gestation
Question 40
Tommy Schmidt, aged 42 years, presents to your remote clinic, as his upper left central incisor was damaged about 10 minutes earlier during a football game. On examination, the tooth is subluxed and mobile within the socket. You arrange an urgent dental appointment in the regional centre three hours away.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Amoxicillin–clavulanate 875 mg/125 mg orally twice daily
B. Arrange urgent orthopantomogram
C. Gently extract damaged tooth and store in milk during transfer to dentist
D. Rinse mouth thoroughly with water and repeat every 15 minutes while awaiting dental appointment
E. Splint damaged tooth with aluminium foil
Correct Answer: E. Splint damaged tooth with aluminium foil
Question 41
Cole Parker, aged 75 years, has had increasing shortness of breath, an increase in sputum production and a change in sputum colour from white to a dirty brown over the past week. Usually, he can walk quickly on flat ground, but today is breathless, even when walking slowly, although not at rest. For the past three days, he has been using salbutamol 100 mcg eight inhalations every four hours. He usually takes tiotropium 18 mcg inhaled daily for chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. On examination, his temperature is 38.0°C, heart rate 88/min regular, blood pressure 130/78 mmHg and oxygen saturation 95% on room air. Chest auscultation reveals rhonchi bilaterally.
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Amoxicillin 500 mg orally three times daily for seven days
B. Budesonide–eformoterol 200 mcg/6 mcg two inhalations twice daily
C. Fluticasone propionate 100 mcg inhaled twice daily
D. No change to treatment necessary at this time
E. Peak expiratory flow rate readings every four hours, and review in 24 hours
F. Prednisone 30 mg orally daily for three days
G. Prednisone 30 mg orally daily plus doxycycline 100 mg orally daily for five days
H. Refer for home oxygen therapy
I. Refer for pulmonary rehabilitation
J. Transfer to emergency department
Correct Answer: G. Prednisone 30 mg orally daily plus doxycycline 100 mg orally daily for five days
Question 42
Rita Barillo, aged 65 years, has had three weeks of right-sided facial pain. Initially she experienced sharp spasms of pain that lasted about a minute and radiated from the corner of her mouth towards the angle of her jaw. This week, she has had a constant ache in the area, but still experiences the sharp spasms as well. The pain occurs most often when she is drinking a hot beverage or when the cold air conditioning blows on her face in the car. Her physical examination is unremarkable.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise her to see the dentist for review
B. Amitriptyline 25 mg orally at night
C. Carbamazepine 100 mg orally twice daily
D. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
E. Magnetic resonance imaging right temporomandibular joint
F. Paracetamol–codeine 500 mg/30 mg orally every six hours, as required
G. Prednisolone 50 mg orally daily for five days
H. Sumatriptan 50 mg orally at the first sign of symptoms
I. Temporal artery biopsy
J. X-ray right temporomandibular joint
Correct Answer: C. Carbamazepine 100 mg orally twice daily
Question 43
Chris Murray, aged 46 years, is rushed to your rural emergency department with severe, central abdominal pain. The pain started four hours earlier, and radiates to his back and flanks. He looks distressed, and is pale and sweating profusely. He has vomited once and had two loose bowel motions today. On examination, his temperature is 37.2°C, heart rate 110/min regular, blood pressure 104/68 mmHg and respiratory rate 18/min. His abdomen is distended with a tender epigastrium and rebound tenderness.
Which investigation is MOST appropriate to confirm the provisional diagnosis?
A. Amylase
B. Electrocardiogram
C. Lipase
D. Liver function tests
E. Ultrasound kidneys, ureters and bladder
Correct Answer: C. Lipase
Question 44
Mick Kors, aged 42 years, is anxious about giving the eulogy at his father’s funeral. He usually avoids public speaking, as it causes him to sweat, feel nauseated and develop palpitations. You have seen him previously about his generalised anxiety disorder, for which he takes sertraline 50mg orally daily and sees a psychologist regularly. On examination, his heart rate is 90/min regular, blood pressure 130/85 mmHg and heart sounds are dual.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Alprazolam 0.5 mg orally twice daily, as required
B. Amitriptyline 10 mg orally the night before the event
C. Change sertraline to escitalopram 10 mg orally daily
D. Change sertraline to venlafaxine extended release 75 mg orally daily
E. Plasma metanephrines
F. Propranolol 10 mg orally 30 minutes prior to event
G. Thyroid function test
H. Zopiclone 7.5 mg orally the night before the event
Correct Answer: F. Propranolol 10 mg orally 30 minutes prior to event
Question 45
Aoge Obete, aged 79 years, is brought in by his daughter who is concerned about his vision. Aoge is a retired businessman from Africa who is currently visiting his daughter while on holiday. His vision has been gradually deteriorating over the past three years, and although he is able to avoid large objects when walking in familiar surroundings, he can no longer go out on his own. He used to enjoy reading, but now finds it difficult to see the words. In the past few days, his central vision has worsened, and he has noticed that straight lines appear distorted. Eye examination reveals bilateral clear corneas and normal red reflexes. Visual acuity is 6/12 (left eye) and 6/60 (right eye).
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Acetazolamide 250 mg intravenously stat dose
B. Aciclovir 3% eye ointment topically five times daily for five days
C. Aspirin 100 mg orally daily
D. Dexamethasone 0.1% eye drops one drop four times daily
E. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
F. HbA1c
G. Latanoprost 0.005% eye drops one drop daily
H. Recommend vitamin A, vitamin C and beta carotene supplements
I. Timolol 0.5% eye drops one drop daily
J. Urgent referral to an ophthalmologist for intravitreal injection
Correct Answer: J. Urgent referral to an ophthalmologist for intravitreal injection
Question 46
Patrick Smith, aged 4 years, is brought in by his mother for review of his asthma. Patrick has experienced two episodes of asthma in the past six weeks. On the first occasion, Patrick received oral corticosteroids and was managed at home. On the second occasion, he was admitted to the paediatric intensive care unit where he received nebulisers, oxygen, corticosteroids and an intravenous magnesium infusion. In between these episodes, he has been well and has not needed to use his puffer. His current medications are salbutamol 100 mcg inhaler four to six puffs via spacer, when required, and hydrocortisone cream 1% topically for eczema.
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Add fluticasone 100 mcg inhaled twice daily
B. Add montelukast 4 mg orally daily
C. Arrange spirometry to confirm asthma diagnosis
D. Change salbutamol to budesonide–formoterol 100 mcg/6 mcg inhaled, as required
E. Increase salbutamol to 100 mcg 12 puffs via spacer, as required
Correct Answer: A. Add fluticasone 100 mcg inhaled twice daily
Question 47
Joseph McElwaine, aged 30 years, is a medical student who would like to discuss hepatitis B immunisation, which he requires for his upcoming clinical placement. Two years ago, he received two doses of hepatitis B immunisation, one month apart.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Administer a double dose of hepatitis B vaccine today
B. Administer one further dose of hepatitis B vaccine today
C. Arrange hepatitis B surface antibody levels
D. Reassure that no further hepatitis B vaccinations are required
E. Restart hepatitis B vaccination schedule today using a 0-, 1- and 6-month regime
Correct Answer: B. Administer one further dose of hepatitis B vaccine today
Question 48
Rebecca Stevens, aged 24 years, has requested an urgent appointment to see you today for herpes simplex virus testing. Her boyfriend of three months disclosed to her last night that he might have had an earlier episode of genital herpes. Neither Rebecca nor her partner have any current symptoms. Rebecca has had four sexually transmissible infection screens performed in the past 12 months. The most recent screen was performed four weeks ago and was negative. She takes ethinyloestradiol–levonorgestrel 20 mcg/100 mcg orally daily for contraception. Physical examination is normal.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise testing for herpes simplex virus is not indicated at this stage
B. First-pass urine for chlamydia, gonorrhoea and herpes simplex virus polymerase chain
reaction testing
C. Herpes simplex virus serology
D. Perform a high vaginal swab for herpes simplex virus polymerase chain reaction testing
E. Reassure Rebecca she will not contract herpes simplex virus if her partner is asymptomatic
Correct Answer: A. Advise testing for herpes simplex virus is not indicated at this stage
Question 49
Ainsley Harris, aged 55 years, has been feeling very unwell for several months. She has been having ‘attacks’ of flushing that seem to be getting worse. During one of these episodes, she feels light-headed, and her face becomes hot and flushed. Her chest also feels tight and she develops a wheeze. She usually needs to run to the bathroom with abdominal cramps and diarrhoea. She has not been as hungry lately and has lost 2 kg over the past three months. Her physical examination today is normal. Initial blood tests support your provisional diagnosis.
What is the MOST appropriate investigation to confirm the provisional diagnosis?
A. 24-hour urinary catecholamines and metanephrines
B. Computed tomography chest and abdomen
C. Dexamethasone suppression test
D. Magnetic resonance imaging pituitary
E. Ultrasound pelvis
Correct Answer: B. Computed tomography chest and abdomen
Question 50
Mark Berkhowitz, aged 36 years, would like to see a psychologist. He has ‘always kept to himself’ and has never had a partner. He has difficulty meeting people and making friends, and tends to avoid social interactions. He works from home in information technology and says he always performed well academically at university. He says that he feels uncomfortable with change and prefers to follow a routine. You note that throughout the consultation he avoids eye contact and his facial expressions do not match his words.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Adjustment disorder
B. Anxiety disorder
C. Autism spectrum disorder
D. Bipolar disorder
E. Borderline personality disorder
F. Conduct disorder
G. Major depressive disorder
H. Obsessive compulsive disorder
