Case 1: Amber Mann
Amber Mann, aged 26 years, presents to your clinic as a new patient for her annual diabetes review. She was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus, aged 15 years, and has used an insulin pump with insulin lispro for the past five years. Her morning glucose level is usually between 6 and 8 mmol/L and her random glucose levels measured two hours after meals are usually between 7 and 10 mmol/L. She feels well.
Amber has a past medical history of chickenpox in childhood, but no other significant past medical history. She takes no other regular medications and has no known allergies. She uses condoms for contraception. She does not smoke, drink alcohol or use recreational drugs. Her immunisations, cervical screening test and dental checks are up to date. She works as a human resources manager and walks 30 minutes to and from work five days per week. She eats a healthy balanced diet.
On examination, Amber looks well. Her temperature is 37.2 °C, blood pressure 122/74 mmHg, heart rate is 60/min regular, respiratory rate is 14/min, body mass index is 23 kg/m2 and waist circumference is 75 cm.
Question 1
What abnormal findings relevant to diabetes treatment, management and complications should be sought on examination of Amber? Write four (4) specific examination findings.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 2
What initial investigations are appropriate? Select five (5) investigations from the following list.
- Antinuclear antibodies
- Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies
- Coeliac serology
- Cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody
- Extractable nuclear antigen antibodies
- Fasting lipids
- Full blood count
- Glucose tolerance test
- Glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies
- Glycosylated haemoglobin
- Insulin C-peptide
- Iron studies
- Isotope bone scan
- Lipase
- Liver function tests
- Rheumatoid factor
- Serum calcium
- Serum folate
- Serum human beta chorionic gonadotropin
- Thyroid stimulating hormone
- Urea and electrolytes
- Urine albumin: creatinine ratio
- Urine for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
- Vitamin B12
- Vitamin D
Question 3
Amber’s investigations are normal.
Amber says she wants to start a family with her partner and asks if there is anything she needs to do to prepare for pregnancy. She has regular menstrual cycles and no intermenstrual bleeding. She has started a pregnancy multivitamin on the advice of her pharmacist. Her previous general practitioner had checked her rubella and parvovirus serology and told her that she is immune.
You provide routine pregnancy counselling. What advice regarding management of type 1 diabetes mellitus and pregnancy is appropriate to provide to Amber? Write four (4) specific pieces of advice. If your answer includes a medication, dosages are not required.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Case 2: Rosalie Hammer
Rosalie Hammer, aged 45 years, reports a four-day history of a painful right leg. She felt a sudden tearing sensation in the back of her leg while walking up a flight of stairs and has had pain since.
Rosalie has no significant past medical history, takes no regular medications and has no known allergies. She does not smoke and has two standard drinks of alcohol two nights per week.
On examination, Rosalie looks well. Her temperature is 37.1 °C, blood pressure is 128/88 mmHg, heart rate is 82/min regular, respiratory rate is 14/min and body mass index is 24.5 kg/m2. She is very tender on palpation of her right medial mid-calf. Squeezing her calf causes her foot to plantar flex and increases the pain in her calf. The remainder of her examination is normal.
Question 4
What are the most likely differential diagnoses? Write two (2) specific diagnoses.
- …
- …
Question 5
Rosalie’s investigations confirm the most likely diagnosis.
What non-pharmacological management actions are appropriate? Write five (5) specific non-pharmacological management actions.
- …
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 6
Rosalie present four weeks later reporting increased pain and swelling in her right calf. On examination, Rosalie looks well. Her temperature is 37.0 °C, blood pressure is 124/84 mmHg, heart rate is 76/min, respiratory rate is 14/min, oxygen saturation is 98% on room air and body mass index is 24.5 kg/m2. Her right calf is tender to touch, measures 4cm larger in circumference than her left calf and demonstrates pitting oedema to the level of the knee. The remainder of her examination is normal.
You arrange appropriate investigations that confirm the most likely diagnosis and Rosalie returns for review the same day.
What immediate pharmacological management action is appropriate? Write one (1) specific pharmacological management action (dosing is not required).
- …
Case 3: Ana Perez
Ana Perez, aged 38 years, is brought in to your small rural emergency department by her husband, Diego. Diego says Ana became unwell after putting the washing on the clothesline about one hour ago. She was wearing thongs outside and felt a scratch and assumed she had stepped on a stick or sharp stone. When she came inside, she said her left foot suddenly became very sore. Soon after, she complained of a headache and abdominal pain. She has had one episode of diarrhoea.
Ana has no significant past medical history, takes no regular medications and has no known allergies. She uses the levonorgestrel intrauterine contraceptive device for contraception. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. Ana and Diego live on a farm that is a 30-minute drive from town.
On examination, Ana is sweating profusely and is vomiting. Her temperature is 36.5 °C, blood pressure is 75/42 mmHg, heart rate is 121/min regular, respiratory rate is 20/min, oxygen saturation is 97% on room air and body mass index is 24.5 kg/m2. She has a small wound on her left foot that is oozing blood (see image). The remainder of her examination is normal.
The nearest tertiary hospital is 250 km away by road.
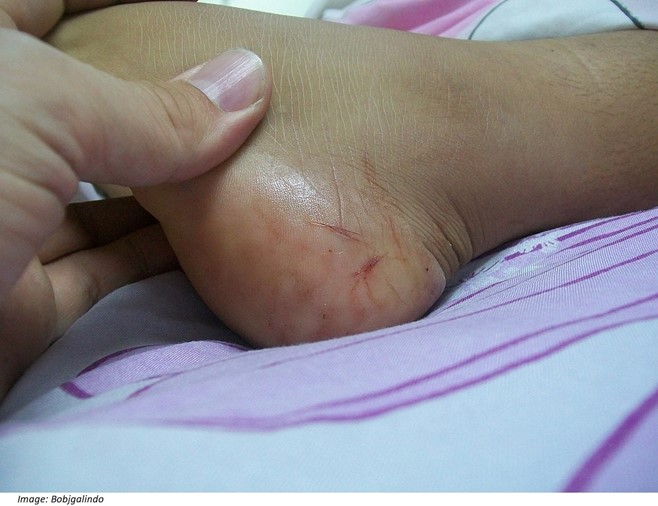
Question 7
What is the single most likely diagnosis? Write one (1) specific diagnosis.
- …
Question 8
You arrange urgent transfer to the nearest tertiary hospital. While awaiting transfer, what immediate management actions are appropriate? Write five (5) specific management actions.
- …
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 9
While awaiting transfer, what initial investigations are appropriate? Select six (6) investigations from the following list.
- Blood cultures
- Blood film
- C-reactive protein
- Cholinesterase red cell
- Coagulation studies
- Computed tomography scan of abdomen
- Computed tomography scan of brain
- Creatine kinase
- D-dimer
- Echocardiogram
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- Fibrinogen
- Full blood count
- Iron studies
- Lactate dehydrogenase
- Liver function tests
- Magnetic resonance angiogram of brain
- Methaemoglobin
- Random blood glucose
- Serum calcium
- Ultrasound scan of abdomen
- Urea and electrolytes
- Urine drug screen
- Urine for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
- X-ray of chest
Case 4: Eric Holdt
Eric Holdt, aged 50 years, reports a three-month history of a blocked nose with intermittent purulent nasal discharge, upper jaw pain and fatigue. For the past seven days he has been taking amoxicillin 500 mg orally three times a day, fexofenadine 180 mg orally daily, saline nasal douches, followed by intranasal fluticasone twice daily, but he has not noticed any improvement.
He has also been using oxymetazoline nasal spray three times a day over the past month but reports that the initial relief is now reducing. He does not have any itching or watering of his eyes.
Eric has no significant past medical history and takes aspirin 100 mg orally daily for colorectal cancer prevention. He has no known allergies. He does not smoke and has two standard drinks of alcohol five nights per week.
On examination, Eric looks well. His temperature is 36.8 °C, blood pressure is 135/80 mmHg, heart rate is 78/min regular, respiratory rate is 14/min and body mass index is 28 kg/m2. You note the following appearance on examination of his nasal passages bilaterally (see image).
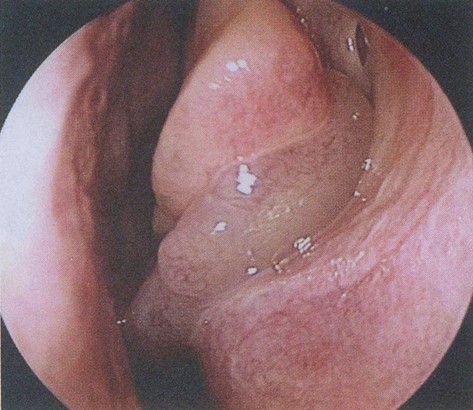
Question 10
Eric asks if he is using his nasal sprays correctly.
What education is appropriate to provide to Eric regarding the correct inhalation technique for the use of nasal sprays? Write four (4) specific education points.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 11
What additional pharmacological management actions are appropriate? Write three (3) specific pharmacological management actions, including dose and duration where appropriate.
- …
- …
- …
Question 12
Eric reports a two-month history of a growing and increasingly tender skin lesion on his left lower leg (see image).
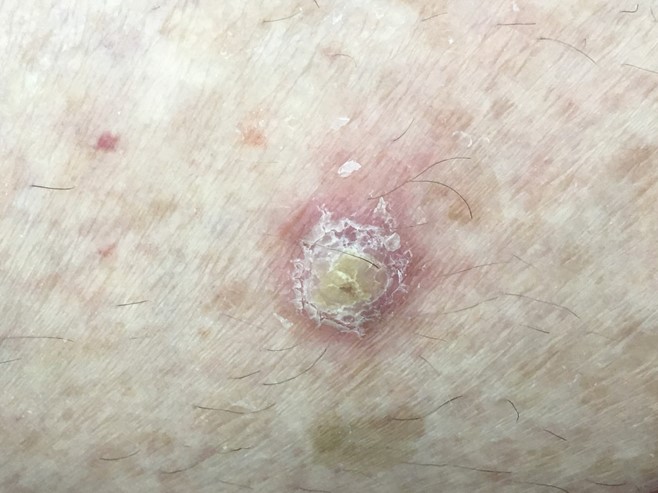
What is the single most likely diagnosis? Write one (1) specific diagnosis.
- …
Case 5: Marcus Pablo
Marcus Pablo, aged 42 years, is brought in to your rural clinic by a member of the public. He is struggling to complete a full sentence and is drooling. Review of his medical records shows that he was seen by another general practitioner four days ago with viral gastroenteritis and was prescribed metoclopramide 10 mg orally three times per day.
Marcus has a past medical history of schizophrenia, for which he takes flupenthixol decanoate 40 mg intramuscularly every two weeks. He has no known allergies. He does not smoke or drink alcohol.
On examination, Marcus is extremely agitated. His temperature is 39.4 °C, blood pressure is
184/98 mmHg, heart rate is 132/min regular, respiratory rate is 20/min, oxygen saturation is
95% on room air and body mass index is 23kg/m2. He is very sweaty and has widespread severe muscle rigidity. His finger-prick blood glucose is 4.8. The remainder of his examination is normal.
The nearest tertiary hospital is 200 km away by road.
Question 13
What is the single most likely diagnosis? Write one (1) specific diagnosis.
- …
Question 14
You arrange urgent transfer to the nearest tertiary hospital.
While awaiting transfer, what immediate management actions are appropriate? Write four (4) specific management actions.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 15
While awaiting transfer, what initial investigations are appropriate? Select four (4) investigations from the following list.
- Blood film
- C-reactive protein
- Cerebrospinal fluid for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
- Coagulation studies – non specific
- Computed tomography scan of brain
- Creatinine kinase
- Echocardiogram
- Electrocardiogram
- Electroencephalogram
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- Faeces for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
- Full blood count
- Herpes simplex virus serology
- Human immunodeficiency virus serology
- Iron studies
- Lactate dehydrogenase
- Lipase
- Liver function tests
- Paracetamol level
- Thyroid stimulating hormone
- Ultrasound scan of abdomen
- Urea and electrolytes
- Urine drug screen
- Urine for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
- X-ray of chest
Case 6: Rufus Humphreys
Rufus Humphreys, aged 71 years, reports a four-month history of increasing fatigue. He has not been sleeping well as he has lower back pain. He is also becoming short of breath on his usual morning walk. He has no other significant symptoms.
Rufus has a past medical history of hypertension, for which he takes perindopril 5 mg orally daily. He has no known allergies. He does not smoke and has two standard drinks of alcohol five nights per week.
On examination, Rufus looks well though tired. His temperature is 36.8 °C, blood pressure is 135/75 mmHg, heart rate is 75/min regular, respiratory rate is 14/min and body mass index is 27 kg/m2. The remainder of his examination is normal.
You arrange investigations with the results shown below.
Glucose (random) – normal Thyroid function tests – normal Iron studies – normal
Vitamin B12 and folate – normal
Haematology
| Test | Result | Normal range |
| Haemoglobin | 98* g/L | 130 – 180 |
| Red cell count | 4.8 x 1012/L | 4.50 – 6.5 |
| Mean cell volume | 88 fL | 80 – 99 |
| Mean cell haemoglobin | 29 pg | 27.0 – 32.0 |
| White cell count | 5.5 x 109/L | 4.0 – 11.0 |
| Platelets | 235 x 109/L | 150 – 450 |
Biochemistry
| Test | Result | Normal range |
| Sodium | 137 mmol/L | 135 – 145 |
| Potassium | 4.3 mmol/L | 3.5 – 5.2 |
| Chloride | 108 mmol/L | 95 – 110 |
| Bicarbonate | 28 mmol/L | 22 – 32 |
| Urea | 18.4* mmol/L | 2.5 – 8.0 |
| Creatinine | 255* mol/L | 45 – 90 |
| Estimated glomerular filtration rate | 24* mL/min/1.73m2 | > 90 |
Liver function tests
| Test | Result | Normal range |
| Urate | 0.34 mmol/L | < 0.42 |
| Total protein | 110* g/L | 60 – 82 |
| Albumin | 50 g/L | 35 – 50 |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 100 mmol/L | 30 – 120 |
| Bilirubin | 18 U/L | < 25 |
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase | 48 U/L | < 51 |
| Aspartate transaminase | 40 U/L | < 41 |
| Alanine aminotransferase | 38 U/L | < 41 |
| Calcium | 2.91* mmol/L | 2.10 – 2.55 |
| Phosphate | 1.21 mmol/L | 0.75 – 1.35 |
Question 16
What is the single most likely diagnosis? Write one (1) specific diagnosis.
- …
Question 17
Which investigations would help to confirm the single most likely diagnosis? Select four (4) investigations from the following list.
- 24-hour urine collection for immunofixation
- 24-hour urine collection for metanephrines
- 24-hour urine collection for proteinuria
- 24-hour urine collection for electrophoresis
- Anticyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies
- Antinuclear antibodies
- Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies
- Bone mineral density scan
- Bone scintigraphy
- Computed tomography scan of abdomen
- Computed tomography scan of brain
- Extractable nuclear antigen antibodies
- Faecal occult blood test
- Haemoglobin electrophoresis
- Parathyroid hormone levels
- Positron emission tomography
- QuantiFERON-TB Gold blood test
- Rheumatoid factor
- Serum immunofixation
- Serum protein electrophoresis
- Skeletal survey
- Urine cytology
- Urine for Bence Jones protein
Question 18
Rufus’ investigations confirm the most likely diagnosis and he is managed appropriately.
Two weeks later, Rufus’ son Maurice, aged 45 years, comes to see you to discuss his father’s illness. He is aware of his father’s diagnosis and is concerned about his own risk of becoming unwell. He asks if he should be tested.
What advice is appropriate regarding Maurice’s request? Write two (2) specific pieces of advice.
- …
- …
Case 7: Lola White
Lola White, aged 33 years, presents requesting a routine skin check. She spent a lot of time outdoors when she was growing up and can recall several blistering sunburns as a child. Lola has no significant past medical history, takes no regular medications and has no known allergies. She does not smoke and has two standard drinks of alcohol two nights per week.
On examination, Lola looks well. Her temperature is 37.1 °C, blood pressure is 114/71 mmHg, heart rate is 72/min regular, respiratory rate is 14/min and body mass index is 22 kg/m2. She consents to a full skin examination.
You detect a pigmented lesion on Lola’s back (see image).
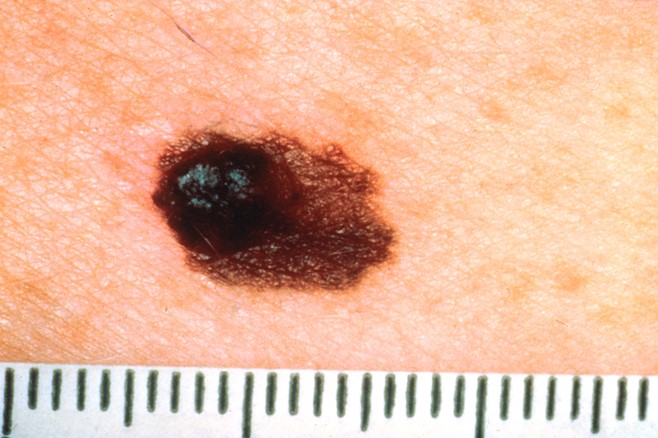
Question 19
What examination findings of this lesion suggest a serious underlying diagnosis? Write three (3) specific examination findings.
- …
- …
- …
What management action is appropriate? Write one (1) specific management action.
- …
Question 21
Lola is managed appropriately and returns for review eight weeks later.
What non-pharmacological management advice is appropriate regarding Lola’s ongoing care in view of her initial presenting skin complaint? Write three (3) specific pieces of nonpharmacological management advice.
- …
- …
- …
Case 8: Eddie Mindell
Eddie Mindell, aged 71 years, presents for the results of routine annual blood tests and an electrocardiogram that he had yesterday. He feels well and has no focal symptoms. Eddie has a past medical history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hypercholesterolaemia and gout. His medications include empagliflozin/metformin 12.5 mg/1000 mg orally twice daily, ramipril 10 mg orally daily, atorvastatin 40 mg orally daily and allopurinol 300 mg orally daily. He has no known allergies. He smokes 20 cigarettes per day, which he has done for the past 55 years, and has two standard drinks of alcohol five nights per week.
On examination, Eddie looks well. His temperature is 36.9 °C, blood pressure is 154/93 mmHg, heart rate is 85/min regular, respiratory rate is 14/min and body mass index is 33 kg/m2. The remainder of his examination is normal.
The results of his investigations, including electrocardiogram (see image), are shown below:
Full blood count – normal Lipids (fasting) – normal
Biochemistry
| Test | Result (6 months ago) | Result (3 months ago) | Result (yesterday) | Normal range |
| Sodium | 139 mmol/L | 140 mmol/L | 141 mmol/L | 135 – 145 |
| Potassium | 4.3 mmol/L | 4.4 mmol/L | 4.2 mmol/L | 3.5 – 5.2 |
| Chloride | 99 mmol/L | 101 mmol/L | 103 mmol/L | 95 – 110 |
| Bicarbonate | 26 mmol/L | 28 mmol/L | 27 mmol/L | 22 – 32 |
| Urea | 8.3* mmol/L | 9.7* mmol/L | 10.5* mmol/L | 2.5 – 8.0 |
| Creatinine | 144* mmol/L | 160* mmol/L | 175* mmol/L | 45 – 90 |
| Estimated glomerular filtration rate | 42* mL/min/1.73m2 | 37* mL/min/1.73m2 | 33* mL/min/1.73m2 | > 90 |
| Urate | 0.33 mmol/L | 0.35 mmol/L | 0.32 mmol/L | < 0.42 |
Glucose
| Test | Result (6 months ago) | Result (3 months ago) | Result (yesterday) | Normal range |
| Glycosylated haemoglobin | 65* mmol/L (8.1*%) | 63* mmol/L (7.9*%) | 57* mmol/L (7.4*%) | 20 – 42 (4.0 – 6.0) |
| Urine albumin:creatinine ratio | 28.0* mg/mmol | 30.0* mg/mmol | 33.0* mg/mmol | < 2.5 – 25.0 |
Electrocardiogram (yesterday) (see image):
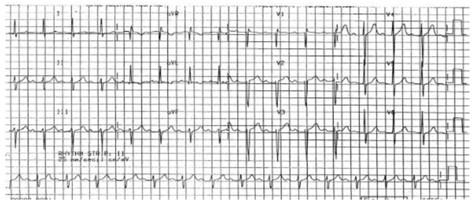
Question 22
What additional initial investigations are appropriate considering the abnormal investigation results? Select four (4) investigations from the following list.
- Adrenocorticotropic hormone
- B-type natriuretic peptide
- Coagulation studies
- Iron studies
- Liver function tests
- Parathyroid hormone
- Plasma metanephrines
- Prostate-specific antigen
- Renin:aldosterone ratio
- Serum albumin
- Serum calcium
- Serum ethanol
- Serum lactate
- Serum magnesium
- Serum osmolality
- Serum phosphate
- Thyroid function tests
- Ultrasound renal artery duplex
- Ultrasound scan of kidneys, ureters, bladder
- Urine cytology
- Urine for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
- Urine osmolality
- Urine oxalate
- X-ray of chest
Question 23
Eddie’s further investigations are normal. What changes to Eddie’s medication are appropriate (medication doses are not required)? Write four (4) specific pharmacological management actions (dosing is not required).
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 24
What dietary advice is appropriate to discuss with Eddie? Write four (4) specific pieces of dietary advice.
- …
- …
- …
- …
