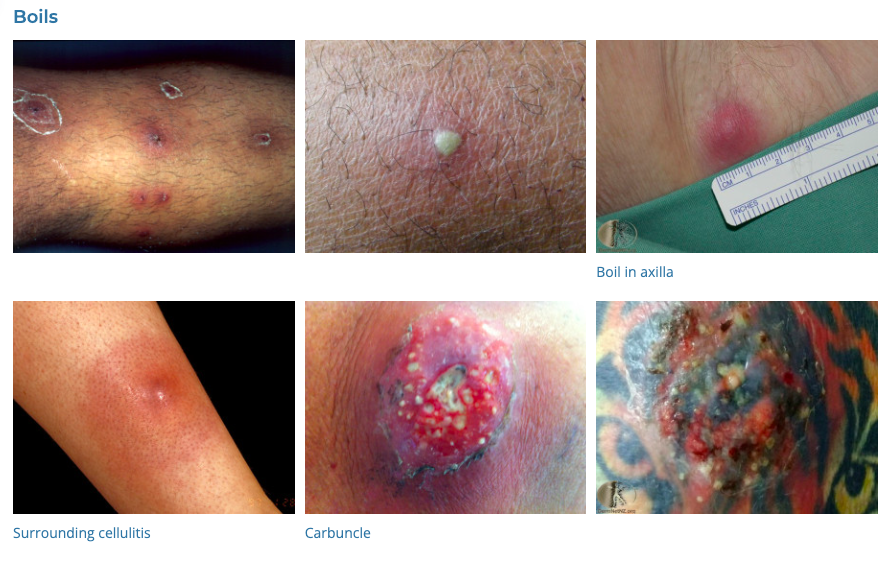
Boils (furuncles) and carbuncles are skin infections typically caused by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. They present as painful, swollen areas on the skin with a central collection of pus and debris.
Causes:
- Bacterial Infection: Most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus, including methicillin-resistant strains (MRSA).
- Hair Follicle Infection: Boils often start in hair follicles.
- Skin Trauma: Minor skin trauma or irritation can predispose to infection.
- Personal Hygiene: Poor hygiene can increase the risk.
- Immune System: Compromised immunity, such as in diabetes, can contribute.
- Close Contact: Spread can occur through skin-to-skin contact with an infected person.
- Environmental Factors: Hot, humid environments can exacerbate the risk.
Diagnosis:
- Clinical Examination: Diagnosis is usually based on the appearance of the skin.
- Culture and Sensitivity: Pus or fluid from the boil can be cultured to identify the causative bacteria and determine antibiotic sensitivity, especially in recurrent cases or if MRSA is suspected.
- Blood Tests: In recurrent or severe cases, blood tests may be done to check for underlying health problems like diabetes.
Differential Diagnosis:
- Cystic Acne: Deep, painful, pus-filled lesions similar to boils but associated with acne.
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Chronic skin condition causing abscesses and scarring.
- Folliculitis: Inflammation of hair follicles, generally less severe than boils.
- Sebaceous Cysts: Blocked sebaceous glands leading to cyst formation.
- Ecthyma: A deeper form of impetigo presenting as pus-filled sores.
- Abscess: A collection of pus that has built up within the tissue.
Management:
- Warm Compresses: Applied several times a day to promote drainage.
- Antibiotics: Needed if the infection is severe, widespread, not draining, or if the patient has fever or other signs of systemic infection. Choice of antibiotics depends on the severity and the likelihood of MRSA.
- Flucloxacillin 500mg oral QID
- Batrim DS i oral BD (MRSA)
- Incision and Drainage: Performed by a healthcare provider in the case of large or resistant boils.
- Hygiene: Maintaining good personal hygiene and proper care of minor skin wounds.
- Do Not Squeeze or Lance at Home: This can spread the infection.
- Pain Management: Analgesics for pain relief, if necessary.
- Treat Underlying Conditions: Manage conditions like diabetes or obesity that may contribute to recurrent skin infections.
- Prevention of Spread: Wash hands regularly, use a personal towel, and avoid sharing personal items.
When to Refer:
- Recurrent episodes of boils or carbuncles.
- Lack of response to initial treatment.
- Presence of complicating factors like diabetes or immune suppression.
- If the infection is spreading rapidly or the patient is systemically unwell.
Preventative Measures:
- Good personal hygiene.
- Careful management of cuts and abrasions.
- Avoiding sharing personal items like towels or razors.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle to support the immune system.
Follow-up:
- Monitor for signs of infection spread.
- Ensure completion of any antibiotic course.
- Education on signs of recurrence and when to seek further medical advice.
https://dermnetnz.org/topics/boil