Dermatology is a key part of General Practice. Here is a list of 101 common dermatological conditions in approximate order of incidence. Click on the link for more details.
- Acne
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Contact Dermatitis
- Psoriasis
- Seborrheic Dermatitis
- Rosacea
- Urticaria
- Tinea
- Herpes Simplex
- Varicella Zoster
- Impetigo
- Scabies
- Cellulitis
- Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Melanoma
- Actinic Keratosis
- Alopecia
- Warts
- Corns and Calluses
- Athlete’s Foot
- Nail Fungal Infections
- Molluscum Contagiosum
- Vitiligo
- Pityriasis Rosea
- Ichthyosis
- Keratosis Pilaris
- Lichen Planus
- Sunburn
- Photodermatoses
- Cutaneous Drug Reactions
- Intertrigo
- Pilonidal Cyst
- Epidermoid Cysts
- Lipomas
- Folliculitis
- Milia
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Perioral Dermatitis
- Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus
- Scleroderma
- Cutaneous Candidiasis
- Dermatophytosis
- Erythema Multiforme
- Telangiectasia
- Spider Naevi
- Angiomas
- Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars
- Melasma
- Hand Dermatitis
- Dyshidrotic Eczema
- Pediculosis
- Bed Bug Bites
- Cherry Angiomas
- Sebaceous Hyperplasia
- Seborrheic Keratosis
- Acanthosis Nigricans
- Lentigines
- Purpura
- Cutaneous Tags
- Stasis Dermatitis
- Cutaneous Vasculitis
- Cutaneous Sarcoidosis
- Pemphigus Vulgaris
- Bullous Pemphigoid
- Dermatomyositis
- Paronychia
- Erysipelas
- Naevi
- Pyogenic Granuloma
- Pityriasis Alba and Pityriasis Versicolour
- Pityriasis Lichenoides
- Discoid Eczema
- Pruritus Ani
- Pruritus Vulvae
- Mastocytosis
- Ganglion Cyst
- Hemangiomas
- Raynaud
- Erythema Nodosum
- Lichen Sclerosus
- Granuloma Annulare
- Morphea
- Lichen Simplex Chronicus
- Actinic Prurigo
- Dermatofibroma
- Harlequin Ichthyosis
- Acrodermatitis Enteropathica
- Rosacea Fulminans
- Syringomas
- Fox
- Porokeratosis
- Darier’s Disease
- Perforating Dermatoses
- Behçet’s disease
- Xanthomas
- Erythrasma
- Condyloma Acuminatum
- Erythema Ab Igne
- Porphyria
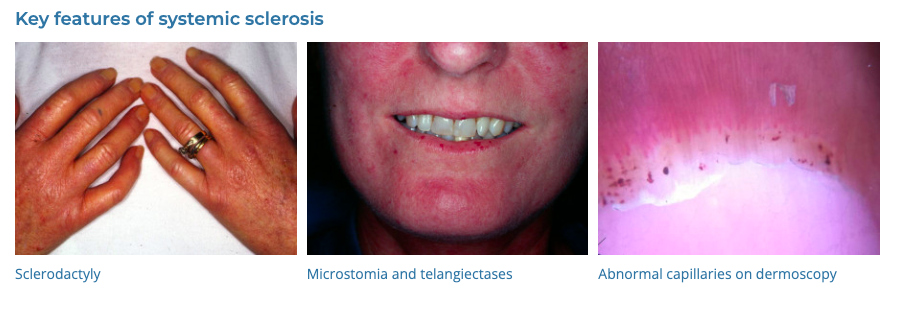
41. Scleroderma
- Description: Chronic autoimmune disease causing hardening and tightening of the skin.
- Associations: Genetic predisposition, environmental triggers.
- Management: Managing symptoms, physical therapy, medications to control symptoms
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/scleroderma
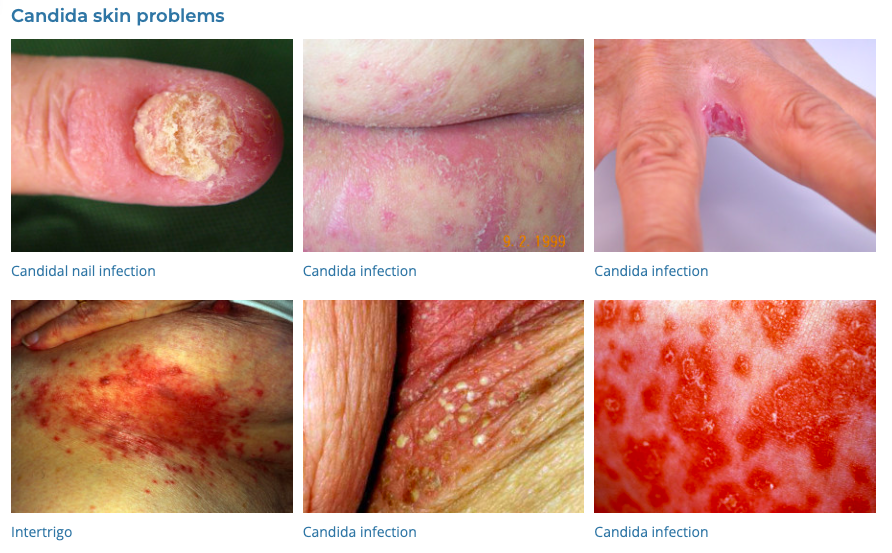
42. Cutaneous Candidiasis
- Description: Fungal infection of the skin caused by Candida species.
- Associations: Common in warm, moist areas; associated with immunocompromised states.
- Management: Antifungal creams (clotrimazole) or oral medication (fluconazole).
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/candida
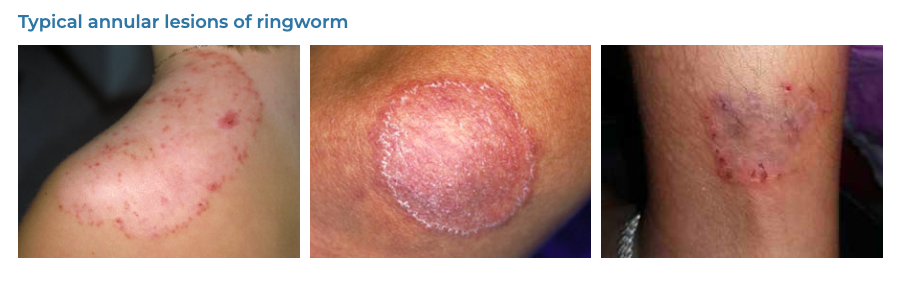
43. Dermatophytosis
- Description: Fungal infection causing small, discolored patches of skin.
- Associations: More common in hot, humid climates.
- Management: Antifungal creams, lotions, or shampoos.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/tinea-corporis
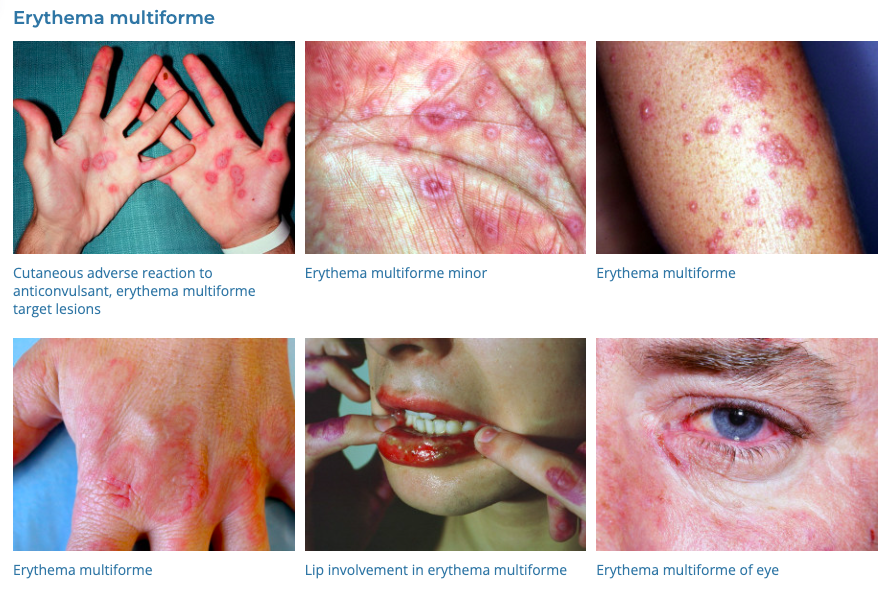
44. Erythema Multiforme
- Description: Reaction causing red, target-like or bull’s-eye patches.
- Associations: Often a reaction to infections or medications.
- Management: Address underlying cause, topical steroids, antihistamines.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/erythema-multiforme
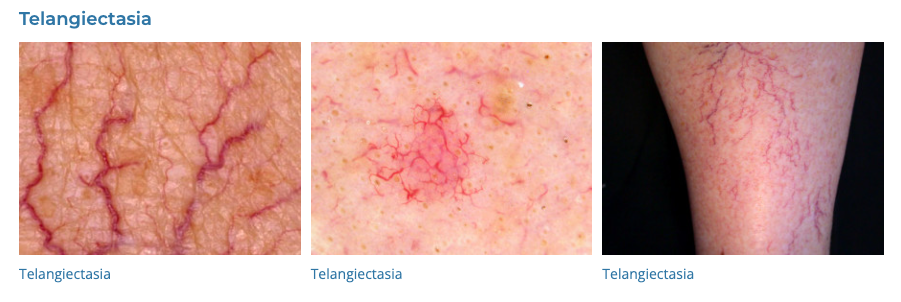
- Description: Small, widened blood vessels on the skin.
- Associations: May be associated with various diseases, including rosacea.
- Management: Laser therapy, electrocautery.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/telangiectasia
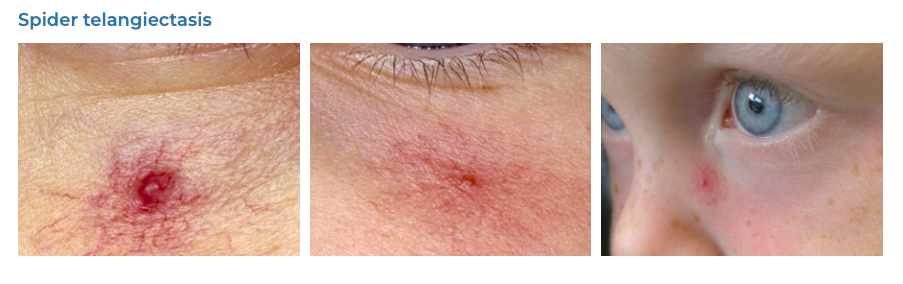
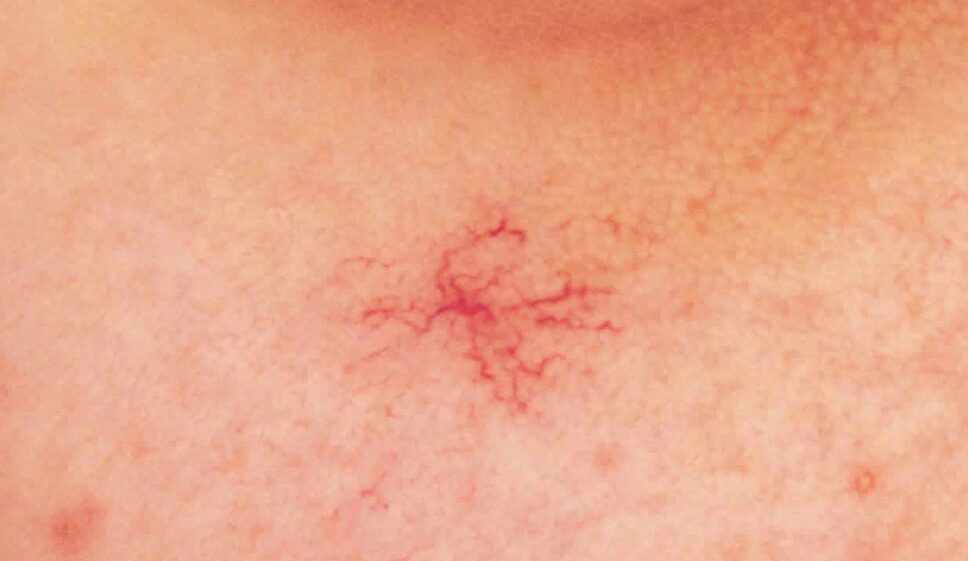
46. Spider Naevi
- Description: Small, red, purple, and blue vessels that have a spider like appearance
- Associations: Liver disease, alcohol, high oestrogen (COCP)
- Management: Laser treatment, sclerotherapy.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/spider-telangiectasis
47. Angiomas
- Description: Benign growths made up of small blood vessels.
- Associations: May appear at birth or develop later in life.
- Management: Usually not needed; laser or surgical removal if desired.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/vascular-proliferations-and-abnormalities-of-blood-vessels
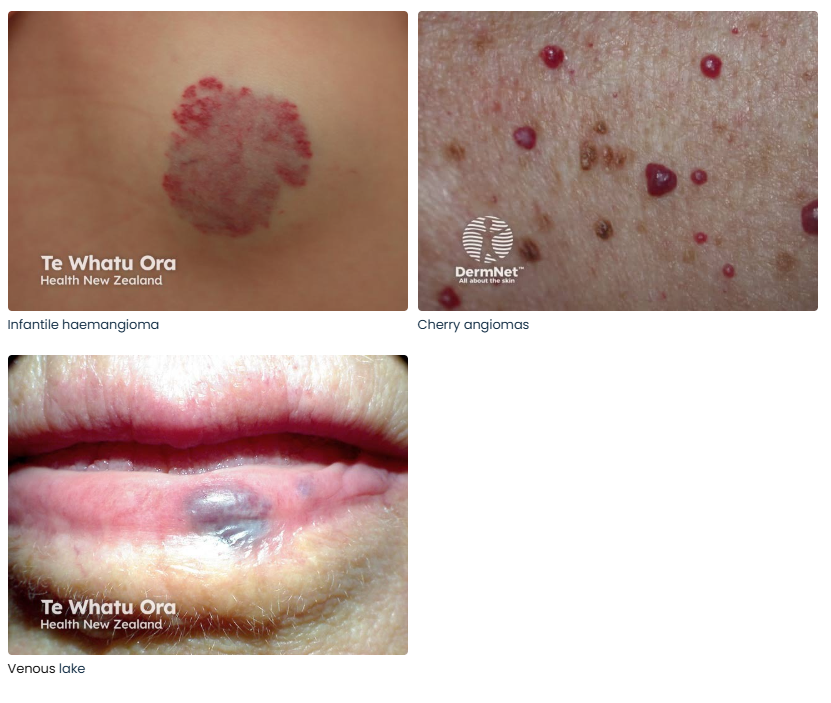
48. Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars
- Description: Overgrowth of scar tissue at the site of a healed skin injury.
- Associations: More common in darker skin.
- Management: Steroid injections, laser therapy, surgery.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/keloid-and-hypertrophic-scar
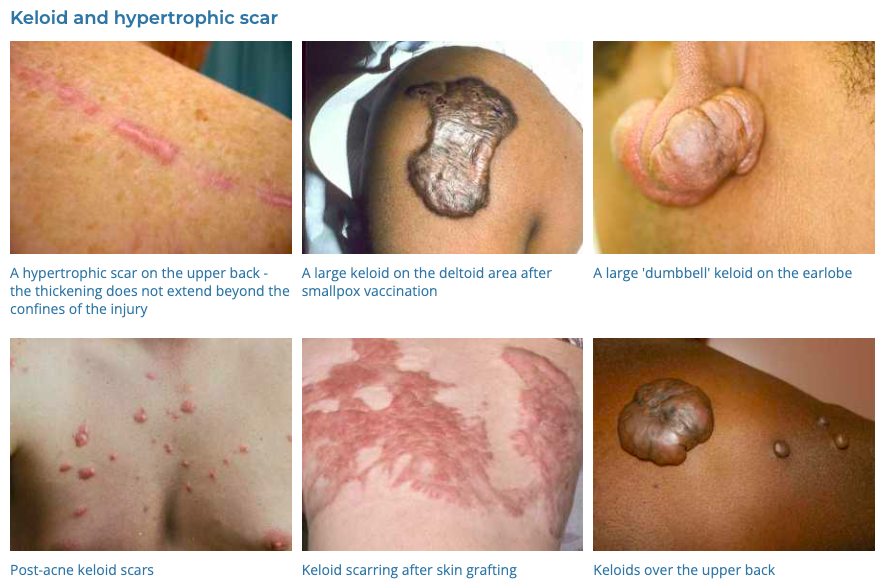
49. Melasma
- Description: Brown or gray-brown patches on the face.
- Associations: Often triggered by COCP, pregnancy, hypothyroidism, sun exposure, chemical peels/laser
- Management: Sun protection, topical bleaching agents, laser therapy.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/melasma
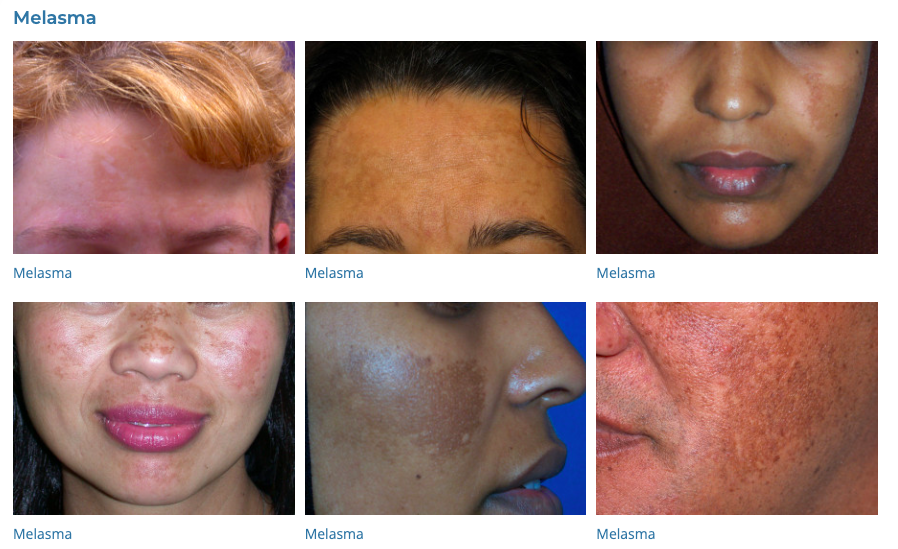
50. Hand Dermatitis
- Description: Inflammation of the skin on the hands.
- Associations: Often due to contact with irritants or allergens.
- Management: Avoidance of triggers, moisturizers, topical steroids.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/hand-dermatitis
51. Dyshidrotic Eczema
- Description: Small, itchy blisters on the edges of the fingers, toes, palms, and soles.
- Associations: Related to seasonal allergies, stress.
- Management: Moisturizing lotions, steroid creams, avoiding irritants.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/dyshidrotic-eczema
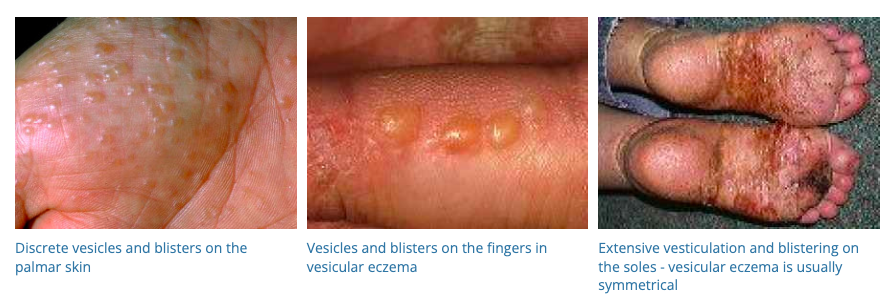
52. Pediculosis
- Description: Infestation of the skin with lice.
- Associations: Spread through close contact.
- Management: Lice-killing lotions, combing out nits.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/images/pediculosis-images

53. Bed Bug Bites
- Description: Small, red, itchy welts on the skin.
- Associations: Caused by bites of bed bugs.
- Management: Symptomatic treatment, exterminating bed bugs.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/bed-bugs
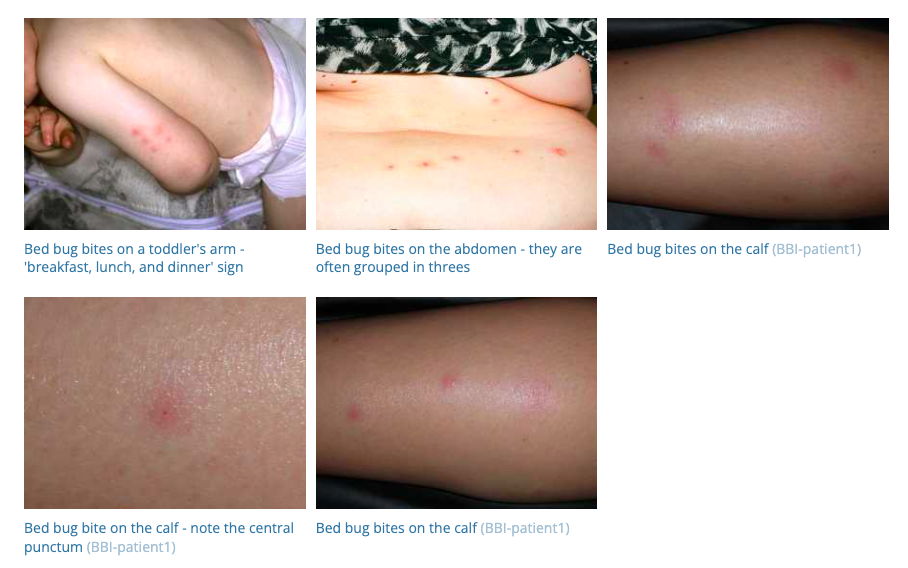
54. Cherry Angiomas
- Description: Small, bright red growths on the skin.
- Associations: Increase with age.
- Management: Usually not necessary; laser or electrocautery if desired.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/cherry-angioma
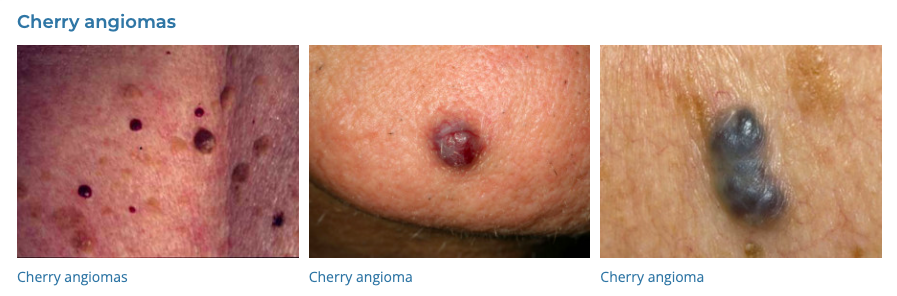
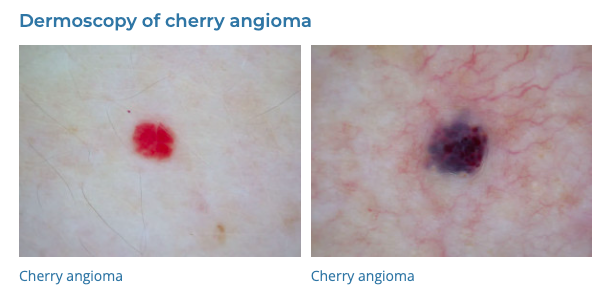
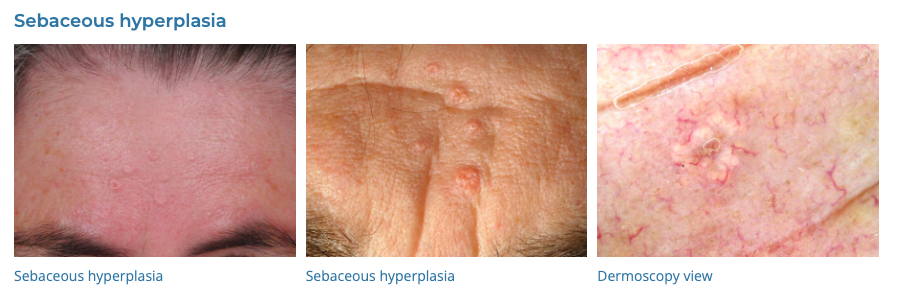
55. Sebaceous Hyperplasia
- Description: Enlarged sebaceous glands appearing as small, yellow bumps.
- Associations: More common in middle-aged or older people.
- Management: Usually cosmetic; cryotherapy, laser therapy.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/sebaceous-hyperplasia
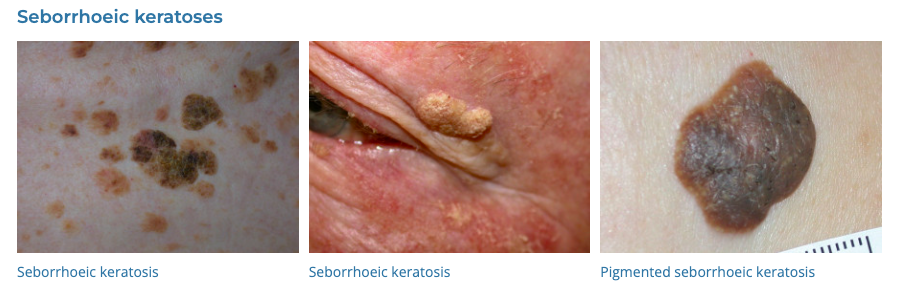
56. Seborrheic Keratosis
- Description: Brown, black, or light tan growths on the skin.
- Associations: Common in older adults.
- Management: No treatment necessary; removal for cosmetic reasons.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/seborrhoeic-keratosis
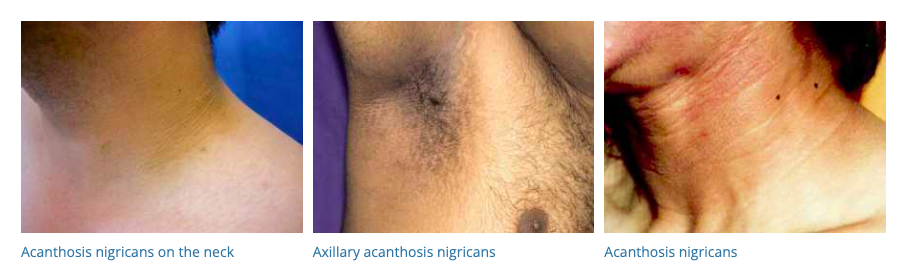
57. Acanthosis Nigricans
- Description: Darkening and thickening of the skin, especially in body folds.
- Associations: Often associated with obesity, diabetes, and hormonal conditions.
- Management: Treat underlying condition; topical retinoids, laser therapy.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/acanthosis-nigricans
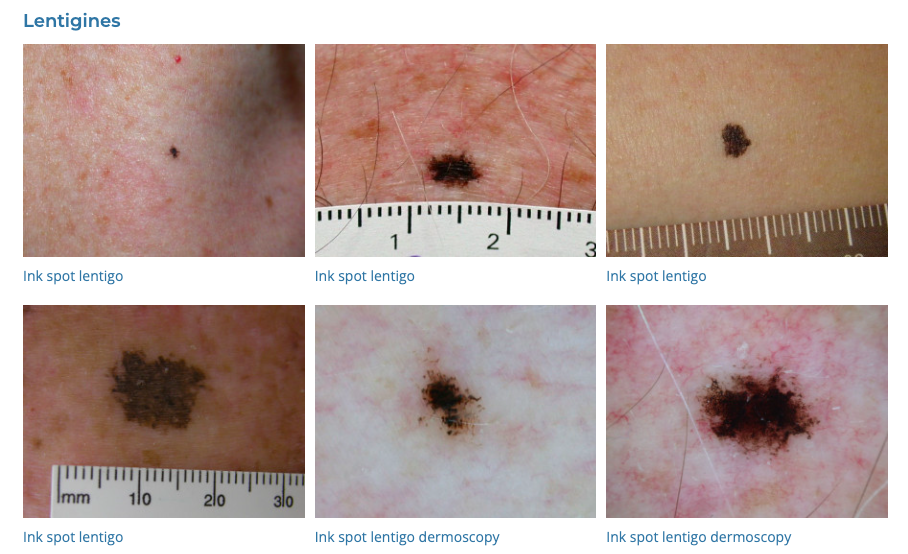
58. Lentigines
- Description: Small, flat, brown spots due to sun exposure.
- Associations: Common in older adults.
- Management: Prevention with sun protection; bleaching creams, laser therapy.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/lentigo
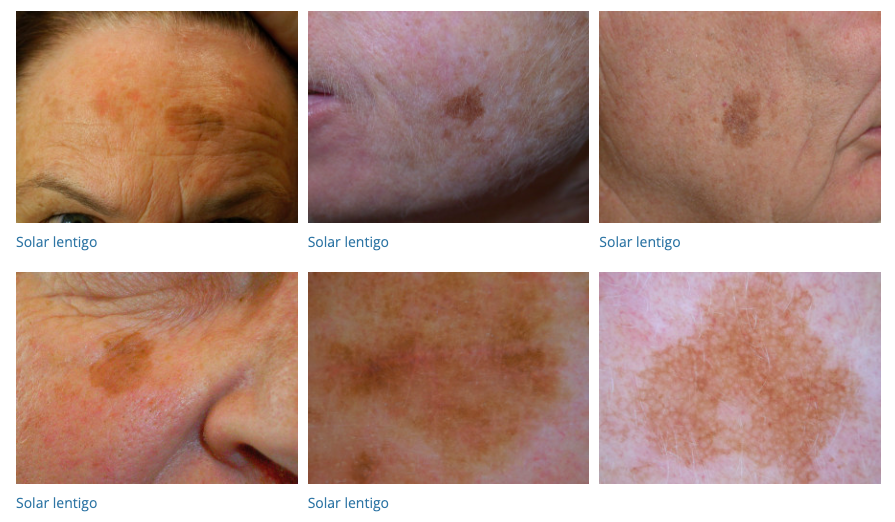
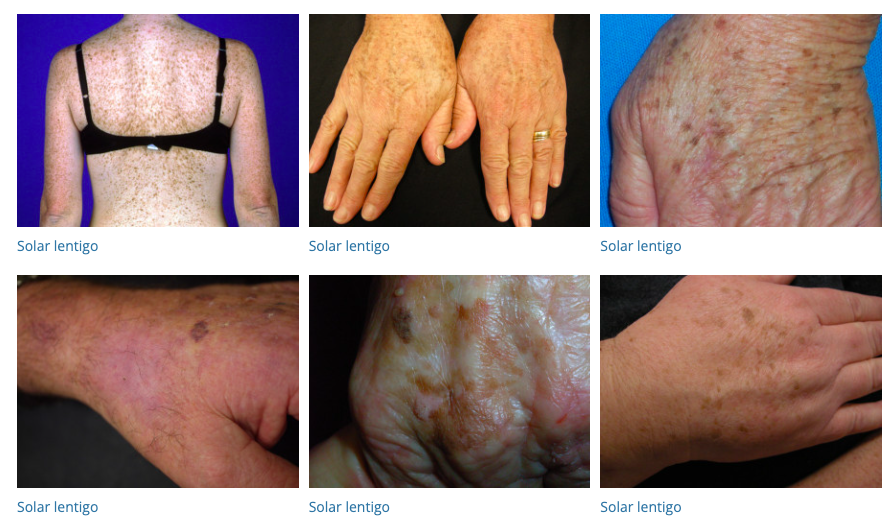
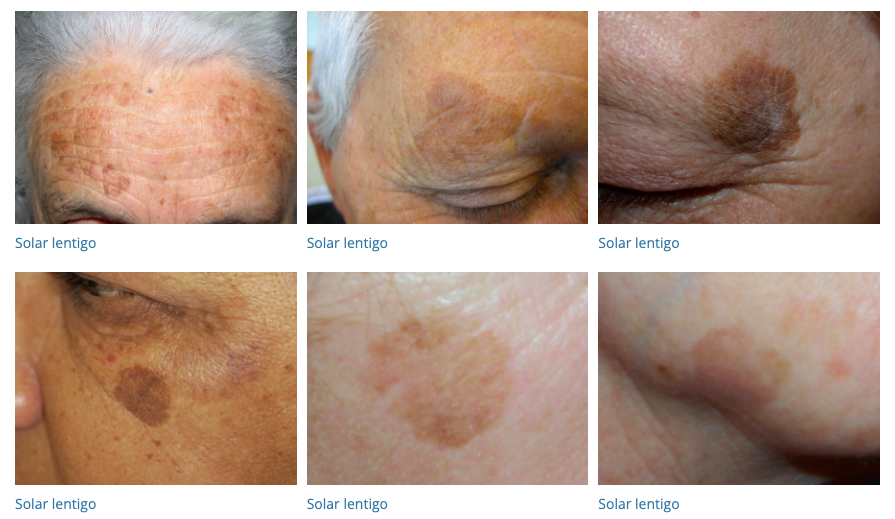
59. Purpura
- Description: Purple-colored spots and patches on the skin.
- Associations: Steroids, anticoagulants, vasculitis, thrombocytopaenia
- Management: Depends on underlying cause.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/purpura
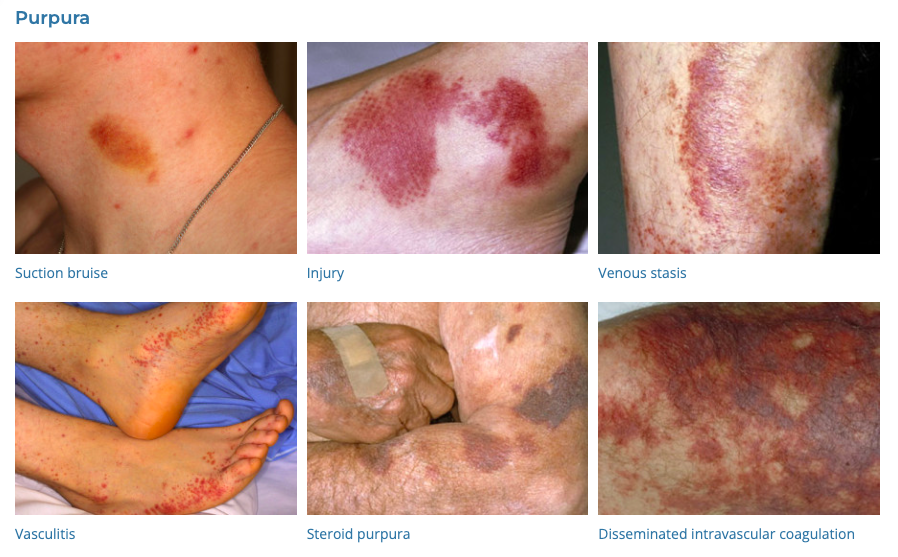
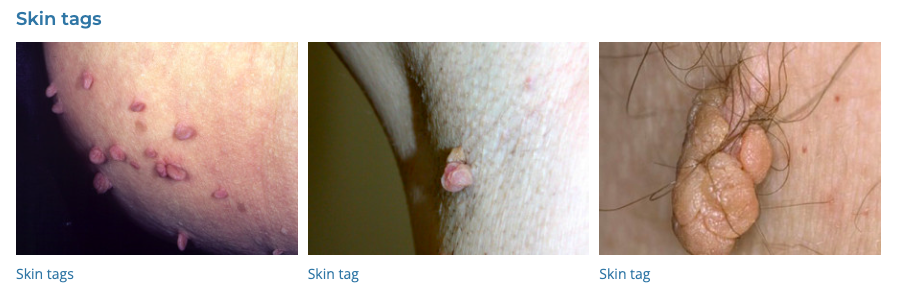
60. Cutaneous Tags
- Description: Small, soft, skin-colored growths.
- Associations: More common in older adults and obese individuals.
- Management: Snipping, freezing, or burning off.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/skin-tag