Question 1
Ben Bird, aged 24 years, has felt unwell since returning from a white water rafting trip in the Amazon. Ben is up to date with all of his usual childhood vaccinations and had a hepatitis A and a yellow fever vaccination before he went to the Amazon. He is still on atovaquone-proguanil for malaria prophylaxis. Just prior to flying home, he developed fevers, myalgia, and a frontal headache. He has felt unwell for five days but today has had significant bilateral calf pain and nausea. Appropriate COVID-19 testing was negative. On examination, his temperature is 38 °C and he appears mildly jaundiced.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Acute hepatitis B infection
B. Acute hepatitis E infection
C. Deep vein thrombosis
D. Drug-related hepatitis
E. Gilbert syndrome
F. Leptospirosis
G. Plasmodium vivax
H. Schistosomiasis
Correct Answer: F. Leptospirosis
Question 2
Millie House, aged 25 years, has experienced menstrual bleeding for the last 12 days. Her periods have been irregular for many years with between 21 and 90 days between periods. Her periods started at age 14 years. She has gained 10 kg in the last five years and her body mass index is 31 kg/m2. She has tried many treatments to control her acne and uses multiple products to help control coarse hair on her upper lip.
You request a pelvic ultrasound to help confirm your provisional diagnosis.
What feature are you MOST likely to find on a pelvic ultrasound to confirm your provisional diagnosis?
A. Adnexal mass
B. Cervical mass
C. Endometrial polyp
D. Endometrial thickening greater than 8 mm
E. More than 20 follicles within each ovary
F. Ovarian endometrioma
G. Primarily follicles in one ovary
H. Submucosal fibroids
I. Thickened fallopian tubes
Correct Answer: E. More than 20 follicles within each ovary
Question 3
John Peters, aged 56 years, recently moved from interstate. He has a history of non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome six months ago. He has had type 2 diabetes for 10 years. He has a 15 pack year cigarette smoking history but quit 10 years ago when diagnosed with diabetes. Since his diabetes diagnosis, he has lost 15 kg through diet and exercise.
His current medications are aspirin 100 mg orally daily, clopidogrel 75 mg orally daily, enalapril 2.5 mg orally daily, metoprolol 25 mg orally twice daily, rosuvastatin 10 mg orally daily and metformin 1000 mg orally twice daily. On examination, his heart rate is 70/min regular, blood pressure 125/78 mmHg, and his heart sounds are normal.
He brings copies of his most recent blood tests, performed two weeks ago. Full blood examination is normal.
| Biochemistry | Result | Normal range |
| Sodium | 137 mmol/L | 135 – 145 |
| Potassium | 3.8 mmol/L | 3.5 – 5.2 |
| Chloride | 98 mmol/L | 95 – 110 |
| Bicarbonate | 29 mmol/L | 22 – 32 |
| Urea | 5.7 mmol/L | 2.5 – 8.0 |
| Creatinine | 85 µmo/L | 45 – 90 |
| Estimated glomerular filtration rate | > 90 mL/min/1.73m2 | > 90 |
| Urate | 0.36 mmol/L | < 0.42 |
| Glycated haemoglobin | 7.4*% | < 6% |
| Urine albumin / creatinine ratio | 3.2 mg/mmol | < 3.5 |
| Lipid studies | Result | Desirable range (fasting) |
| Total cholesterol | 3.9 mmol/L | < 5.6 |
| High-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol | 1.2 mmol/L | < 1.0 |
| Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol | 1.8 mmol/L | < 2.5 |
| Triglyceride | 1.2 mmol/L | < 1.5 |
| Cholesterol / HDL ratio | 3.25 | < 4.5 |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Cease clopidogrel
B. Empagliflozin 10 mg orally daily
C. Ezetimibe 10 mg orally daily
D. Hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg orally daily
E. Increase rosuvastatin to 20 mg orally daily
F. Insulin glargine 100 units/mL 0.2 units/kg (up to 30 units) subcutaneously daily
G. Rosiglitazone 4 mg orally daily
H. Saxagliptin 5 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: B. Empagliflozin 10 mg orally daily
Question 4
Jason McRae, aged 35 years, developed a localised painful rash on his left chest wall (see image) three days ago while on a camping trip. He has not noticed a rash in any other areas. He has a mild headache and feels more tired than usual. Jason was commenced on antiviral treatment and regular paracetamol by another doctor while away. Jason has significant pain within the area of his chest associated with the rash and is seeking symptom relief as soon as possible.
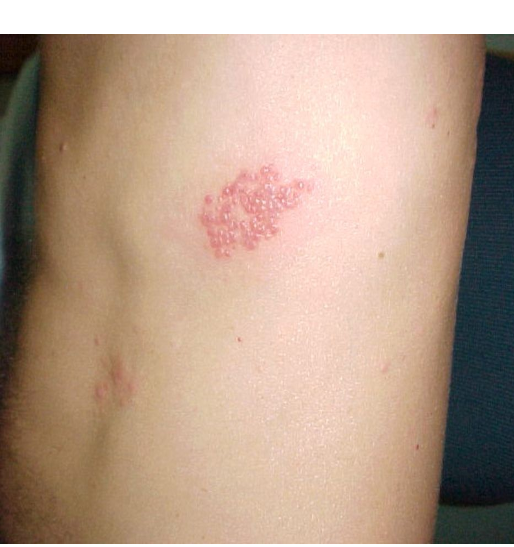
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Carbamazepine 200 mg orally twice daily
B. Dicloxacillin 500 mg four times orally daily for seven days
C. Duloxetine 30 mg orally daily increasing to 60 mg orally daily after four weeks
D. Gabapentin 300 mg orally twice daily increasing to 600 mg orally twice daily
E. Oxycodone modified-release 5 mg orally twice daily
F. Prednisolone 50 mg orally daily for seven days
G. Send swab for microscopy, culture and sensitivity, and then review with results within two days
H. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole 160 mg/800 mg orally twice daily for five days
Correct Answer: D. Gabapentin 300 mg orally twice daily increasing to 600 mg orally twice daily and F. Prednisolone 50 mg orally daily for seven days
Question 5
Ying Wu, aged 48 years, has had central chest pain and felt breathless when walking around the house for the past two days. The chest pain improves when she sits upright and leans forward. She had an upper respiratory tract infection last week and was off work for a few days with fever and a cough, but these symptoms have now settled. She had appropriate COVID-19 testing which was negative. On examination, her heart rate is 82/min regular, blood pressure 105/75 mmHg, respiratory rate 15/min, and temperature 37.5 °C. Her heart sounds are dual with no murmurs, jugular venous pressure is 5 cm above the sternal angle, and her liver is tender and palpable 4 cm below the costal margin.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Acute pulmonary oedema
B. Asthma
C. Bronchopneumonia
D. Dissecting aortic aneurysm
E. Mycoplasma pneumoniae
F. Myocardial infarction
G. Pericarditis
H. Pulmonary embolus
I. Spontaneous pneumothorax
Correct Answer: Pericarditis
Question 6
Kyle Gonzoles, aged 37 years, is concerned that he may have prostate trouble like his father experienced. Kyle’s urine stream is getting progressively weaker and it seems to take longer to empty his bladder. He has had soreness and irritation around the urethral meatus and his foreskin is increasingly difficult to retract fully. On examination, his penis appears as shown (see image).
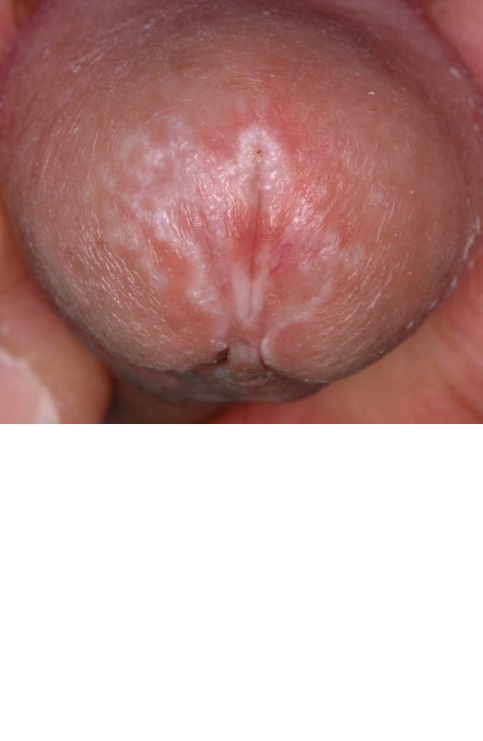
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Atrophic urethritis
B. Behcet disease
C. Chlamydia trachomatis
D. Contact dermatitis
E. Lichen simplex
F. Paraphimosis
G. Penile lichen sclerosus
H. Peyronie disease
I. Prostate cancer
J. Psoriasis
K. Squamous cell carcinoma
Correct Answer: G. Penile lichen sclerosus
Question 7
Tim Kenty, aged 25 years, presents to your rural clinic with increasing right shoulder pain after playing basketball earlier today. There was no trauma sustained during the game. On examination, his temperature is 37.1°C, heart rate 100/min regular, respiratory rate 24/min, blood pressure 122/70 mmHg, oxygen saturation 97% on room air and body mass index 19 kg/m2. Range of motion in his shoulder is normal. You arrange an X-ray (see image).
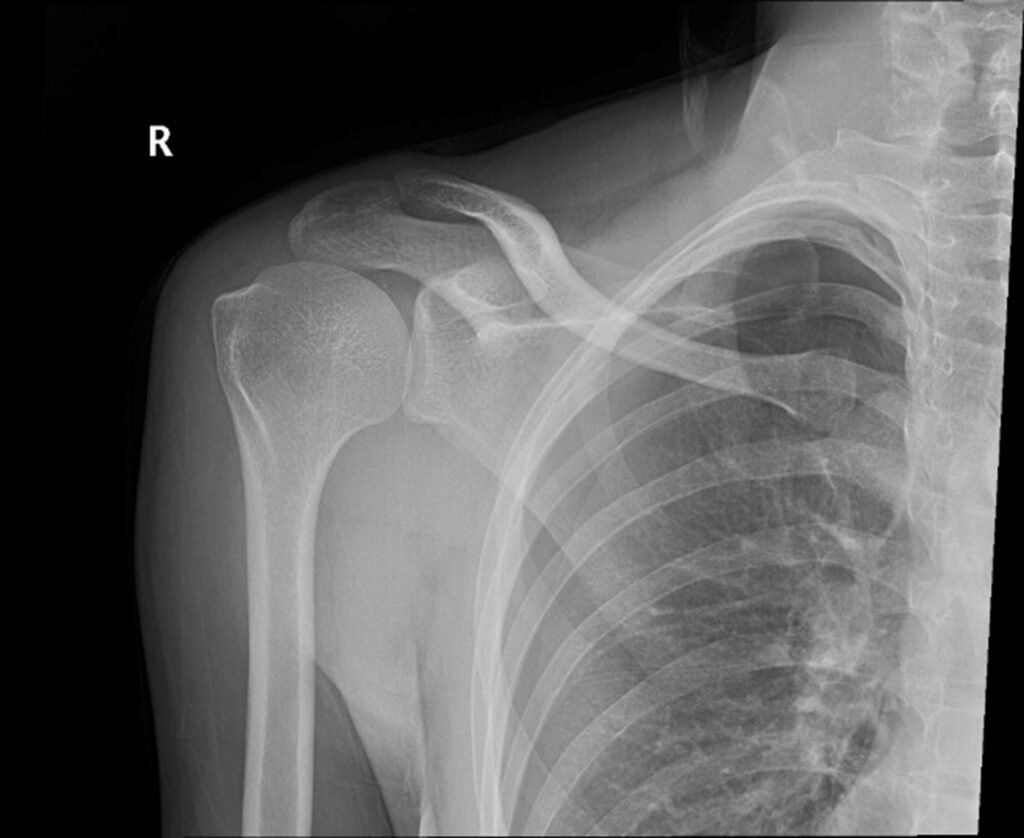
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Immobilise arm in broad-arm sling for six weeks, then review
B. Refer to a physiotherapist for stretching and strengthening
C. Subacromial corticosteroid injection
D. Ultrasound shoulder
E. Urgent X-ray chest
Correct Answer: E. Urgent X-ray chest
Question 8
Rachael Burns, aged 39 years, has a rash on her right wrist (see image) that has worsened over the last two months. The rash is often very itchy.
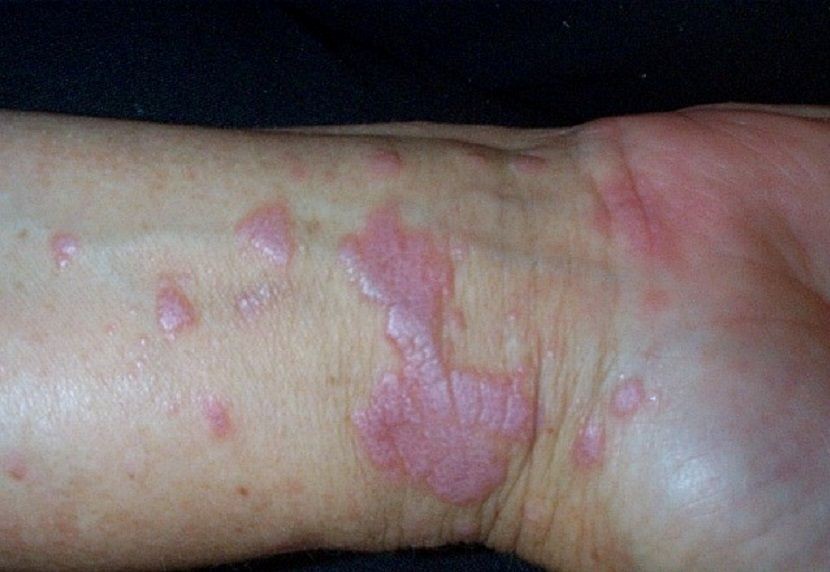
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% ointment topically daily
B. Clotrimazole cream 1% topically twice daily and continue for one week after rash has resolved
C. Methotrexate 10 mg orally once weekly with folic acid supplementation
D. Permethrin cream 5% topically from neck down one application tonight and repeated in one week
E. Prednisolone 25 mg orally daily for seven days
Correct Answer: A. Betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% ointment topically daily
Question 9
Michelle Lindsay, aged 46 years, has an irritated and painful red eye (see image). The pain has been increasing over the past 24 hours but she cannot recall any preceding trauma. There has been no discharge from the eye and bright lights do not bother her. Michelle has rheumatoid arthritis and her symptoms are well controlled on methotrexate 10 mg orally weekly.
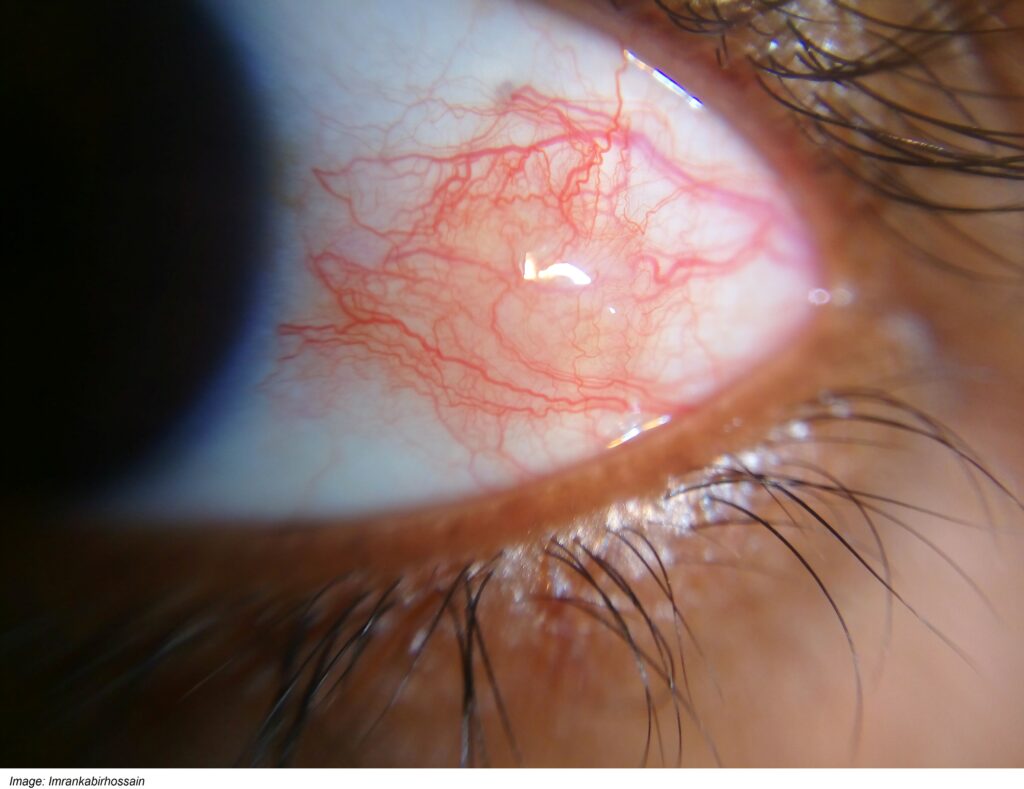
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Acute glaucoma
B. Allergic conjunctivitis
C. Blepharitis
D. Dendritic ulcer
E. Episcleritis
F. Foreign body
G. Iritis
H. Pterygium
I. Sub-conjunctival haemorrhage
J. Uveitis
K. Viral conjunctivitis
Correct Answer: E. Episcleritis
Question 10
June Ball, aged 62 years, has had difficulty coping since her husband died suddenly six weeks ago from a heart attack. She cries most of the day and finds it difficult to concentrate on tasks. She has felt very tired but has been sleeping through the night. She has supportive friends and family. She prefers not to go out with friends but likes doing the gardening. She has enjoyed going to the cinema a couple of times recently.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Diazepam 5 mg orally three times daily as required
B. Escitalopram 10 mg orally daily
C. Offer support and provide regular follow-up
D. Organise blood tests including a full blood count, C-reactive protein and electrolytes
E. Refer her to a psychologist for cognitive behavioural therapy
Correct Answer: C. Offer support and provide regular follow-up
Question 11
Shirley Knight, aged 86 years, has severe Alzheimer’s disease. She lives in a residential aged are facility. She has been deemed not competent to make her own health decisions and she has a medical Enduring Power of Attorney. For the last six months Shirley has been arguing with the other residents and sometimes tries to hit them. The staff report increasing difficulty managing Shirley’s behaviour and are worried that she might harm herself or others. Recent appropriate examinations and investigations revealed no new organic pathology. All appropriate non-pharmacological measures have been implemented and medication is now being considered for the safety of Shirley and others around her. Her family and her Enduring Power of Attorney agree a trial of medication is the most appropriate next course of action.
What is the MOST appropriate initial medication?
A. Alprazolam 1 mg orally as required every four hours
B. Escitalopram 20 mg orally daily
C. Haloperidol 0.5 mg orally twice daily
D. Risperidone 0.25 mg orally twice daily
E. Sodium valproate 200 mg orally twice daily
Correct Answer: D. Risperidone 0.25 mg orally twice daily
Question 12
Geoff Idol, aged 15 years, has been having difficulties at school and has missed 10 days of school within the last term. Geoff grasps concepts quickly and often scores very well in tests. He is well liked and has several close friends. His teachers have noticed he spends a lot of time lining up his pens at the top of his desk and becomes distressed if anyone moves them. Pointing out his behaviour makes him agitated and the behaviours become worse. He was noted to be flustered in one of the exams and did not attend for the remaining exams. He often feels very anxious when he cannot stop thinking about how to appropriately organise his homework. He spends a lot of time playing computer games and says playing games distracts him from worrying about homework.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Agoraphobia
B. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
C. Autism spectrum disorder
D. Bipolar disorder
E. Central auditory processing disorder
F. Childhood onset fluency disorder
G. Conduct disorder
H. Generalised anxiety disorder
I. Intellectual impairment
J. Obsessive compulsive disorder
K. Post-traumatic stress disorder
L. Social anxiety disorder
M. Specific learning disorder (dyslexia)
Correct Answer: J. Obsessive compulsive disorder
Question 13
Ethan Edwards, aged 6 years, is only passing one hard and painful bowel movement per week. Recently, he has soiled his underwear a couple of times per week. Ethan was having daily bowel motions with normal stool consistency until he started school six months ago. On review of Ethan’s records, you note his parents have been advised to increase fibre and fluids in Ethan’s diet and have been given toileting behaviour modification strategies. Ethan has been prescribed paraffin oil 10 mL orally daily as needed. On examination, there is a palpable mass in his left lower abdomen. Visual examination of his perianal area is normal.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Abdominal ultrasound
B. Abdominal X-ray
C. Colonic transit time study
D. Docusate sodium 50 mg one tablet nightly until satisfactory bowel evacuation
E. Glycerin 1 g suppository single dose administered rectally
F. Macrogol 3350 17 g orally daily, dose increasing daily until satisfactory bowel evacuation
G. Microlax™ enema administer single dose rectally
H. Perform digital rectal examination
I. Refer to a paediatrician for developmental assessment
J. Sodium picosulfate drops 10 drops nocte until satisfactory bowel evacuation
Correct Answer: F. Macrogol 3350 17 g orally daily, dose increasing daily until satisfactory bowel evacuation
Question 14
Carolina Ramirez, aged 52 years, would like advice regarding screening for bowel cancer. Her father was diagnosed with bowel cancer at age 60 years, and her paternal uncle was diagnosed with prostate cancer at age 78 years. You discuss the use of low-dose aspirin for bowel cancer chemoprophylaxis.
What is the MOST appropriate screening to recommend?
A. Colonoscopy every five years
B. Colonoscopy every two years
C. Faecal occult blood test every two years
D. Faecal occult blood test every two years PLUS colonoscopy every five years
E. Referral to a family cancer centre for genetic testing
Correct Answer: C. Faecal occult blood test every two years
Question 15
Ashley Peters, aged 57 years, has an intensely itchy rash on his chest and back (see image). The rash has been present for a few months but has recently worsened and the itch is now keeping him awake at night. The rash extends up his neck and onto his upper arms; his hands have not been affected. The rash is worse when he sweats and he now wears very light weight clothing. He has taken an over-the-counter antihistamine with some improvement in his symptoms.
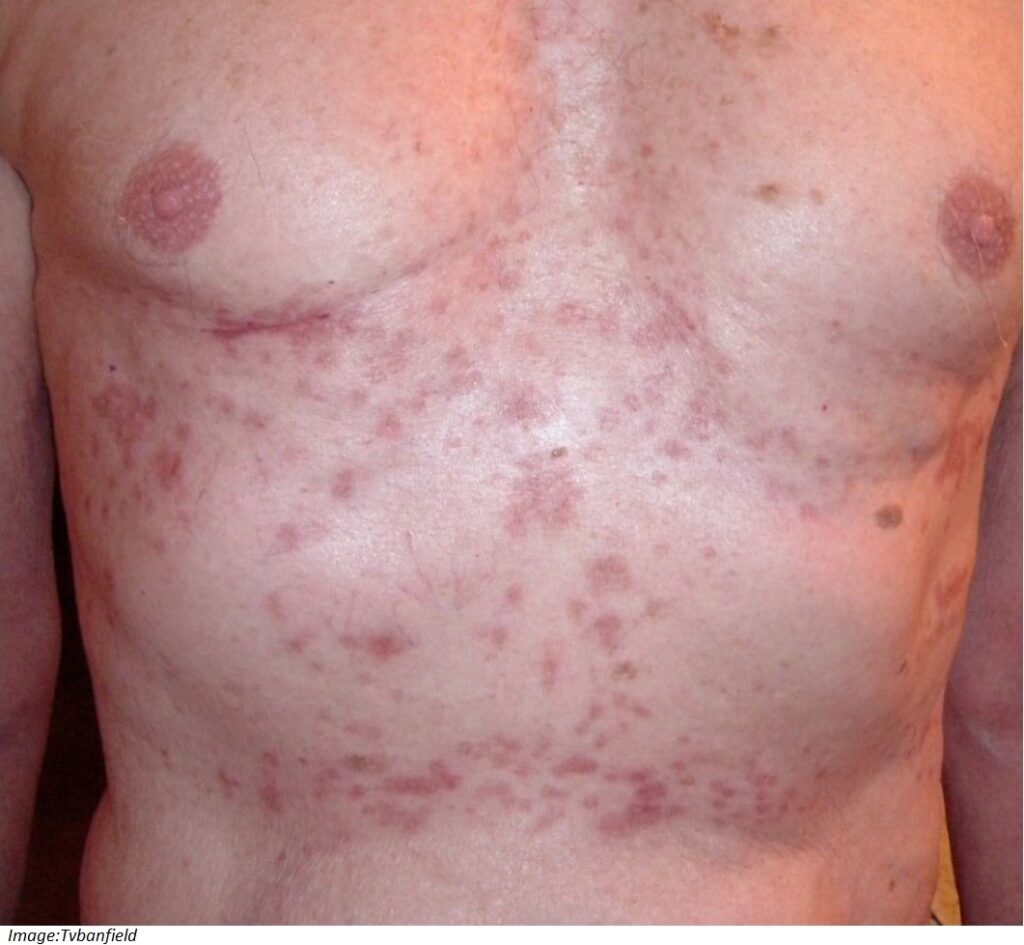
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Calcipotriol 50 mcg/g gel topically daily
B. Clindamycin 1% solution topically twice daily
C. Permethrin 5% cream topically at night and then repeated one week later
D. Terbinafine 1% cream topically daily
E. Triamcinolone acetonide 0.02% cream topically twice daily
Correct Answer: E. Triamcinolone acetonide 0.02% cream topically twice daily
Question 16
Jamie Mathers, aged 12 years, fell off a slide at school yesterday and injured his left wrist. His mother brings him for review today as he is still saying his wrist is sore. On examination, there is mild swelling of the wrist and tenderness laterally. An X-ray is performed (see images).
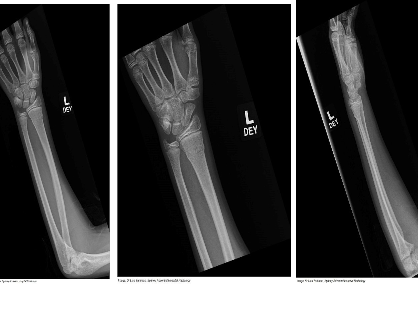
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise rest, ice, compression and elevation of the wrist until symptoms resolve
B. Apply a wrist splint for three to four weeks
C. Closed reduction with immobilisation in above-elbow cast for six weeks
D. Computed tomography scan left wrist
E. Encourage range of movement exercises and stretching
Correct Answer: B. Apply a wrist splint for three to four weeks
Question 17
Francene Miller, aged 82 years, has had left hip pain since she fell three days ago at the residential aged care home where she lives. She is unable to weight-bear due to the pain. She was taken to the local emergency department on the day of the fall and the discharge summary states that X-rays of the left hip/pelvis and blood tests were normal. On examination, there is no obvious deformity of the left leg and her range of motion of the left hip is globally reduced due to pain. Spinal examination is normal. Her body mass index is 19 kg/m2, which is unchanged since 12 months ago.
What is the MOST appropriate investigation to confirm your provisional diagnosis?
A. Bone density scan
B. Bone scan left hip/pelvis
C. Magnetic resonance imaging left hip
D. Repeat X-ray left hip/pelvis
E. Ultrasound left hip
Correct Answer: C. Magnetic resonance imaging left hip
Question 18
John Matthews, aged 4 years, returns to your clinic in a remote Aboriginal community as he has ongoing tiredness and a loss of appetite. You note that he presented with the same symptoms two weeks ago and his stool tested positive for hookworm. He was treated with a stat dose of albendazole 400 mg orally.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Full blood count
B. Mebendazole 100 mg orally twice daily for three days
C. Repeat dose of albendazole 400 mg orally stat
D. Repeat stool microscopy, culture and sensitivities
E. Tinidazole 2 g orally stat
Correct Answer: A. Full blood count
Question 19
Winifred Smith, aged 79 years, is accompanied by her son, Michael, who is concerned that Winifred has seemed increasingly confused and lethargic for the last three weeks. Winifred explains she has not been eating as she has been feeling nauseous. Winifred has a slim build but has not lost any weight. Following the death of her husband several months ago, Winifred was diagnosed with major depression. She was commenced on sertraline 50 mg orally daily five weeks ago. She takes no other regular medication. You suspect she is experiencing an adverse reaction to her medication.
Given your provisional diagnosis, what is the MOST likely expected investigation finding?
A. Hypercalcaemia
B. Hyperglycaemia
C. Hyperkalaemia
D. Hyponatraemia
E. Hypothyroidism
F. Vitamin B12 deficiency
G. Vitamin D deficiency
Correct Answer: D. Hyponatraemia
Question 20
Shane Maxwell, aged 42 years, presents for results two days after excision of an atypical pigmented lesion from his left chest. His histology report is as follows:
Excision left chest:
- Clark level 2 melanoma, Breslow thickness is 0.38 mm
- No ulceration
- No dermal mitoses seen (0 per mm2)
- Arising in a dysplastic compound naevus
- Peripheral margins are clear by 2 mm
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. No further treatment required
B. Positron emission tomography scan
C. Sentinel lymph node biopsy
D. Wider excision with a 10 mm margin
E. Wider excision with a 20 mm margin
Correct Answer: D. Wider excision with a 10 mm margin
Question 21
Meryl Noonan, aged 77 years, is rushed into your clinic with severe, central crushing chest pain. On examination, she is pale and sweaty, her heart rate is 96/min regular, blood pressure 85/60 mmHg, respiratory rate 16/min and SpO2 95% on room air. An electrocardiogram is performed (see image) and you arrange an ambulance transfer to hospital. Intravenous access is secured and you administer aspirin 300 mg orally.
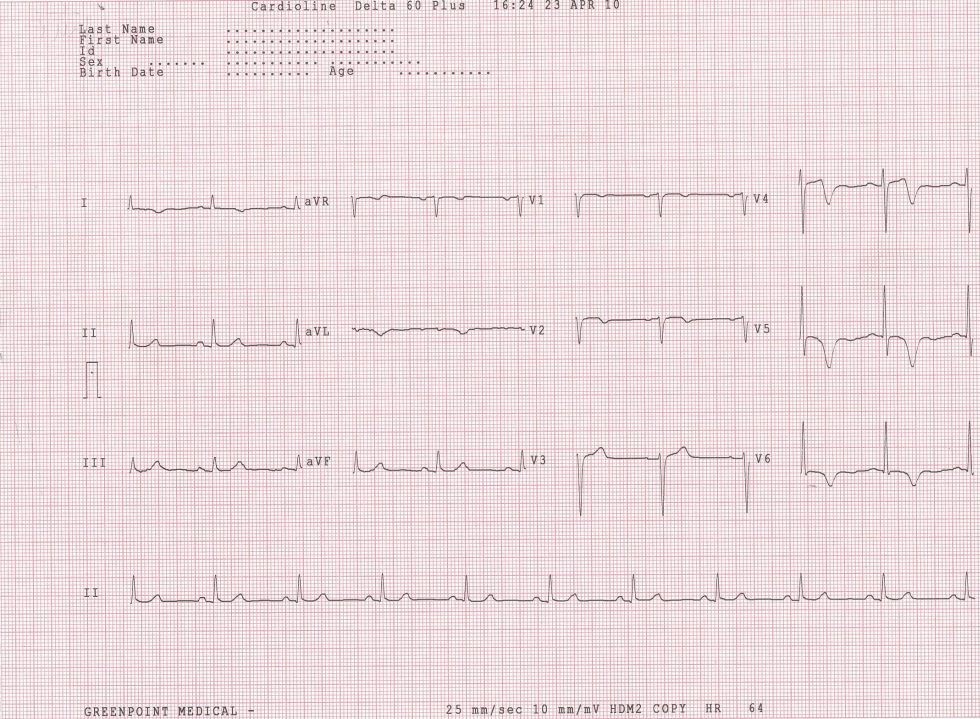
What is the MOST appropriate next immediate management?
A. Clopidogrel 600 mg orally stat
B. Glyceryl trinitrate 25 mg patch topically stat
C. Morphine 2.5 mg intravenously stat
D. Nitroglycerin 400 mcg sublingual spray orally stat
E. Oxygen 6 L/min via Hudson mask
Correct Answer: Morphine 2.5 mg intravenously stat
Question 22
Mikayla Yates, aged 12 years, presents with her parents on the advice of her physiotherapist. Ten weeks ago, Mikayla suffered an inversion injury to her ankle while playing netball at school. Imaging excluded a fracture and she was diagnosed with a lateral ankle sprain. Her pain has not improved with physiotherapy.
The pain is now ‘all over her foot’. She mobilises with crutches as she is unable to weight-bear or even wear socks or shoes. At times her foot appears pale. Palpation of her foot and ankle reveals general tenderness within all areas globally. Her skin appears mildly dry and mottled with no oedema. Pedal pulses are normal.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Begin mobilisation with air cast walking boot
B. Bone scan of the foot
C. Ibuprofen 10 mg/kg (up to 400 mg) orally three times daily
D. Magnetic resonance imaging of the ankle
E. Refer to orthopaedic surgeon for open surgical exploration
F. Referral to multidisciplinary pain clinic
G. Urgent referral to emergency department
H. Venous duplex ultrasound of the leg
Correct Answer: F. Referral to multidisciplinary pain clinic
Question 23
Sam Heady, aged 6 years, comes in with his father, Jack, with bleeding from his nose. There is a lot of blood on Sam’s shirt. His nose was hit by a soccer ball at school and has been bleeding for a few minutes. You show Jack how to pinch the cartilage of Sam’s nose, which he does.
What is the MOST appropriate position to place Sam in?
A. Sitting, head forward
B. Sitting, head back
C. Lying on his front, head facing downwards off the end of the treatment bed
D. Lying on his side; advise him to spit out blood in his mouth
E. Lying on his back; advise him to swallow blood in his mouth
Correct Answer: A. Sitting, head forward
Question 24
Amena Hado, aged 22 years, is a refugee who has recently arrived from Syria. She has had a persistent vaginal discharge for the past few months. On examination, she has a profuse, frothy, yellow, slightly blood-stained discharge that has a strong odour. Appropriate further investigations are performed.
What is the MOST appropriate next pharmacological step?
A. Azithromycin 1 g orally stat
B. Ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly stat
C. Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for seven days
D. Fluconazole 150 mg orally stat
E. Metronidazole 2 g orally stat
Correct Answer: E. Metronidazole 2 g orally stat
Question 25
Margaret Sullivan, aged 76 years, has a burning feeling in her legs when walking. The pain begins after walking 200 metres and then she needs to stop, which slowly relieves the discomfort. She has a 10 pack year smoking history but quit 12 years ago. She has hypertension controlled with ramipril 10 mg orally daily and hyperlipidaemia controlled with atorvastatin 40 mg orally daily. She chooses to take aspirin 100 mg orally daily ‘for her blood’. On examination, her heart rate is 70/min regular and blood pressure is 130/85 mmHg. Her pedal pulses are reduced bilaterally with no oedema or ulceration on the lower limbs.
Full blood examination and biochemistry are within normal limits. Further investigation results are as follows:
| Lipid studies | Result | Normal range |
| Total cholesterol | 3.8 mmol/L | < 5.6 |
| High-density lipoprotein | 1.8 mmol/L | < 1.0 |
| Low-density lipoprotein | 1.9 mmol/L | < 2.5 |
| Triglyceride | 1.4 mmol/L | < 1.5 |
Lower limb arterial duplex ultrasonography: Calcified and hypoechoic plaque present bilaterally with no focal haemodynamically significant stenosis. Ankle brachial indices are:
0.7 on the right and 0.8 on the left.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Clopidogrel 75 mg orally daily
B. Computed tomography angiogram lower limbs
C. Ezetimibe 10 mg orally daily
D. Graduated walking program
E. Increase atorvastatin to 80 mg orally daily
F. Increase ramipril to 15 mg orally daily
G. Isosorbide mononitrate modified-release 30 mg orally daily
H. Lercanidipine 10 mg orally daily
I. Refer to vascular surgeon for angioplasty
Correct Answer: D. Graduated walking program
Question 26
John Finlay, aged 20 years, presents to your rural clinic with pain in his left wrist after a fall on his outstretched hand this morning while playing soccer. On examination, there is tenderness over the radial side of the wrist within marked area (see image 1). You arrange an X ray (see image 2).
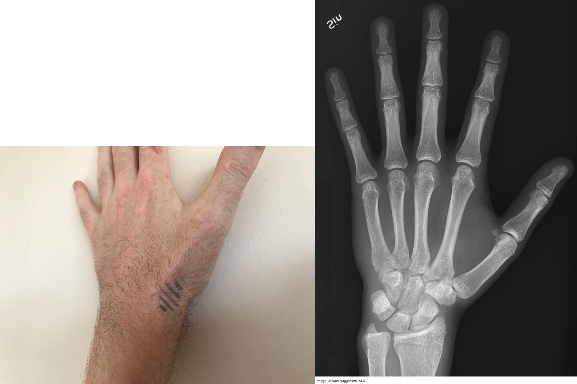
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Advise to wear wrist splint for two weeks and review if pain continues
B. Apply plaster in a glass-holding position and incorporate the proximal phalanx of the thumb
C. Recommend wrist stretching and strengthening exercises
D. Refer for ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection
E. Urgent referral for open reduction and internal fixation
Correct Answer: B. Apply plaster in a glass-holding position and incorporate the proximal phalanx of the thumb
Question 27
Greg O’Connell, aged 51 years, injured his right knee two days ago playing cricket. After jumping to catch the ball, he landed awkwardly and felt some pain in his knee. He stopped playing and applied an ice pack for 15 minutes.
On examination, he walks with a slight limp. There is no joint swelling or tenderness on appropriate knee palpation. He can flex his knee to 90 degrees, though with some mild discomfort. With the knee in 15 degrees of flexion, anterior motion of the tibia is elicited with a firm end point.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Computed tomography scan of the knee
B. Magnetic resonance imaging of the knee
C. Nuclear bone scan of the knee
D. Plain X-ray of the knee
E. Refer to orthopaedic surgeon for arthroscopy
F. Refer to physiotherapy for rehabilitation exercises
G. Send urgently to emergency department
H. Ultrasound of the knee
Correct Answer: F. Refer to physiotherapy for rehabilitation exercises
Question 28
Lyn Stevens, aged 50 years, is an Aboriginal woman who presents for her routine Indigenous health check. She is well and takes no regular medications. She completed all of her routine childhood vaccinations as per the vaccination schedule. You note her vaccination record as
follows:
| Vaccination | Given |
| Tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis | 9 years ago |
| Hepatitis A | 10 years ago and 9 years ago |
| Influenza | 6 months ago |
What is the MOST appropriate vaccination to recommend today?
A. Haemophilus influenzae type B
B. Hepatitis A
C. Herpes zoster
D. Influenza
E. Pneumococcal
F. Polio
G. Rabies
H. Tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis
Correct Answer: C. Herpes zoster and E. Pneumococcal
Question 29
Gretta Wiseman, aged 51 years, would like to start a medication to prevent her migraines but is concerned about weight gain. Over the past four months her migraines have increased from monthly to twice weekly. They interfere with her triathlon training. Appropriate investigation results regarding her migraines are normal. Her asthma is well controlled with fluticasone 100 mcg inhaled twice daily. She takes paroxetine 10 mg orally daily for management of hot flushes. On examination, her heart rate is 50/min, blood pressure 90/60 mmHg and the rest of an appropriate clinical examination is unremarkable.
What is the MOST appropriate medication to initiate?
A. Amitriptyline 25 mg orally once daily
B. Pizotifen 0.5 mg orally once daily
C. Propranolol 20 mg orally once daily
D. Topiramate 25 mg orally once daily
E. Verapamil sustained-release 90 mg orally once daily
Correct Answer: D. Topiramate 25 mg orally once daily
Question 30
John Ryan, aged 63 years, has had several months of gradually increasing pain in his right hip and thigh. It is increasingly difficult to complete his regular morning walk. He has been seeing a myotherapist but this has not helped. On examination, he has an antalgic gait and reduced
range of motion in his right hip.
You refer him for a hip X-ray (see image). The report is as follows:
X-ray of bilateral hips: There are multiple well defined areas of lucency in the right hemipelvis. You organise appropriate analgesia and further investigations to support your provisional diagnosis.
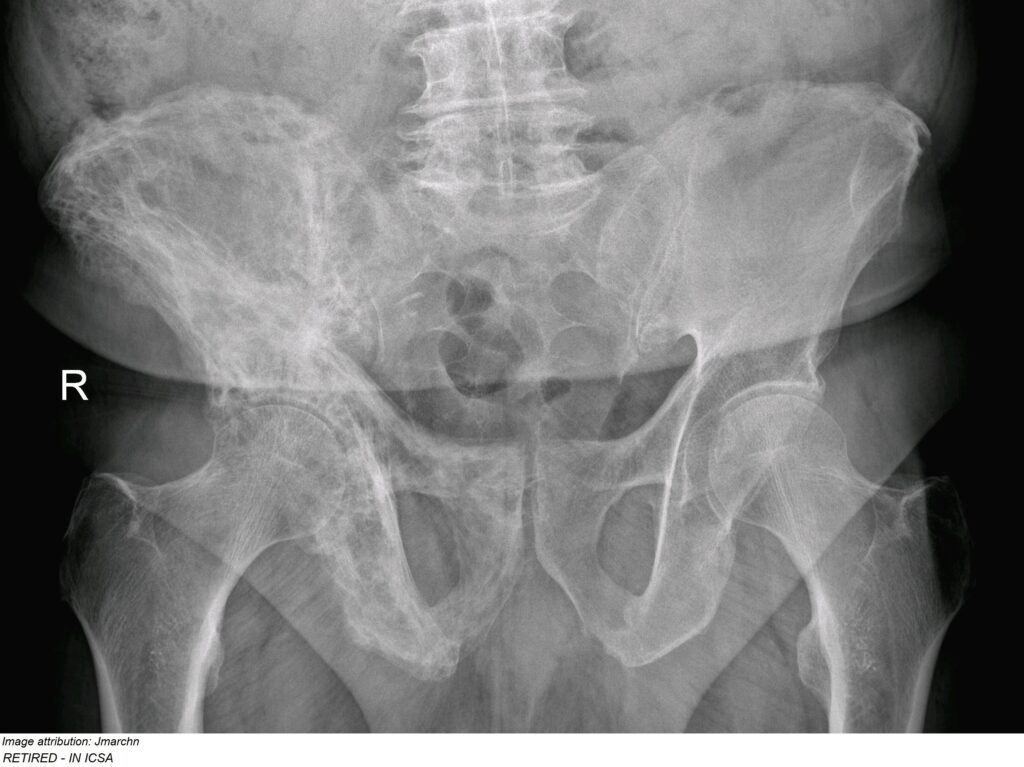
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Calcitonin 100 IU via intramuscular injection
B. Calcitriol 0.25 mcg orally daily
C. Denosumab 60 mg via subcutaneous injection
D. External beam radiation therapy
E. Goserelin (Zoladex) 10.8 mg subcutaneous implant every three months
F. Prednisolone 12.5 mg orally daily
G. Referral to haematologist for bone marrow biopsy
H. Referral to oncologist for monoclonal antibody therapy
I. Zoledronic acid 5 mg via intravenous infusion
Correct Answer: I. Zoledronic acid 5 mg via intravenous infusion
Question 31
Micah Conaghan, aged 5 months, has had frequent vomiting since birth. It has become significantly worse in the past few weeks. He has had unsettled periods where his abdomen has appeared bloated and frequent bowel motions with nappy rash. Micah has not yet started solids but is being weaned onto formula. Today his examination is normal apart from a mild perianal rash. You review his child health record and note that at his four-month check his weight was on the 60th centile. Today his weight is on the 20th centile. Head circumference and length are both on the 50th centile.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Coeliac disease
B. Cow’s milk protein allergy
C. Gastro oesophageal reflux disease
D. Infantile colic
E. Intussusception
F. Malrotation of gut with intermittent volvulus
G. Pyloric stenosis
I. Transient lactase deficiency
J. Urinary tract infection
Correct Answer: B. Cow’s milk protein allergy
Question 32
Samuel Livock, aged 24 years, is becoming increasingly self-conscious about a facial rash, which has been present for several months (see image). He has tried several over-the-counter cleansers and moisturisers but nothing seems to improve the appearance. The rash is not itchy or sore. On examination, there is diffuse scale over most of his scalp with coalescing flaky patches on his hair line and his eyebrows.
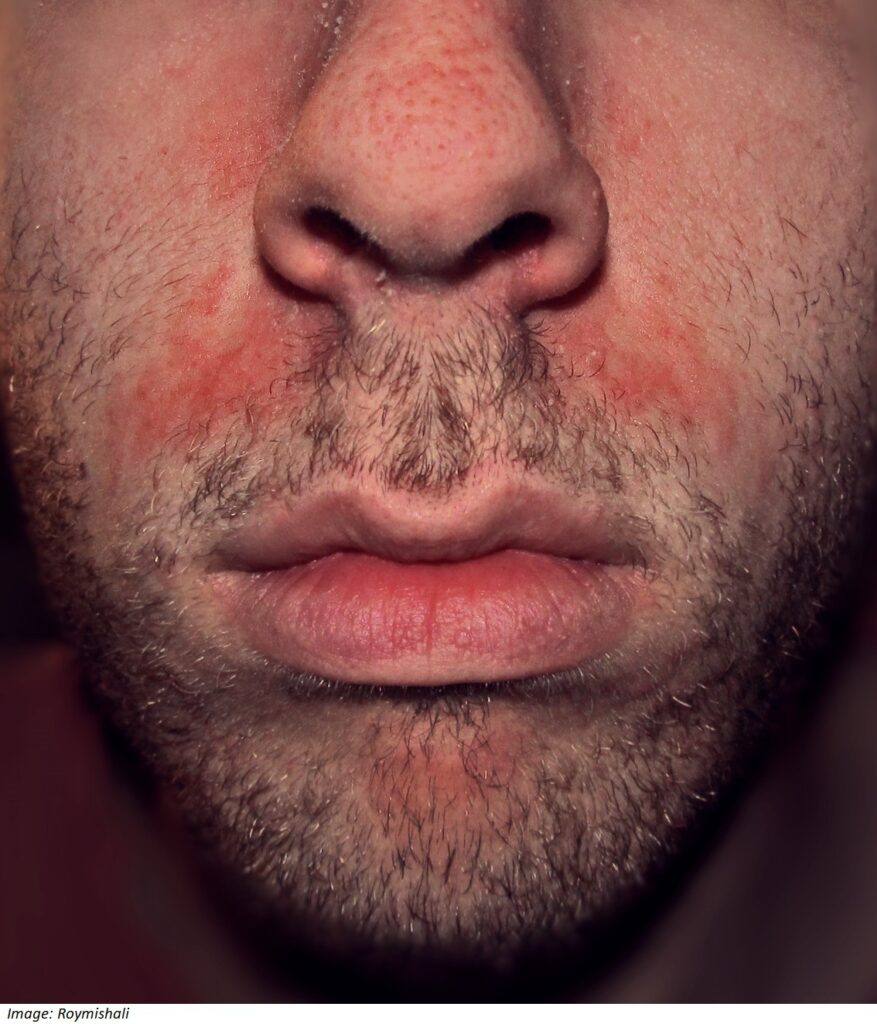
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Calcipotriol-betamethasone dipropionate 50 mcg/500 mcg gel topically daily
B. Doxycycline 50 mg orally daily
C. Hydrocortisone-clotrimazole 1%/1% cream topically twice daily
D. Ivermectin 10 mg/g cream topically daily
E. Metronidazole gel 1% topically daily
Correct Answer: C. Hydrocortisone-clotrimazole 1%/1% cream topically twice daily
Question 33
Matt Richards, aged 27 years, presents with his sister, Sally, who has encouraged Matt to see you for assistance with his cocaine addiction. She explains that Matt started using cocaine while he was working long hours in a corporate marketing role; however, over the past few months his use spiralled out of control. He was dismissed from his job last week due to his aggressive behaviour in the workplace. He lives with Sally, who is concerned about the drug ‘ruining his life’. Matt is reluctant to seek help. He becomes agitated when questioned further about his cocaine use, saying ‘everyone in that industry does it’ and that he does not want to ‘waste anyone’s time’ talking about it.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise him about the harms of cocaine use and encourage regular follow-up
B. Prescribe sertraline 50 mg orally daily
C. Prescribe diazepam and organise a home detoxification program
D. Refer to psychiatrist for inpatient detoxification
E. Refer to psychologist for cognitive behavioural therapy
Correct Answer: A. Advise him about the harms of cocaine use and encourage regular follow-up
Question 34
Jodie Ashmari, aged 40 years, comes to see you for the results of her recent cervical screening test, which is reported as normal. She is concerned that she may have cervical cancer despite the normal test result. You would like to reassure Jodie, and find a report that evaluates cervical screening in Australia.
What parameter within this report is the MOST appropriate to help reassure Jodie?
A. False positive rate for cervical screening
B. Negative predictive value of cervical screening
C. Number needed to screen
D. Population prevalence of cervical cancer
E. Specificity of cervical screening
Correct Answer: B. Negative predictive value of cervical screening
Question 35
You are asked to review the urine results for Brian Naylor, aged 83 years, who is a bed-bound patient in a residential aged care facility. A few days ago he developed a low-grade fever and a urine microscopy and culture was ordered by another doctor. A day later, Brian developed the symptoms of an upper respiratory tract infection and is now improving and he is increasingly feeling well. He had appropriate COVID-19 testing, which was negative, and appropriate isolation was completed. On examination, his temperature is 37.2 °C, heart rate 76/min and regular, chest normal and the urine in his catheter bag looks clear.
His urine microscopy, culture and sensitivity results are as follows:
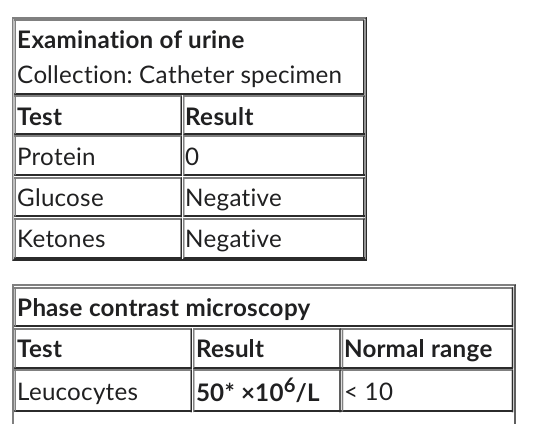
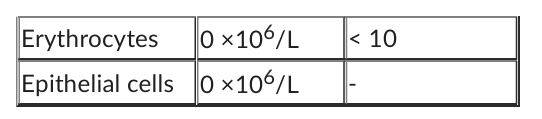
Organism: Klebsiella* > 103 org/mL
Antimicrobial sensitivities (S = sensitive, R = resistant): amoxicillin (S), amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (S), cephalexin (R), trimethoprim (S), nitrofurantoin (S), norfloxacin (S)
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise no further specific investigations or management required
B. Amoxicillin 500 mg orally three times daily for five days
C. Recommend the catheter is removed and he use in-out catheters for seven days
D. Repeat the urine microscopy, culture and sensitivity
E. Trimethoprim 150 mg orally daily for four weeks
Correct Answer: A. Advise no further specific investigations or management required
Question 36
Dorothy Myles, aged 78 years, had an episode of light-headedness associated with an unusual feeling in her chest earlier today. Dorothy takes escitalopram 20 mg orally daily for generalised anxiety disorder and recently began a course of erythromycin 400 mg orally four times daily for an episode of acute purulent paronychia. While an electrocardiogram is being recorded (see image), Dorothy loses consciousness.
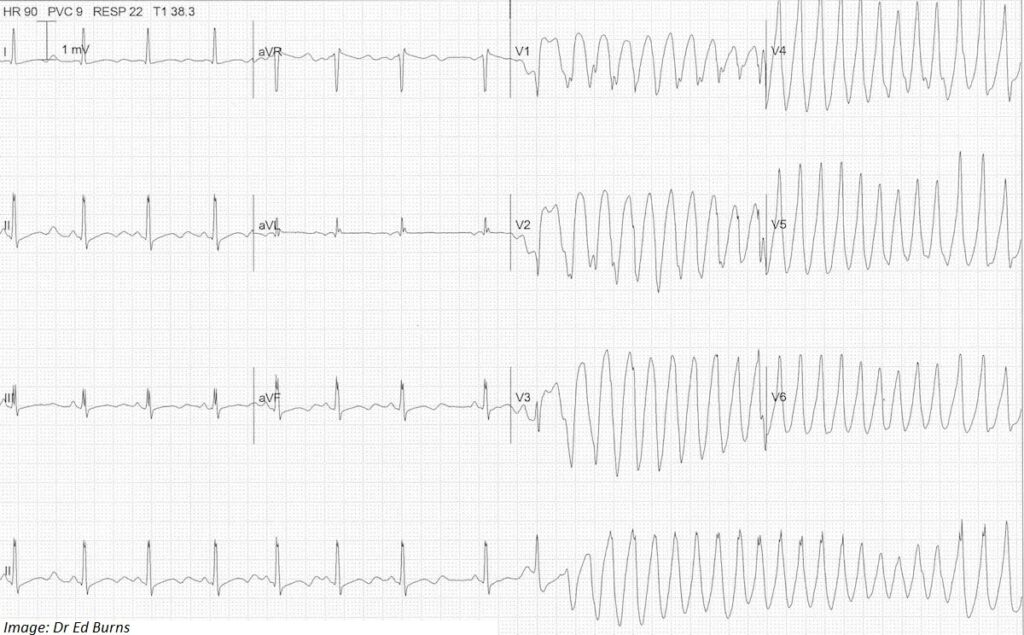
What is the MOST appropriate interpretation of the abnormality seen on the electrocardiogram?
A. Atrial fibrillation
B. Atrial tachycardia
C. Complete heart block
D. Supraventricular tachycardia
E. Torsades de pointes
F. Ventricular fibrillation
G. Sinus tachycardia
H. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
Correct Answer: E. Torsades de pointes
Question 37
Una Marna, aged 36 years, was told by her hairdresser that she has some bald areas on her head. Una has noticed more hair loss while brushing her hair over the past three months since her older sister died following complications of type 1 diabetes. She has not lost hair on any other part of her body. She has been well apart from occasional flare-ups of eczema. On examination, there are multiple patches of hair loss, which have a smooth surface and a few remaining hairs 2–3 mm in length that appear to have broken off. The rest of her clinical examination is unremarkable.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Alopecia areata
B. Alopecia totalis
C. Androgenetic alopecia
D. Coeliac disease
E. Hypothyroidism
F. Tinea capitis
G. Psoriasis
H. Telogen effluvium
I. Trichotillomania
Correct Answer: A. Alopecia areata
Question 38
Ava Burrows, aged 16 days, is brought to the clinic by her mother, Helen, who is concerned about a lump she noticed yesterday on Ava’s neck. Ava was born at term by vaginal delivery requiring a forceps extraction. Ava is feeding well and gaining weight. You examine Ava and notice that her head is turned to the side. Tympanic temperature is 36.8 °C. Ava has a firm palpable 1.5 cm mass on the right side of the neck in the lower sternocleidomastoid region with no overlying skin changes. Her head and ear are tilted towards the affected side. You gently move Ava’s neck from side to side and note that she has a restricted range of passive movement.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Abscess
B. Branchial cyst
C. Neuroblastoma
D. Reactive lymphadenopathy
E. Sternocleidomastoid pseudotumour
Correct Answer: E. Sternocleidomastoid pseudotumour
Question 39
Anne Hazelton, aged 74 years, was concerned about a large skin lesion on her forearm that had been growing over a few months and was bleeding. You removed this lesion with 4 mm macroscopic margins two weeks ago. She has returned today for further review. Histopathology report was as follows: Oriented ellipse of excision tissue 12 × 15 mm in size containing a nodular well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma 8 × 9 mm in size with no perineural invasion. Nearest microscopic margin is 1.5 mm at 9 o’clock referenced to suture placed at 12 o’clock.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise no further surgical management is required for this lesion
B. Advise repeated cryotherapy to the scar four, eight and 12 weeks after the excision is healed
C. Re-excise lesion with 10 mm margins
D. Re-excise lesion with 4 mm margin
E. Treat scar for two weeks with topical imiquimod
Correct Answer: A. Advise no further surgical management is required for this lesion
Question 40
Jessica Frances, aged 32 years, is concerned about a recurrent painful rash in her armpits she has had for several months (see image). She saw one of your colleagues a week ago who took a bacterial swab and commenced mupirocin 2% ointment topically, three times daily for five days, but the rash has not changed. Jessica has always struggled with being overweight and had managed to lose 10 kg prior to her wedding six months ago. However, she remains overweight with a body mass index of 36 kg/m2. She and her husband are considering trying -for a baby soon.
Results of a skin swab of her right axilla reveal a mixed growth of skin flora.
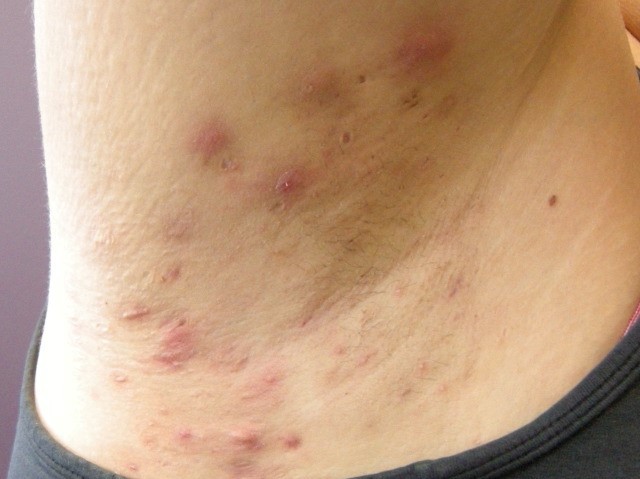
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Acitretin 25 mg orally daily
B. Betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% topically twice daily for four weeks
C. Doxycycline 50 mg orally daily for 12 weeks
D. Erythromycin 250 mg orally twice daily for six weeks
E. Ethinyloestradiol-cyproterone 35 mcg / 2 mg orally daily
F. Flucloxacillin 500 mg orally four times daily for five days
G. Intra-lesional corticosteroid injections
H. Spironolactone 50 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: D. Erythromycin 250 mg orally twice daily for six weeks
Question 41
Sandra Lee, aged 26 years, has just completed a course of antibiotics for an uncomplicated urinary tract infection and is now asymptomatic. Sandra is frustrated by recent recurrent urinary tract infections as this is the third one she has had in the past six months. Sandra’s partner is a fly-in-fly-out worker and she explains that she seems to develop a urinary tract infection every time they have sex. She passes urine before and after intercourse, keeps well hydrated and takes cranberry tablets daily. She has previously had an ultrasound of her renal tract, which was normal. She had an etonogestrel implant (Implanon NXT) inserted 12 months ago. You note cervical screening and testing for sexually transmitted infections were normal last month.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Amoxicillin 500 mg orally three times daily for six months
B. Cephalexin 500 mg orally four times daily for two weeks
C. Computed tomography scan of the kidneys, ureters and bladder
D. Macrogol powder one sachet orally daily
E. Micturating cystourethrogram
F. Oestradiol pessary 500 mcg intravaginally at night
G. Recommend probiotics
H. Refer for cystoscopy
I. Trimethoprim 150 mg orally within two hours after intercourse
Correct Answer: I. Trimethoprim 150 mg orally within two hours after intercourse
Question 42
Geetha Sandhu, aged 59 years, is concerned about her breast cancer risk while taking menopause hormone therapy. She began tibolone 2.5 mg orally daily to manage severe hot flushes that started when she had a hysterectomy 10 years ago. She has tried to stop the tibolone many times but finds the hot flushes debilitating. She has heard that a new study has been published about breast cancer and menopause hormone therapy. She would like your advice about whether she should continue tibolone or switch to a different form of menopause hormone therapy to manage her symptoms while minimising her breast cancer risk. You review the article and the graphic (see image).
Based upon the provided information, what is the MOST appropriate menopause hormone therapy to recommend for Geetha to reduce her breast cancer risk?
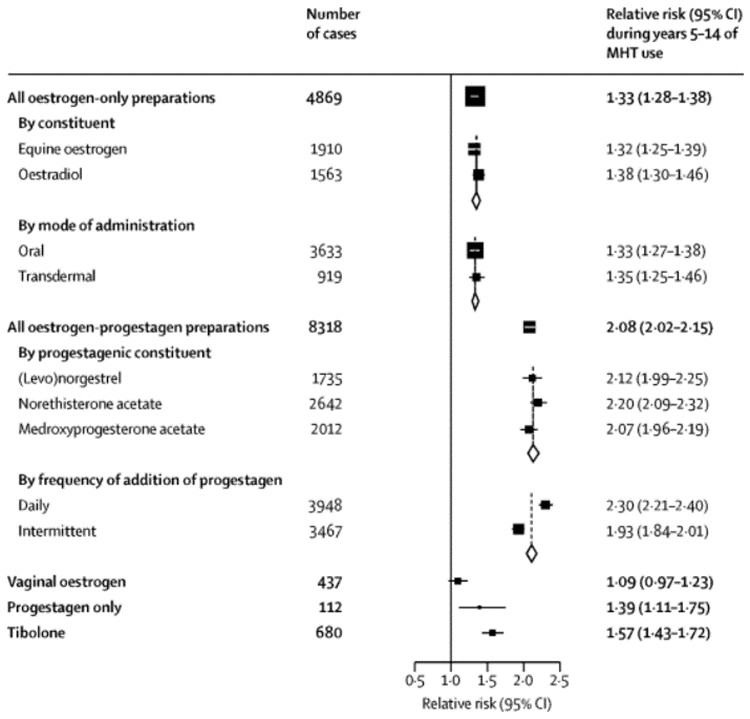
A. Advise that she should continue tibolone 2.5 mg orally daily
B. Conjugated equine oestrogen 0.3 mg orally daily
C. Levonorgestrel intrauterine device 52 mg
D. Norethisterone 5 mg orally daily
E. Oestradiol 1 mg orally daily plus drospirenone 2 mg orally daily
F. Oestradiol 2 mg orally daily and norethisterone acetate 1 mg orally daily
G. Oestradiol 2 mg orally daily with dydrogesterone 10 mg orally daily for 14 days of the month
H. Oestradiol 25 mcg pessary vaginally twice weekly
I. Oestradiol 25 mcg/24-hour patch applied once weekly
Correct Answer: B. Conjugated equine oestrogen 0.3 mg orally daily and I. Oestradiol 25 mcg/24-hour patch applied once weekly
Question 43
Paige Johnson, aged 4 months, is brought in because her mother, Fiona, is worried about her growth. Fiona has been weighing Paige every two weeks at the local child health clinic. Yesterday, one of the child health nurses commented that Paige wasn’t gaining enough weight, and suggested that she might not be getting enough milk because of a posterior tongue tie. Paige was born via vaginal delivery at full term after a normal pregnancy, and is fully breast fed. She smiles and can roll both ways. Paige’s weights have been plotted on her weight for-age growth chart (see image). Her length and head circumference are following the 85th percentile.
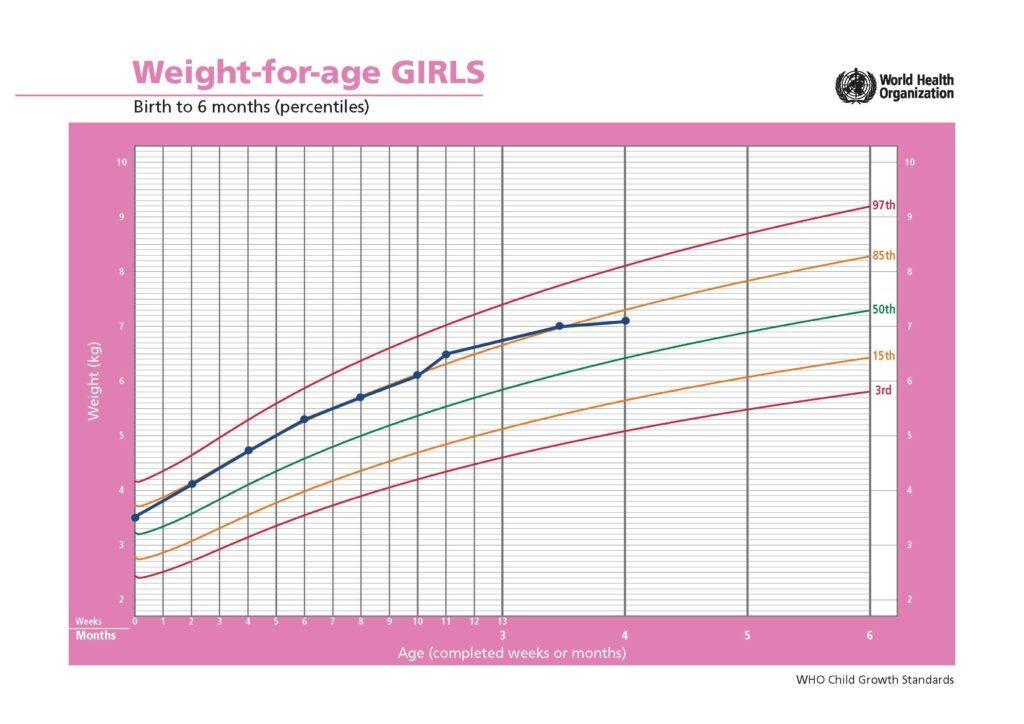
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Arrange a clean catch mid-stream urine microscopy, culture and sensitivity
B. Arrange a faeces test for microscopy, culture, sensitivities and fat globules
C. Prescribe domperidone 10 mg orally three times daily to Fiona
D. Recommend reducing breast milk and start solids
E. Recommend that Fiona stops eating dairy products
F. Referral to a dentist for laser frenotomy
G. Referral to a lactation consultant
H. Referral to a paediatric speech pathologist
I. Referral to a paediatrician
J. Review and reweigh Paige in two weeks
K. Supplement Paige’s breast-feeds with formula top-ups
Correct Answer: J. Review and reweigh Paige in two weeks
Question 44
Archie Jamieson, aged 18 months, is brought in by his father, Michael, who is concerned about a rash that has been present on Archie’s feet for the past two days. Archie has been a bit irritable and is reluctant to eat his usual solids, but he is drinking well. His immunisations are up to date. On examination, Archie is alert and interactive, temperature is 37.5 °C, he has clear rhinorrhoea and a rash present on both feet (see image), with similar appearance also on his hands.
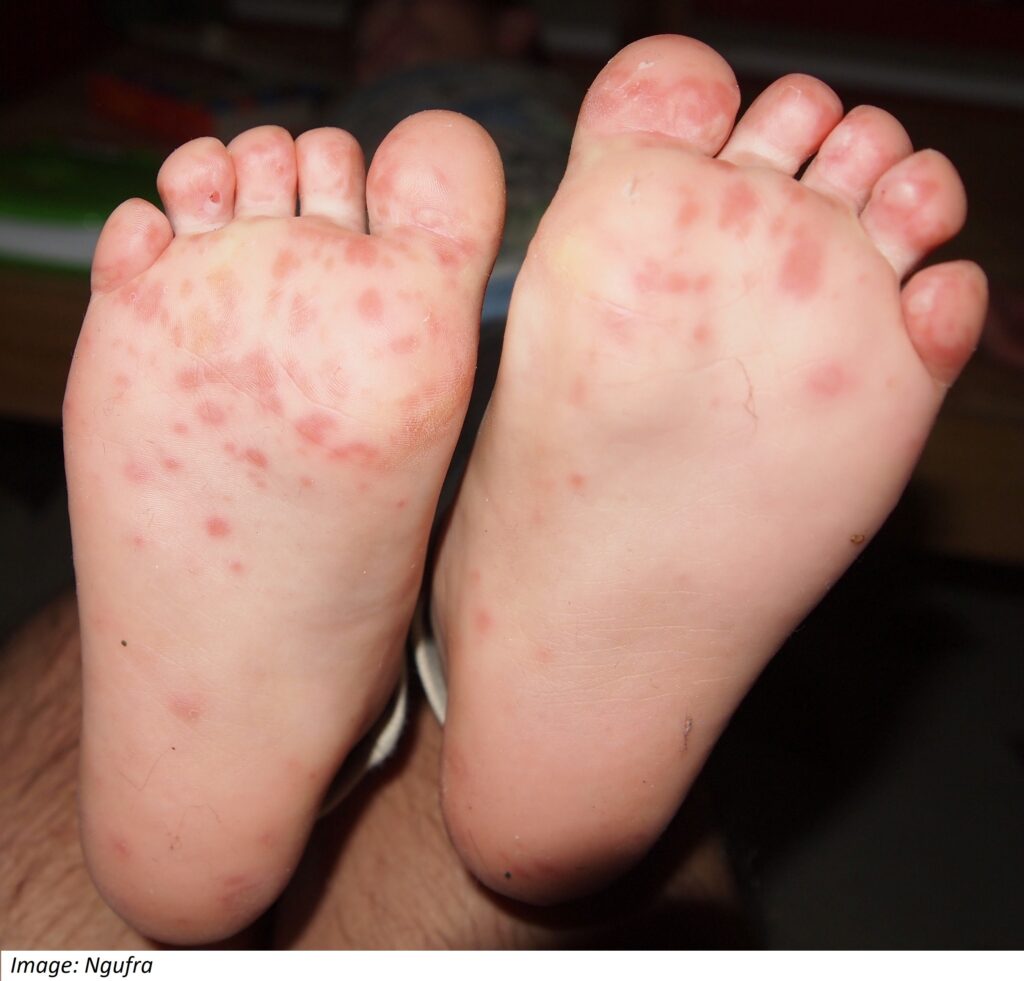
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Fexofenadine 15 mg orally twice daily until resolved
B. Hydrocortisone 1% cream topically twice daily for seven days
C. Prednisolone 1 mg/kg orally stat dose
D. Reassure that the rash will resolve spontaneously within 10 days
E. Referral to immunologist for skin patch testing
Correct Answer: D. Reassure that the rash will resolve spontaneously within 10 days
Question 45
Sarah Jones, aged 33 years, has come to you seeking help for her problem gambling. Her husband recently left her and they are in significant financial distress. Sarah started gambling around 12 months ago, using an online betting app. Initially, she would have the occasional ‘wager’ but now she is finding it increasingly difficult to stop. She won a large sum of money approximately six months ago and explains she ‘just needs one more win’ to fix their financial issues. She has heard of gamblers anonymous but does not want to go. Further screening reveals no significant symptoms of depression or anxiety. She has three standard drinks of alcohol per week and does not use illicit substances.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Aripiprazole 10 mg orally daily
B. Diazepam 5 mg orally twice daily as needed
C. Naltrexone 50 mg orally daily
D. Quetiapine 50 mg orally at night
E. Reassure her that deleting the app from her online devices should resolve her problem
F. Recommend she place a lock on the computer to prevent access to gambling websites
G. Referral to psychiatrist
H. Referral to psychologist for cognitive behavioural therapy
I. Sertraline 50 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: H. Referral to psychologist for cognitive behavioural therapy
Question 46
Michelle Flannery, aged 34 years, has had a runny nose, fever, fatigue and pain in her neck and jaw for the last two weeks. She had negative COVID-19 testing as the beginning of her symptoms. She has been anxious and has been aware of her heart beating at times. She has lost 2 kg over this time. Michelle has been taking ibuprofen 400 mg orally three times daily for her symptoms. On examination, her heart rate is 110/min regular, blood pressure 110/75 mmHg, tympanic temperature 37.5 °C. She is tender over her anterior neck and has a fine tremor in both hands.
Investigation results are shown below. Full blood examination, liver and renal function are within normal limits.
| Tests | Results | Normal range |
| Thyroid stimulating hormone | 0.12* mIU/L | 0.35 – 5.5 |
| Free T4 | 44* pmol/L | 9.0 – 25.0 |
| Free T3 | 6.8* pmol/L | 3.5 – 6.5 |
| Peroxidase antibody (TPOAb) | 32 IU/mL | 0 – 35 |
| Thyroid stimulating hormone receptor antibodies (TRAbs) | 1 IU/L | < 2 |
| Erythrocyte sedimentation rate | 66* mm/hour | < 21 |
Electrocardiogram: Sinus tachycardia 112 beats/minute
Nuclear thyroid scan: No significant uptake within the thyroid gland
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Atenolol 25 mg orally once daily
B. Carbimazole 10 mg orally three times daily
C. Computed tomography of the neck
D. Fine needle aspiration of the thyroid gland
E. Levothyroxine 25 mcg orally daily
F. Propylthiouracil 150 mg orally three times daily
G. Ultrasound of the thyroid gland
H. Urinary iodine
Correct Answer: A. Atenolol 25 mg orally once daily
Question 47
Mukesh Sharma, aged 63 years, is seeing his dentist next week for a large dental filling, and asks your advice about an article he read online stating that he may need to take antibiotics for this procedure. He has made a good recovery from a total hip replacement, completed with prosthetic implants, six months ago for moderately severe osteoarthritis.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Amoxicillin 2 g orally one hour before the procedure
B. Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid 875 mg/125 mg orally stat one hour before the procedure and repeated six hours after the procedure
C. Clindamycin 600 mg orally one hour before the procedure
D. Discuss the need for prophylactic antibiotics with his orthopaedic surgeon
E. No antibiotic prophylaxis is required
Correct Answer: E. No antibiotic prophylaxis is required
Question 48
Isabelle Jenkins, aged 18 months, is brought to your rural hospital emergency department by her parents. Isabelle has been unwell for the past three days with intermittent fevers, a runny nose and a dry, barking cough with a husky voice. She was up for most of last night coughing and her parents also noted noisy breathing but this has settled this morning. Her COVID-19 test was negative. On examination, her heart rate is 140/min regular, respiratory rate 28/min, tympanic temperature 37.6 °C and both tympanic membranes appear mildly inflamed. She has clear rhinorrhoea. Respiratory examination reveals clear auscultation with mild chest wall retraction.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Amoxicillin 15 mg/kg (max 500 mg) orally three times daily for five days
B. Azithromycin 10 mg/kg up to 500 mg orally daily for five days
C. Dexamethasone 0.15 mg/kg orally as a single dose
D. Intranasal saline drops as required
E. Oseltamivir 30 mg orally twice daily for five days
F. Reassurance the illness is self-limiting and that no specific treatment is required
G. Salbutamol 100 mcg two actuations via mask and spacer
H. Urgent chest X-ray
Correct Answer: C. Dexamethasone 0.15 mg/kg orally as a single dose
Question 49
Jane Graham, aged 48 years, is concerned about her chronic cough. Jane describes a cough with pale yellow sputum every day for the past three years. If she ‘catches a cold’, the sputum becomes darker and she gets short of breath and wheezy. She usually sees a doctor for antibiotics when this happens.
Jane is otherwise well, and has never smoked. She remembers having ‘bronchitis’ several times as a child, including one episode at age 10 when she was in hospital for four days.
A recent chest X-ray is reported as normal.
Spirometry results are as follows:
| Test | Pre- bronchodilator | Predicted | Post- bronchodilator | Percentage change |
| Forced vital capacity (FVC) | 3.10 L | > 3.45 L | 3.22 L | 4% |
| Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) | 2.02 L | > 2.76 L | 2.10 L | 4% |
| FEV1/FVC | 65% | > 70% | 65% |
What is the MOST appropriate investigation to confirm your provisional diagnosis?
A. Aspergillus serology
B. Bronchoscopy
C. Carbon monoxide diffusion capacity
D. Computed tomography pulmonary angiogram
E. High-resolution computed tomography scan chest
F. Human immunodeficiency virus serology
G. Serum angiotensin converting enzyme level
H. Serum immunoglobulin levels
I. Sputum cytology
J. Sputum for acid fast bacilli
K. Sputum microscopy and culture
L. Sweat test
Correct Answer: E. High-resolution computed tomography scan chest
Question 50
Janet Long, aged 68 years, has felt feverish, with a runny nose, sore throat and nausea since yesterday morning. She was diagnosed with adrenocortical suppression recently and prescribed hydrocortisone 16 mg orally mane and 8 mg orally mid-afternoon. This is her first illness since diagnosis and she is anxious about how to manage it. Her COVID-19 test was negative. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 38.0 °C and blood pressure 128/68 mmHg. She has mild enlargement of the cervical nodes and redness of her throat. Her further examination is unremarkable.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Amoxicillin 1 g orally twice daily for seven days
B. Ciprofloxacin 500 mg orally twice daily for seven days
C. Hydrocortisone 20 mg orally three times daily for three days and then taper to normal dose
D. Metoclopramide 10 mg orally three times daily if required for nausea
E. Oseltamivir 75 mg orally twice daily for five days
F. Prednisolone 50 mg orally daily for five days
G. Recommend paracetamol and return in two days if not improving
H. Refer her urgently to the nearest emergency department
