Dermatology is a key part of General Practice. Here is a list of 101 common dermatological conditions in approximate order of incidence. Click on the link for more details.
- Acne
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Contact Dermatitis
- Psoriasis
- Seborrheic Dermatitis
- Rosacea
- Urticaria
- Tinea
- Herpes Simplex
- Varicella Zoster
- Impetigo
- Scabies
- Cellulitis
- Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Melanoma
- Actinic Keratosis
- Alopecia
- Warts
- Corns and Calluses
- Athlete’s Foot
- Nail Fungal Infections
- Molluscum Contagiosum
- Vitiligo
- Pityriasis Rosea
- Ichthyosis
- Keratosis Pilaris
- Lichen Planus
- Sunburn
- Photodermatoses
- Cutaneous Drug Reactions
- Intertrigo
- Pilonidal Cyst
- Epidermoid Cysts
- Lipomas
- Folliculitis
- Milia
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Perioral Dermatitis
- Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus
- Scleroderma
- Cutaneous Candidiasis
- Dermatophytosis
- Erythema Multiforme
- Telangiectasia
- Spider Naevi
- Angiomas
- Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars
- Melasma
- Hand Dermatitis
- Dyshidrotic Eczema
- Pediculosis
- Bed Bug Bites
- Cherry Angiomas
- Sebaceous Hyperplasia
- Seborrheic Keratosis
- Acanthosis Nigricans
- Lentigines
- Purpura
- Cutaneous Tags
- Stasis Dermatitis
- Cutaneous Vasculitis
- Cutaneous Sarcoidosis
- Pemphigus Vulgaris
- Bullous Pemphigoid
- Dermatomyositis
- Paronychia
- Erysipelas
- Naevi
- Pyogenic Granuloma
- Pityriasis Alba and Pityriasis Versicolour
- Pityriasis Lichenoides
- Discoid Eczema
- Pruritus Ani
- Pruritus Vulvae
- Mastocytosis
- Ganglion Cyst
- Hemangiomas
- Raynaud
- Erythema Nodosum
- Lichen Sclerosus
- Granuloma Annulare
- Morphea
- Lichen Simplex Chronicus
- Actinic Prurigo
- Dermatofibroma
- Harlequin Ichthyosis
- Acrodermatitis Enteropathica
- Rosacea Fulminans
- Syringomas
- Fox
- Porokeratosis
- Darier’s Disease
- Perforating Dermatoses
- Behçet’s disease
- Xanthomas
- Erythrasma
- Condyloma Acuminatum
- Erythema Ab Igne
- Porphyria
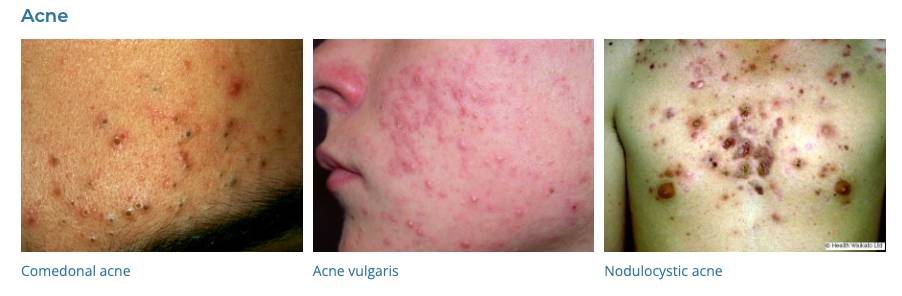
1. Acne
- Description: Inflammatory skin condition characterized by pimples, blackheads, and cysts, primarily on the face, back, and chest.
- Associations: Hormonal changes, genetics, stress, and certain medications.
- Management: Topical retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, antibiotics; oral isotretinoin for severe cases; hormonal therapy in some cases.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/acne
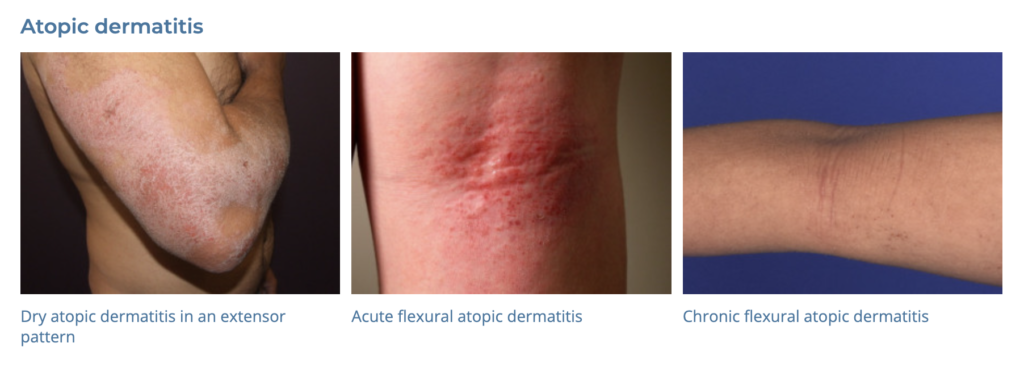
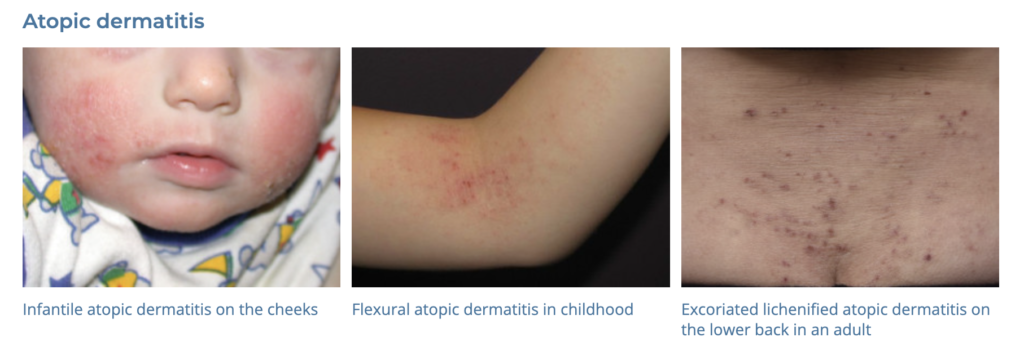
2. Atopic Dermatitis
- Description: Chronic, itchy rash that is often scaly and reddened.
- Associations: Family history of allergies or asthma, environmental factors.
- DDx: Granular parakeratosis can look very similar Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/granular-parakeratosis
- Management: Moisturizers, topical corticosteroids, avoiding triggers, antihistamines for itch relief.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/dermatitis
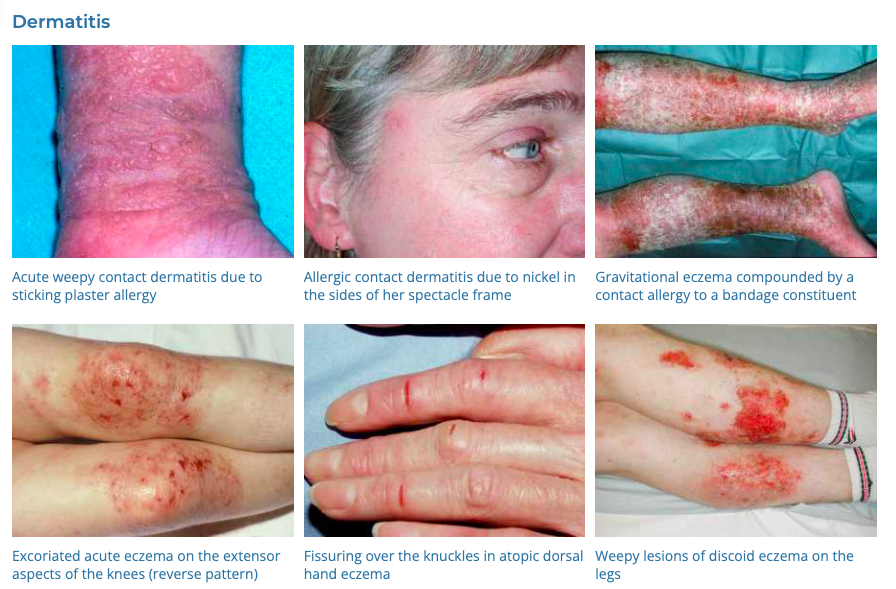
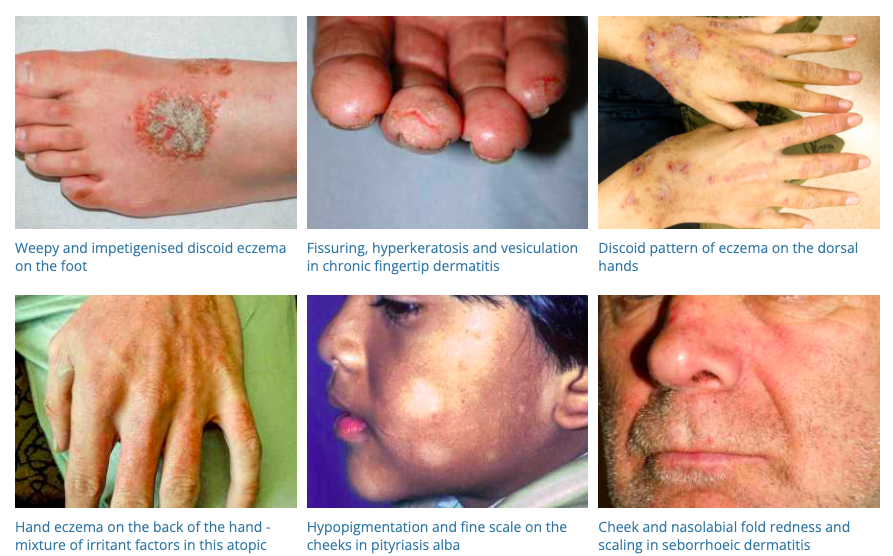
3. Contact Dermatitis
- Description: Red, itchy rash caused by direct contact with a substance or an allergic reaction to it.
- Associations: Exposure to irritants or allergens (like nickel, fragrances, plants).
- Management: Avoidance of the irritant or allergen, topical corticosteroids, oral antihistamines for severe cases.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/contact-dermatitis
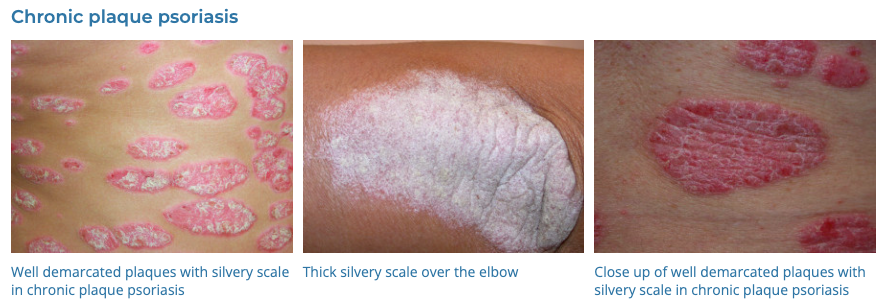
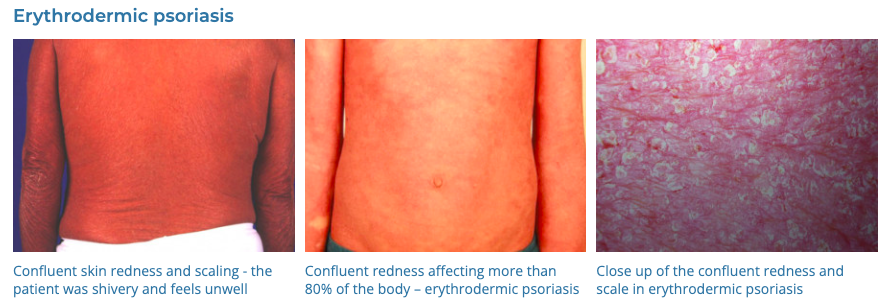
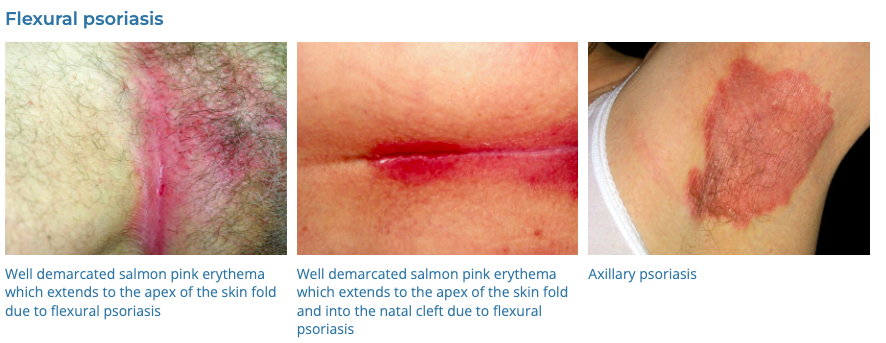
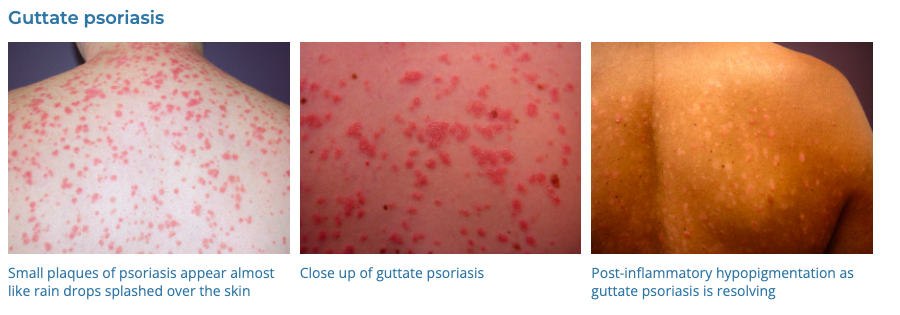
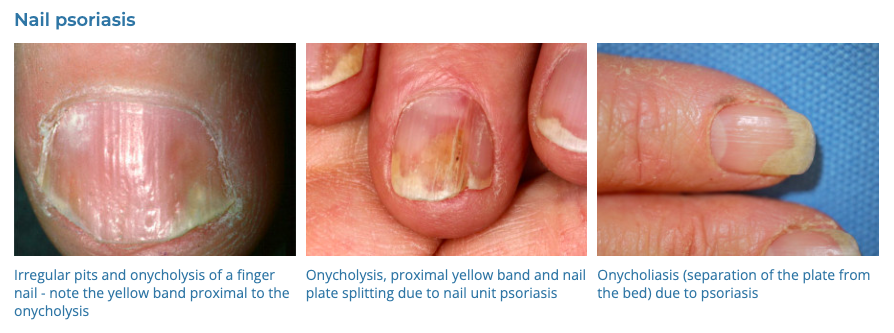
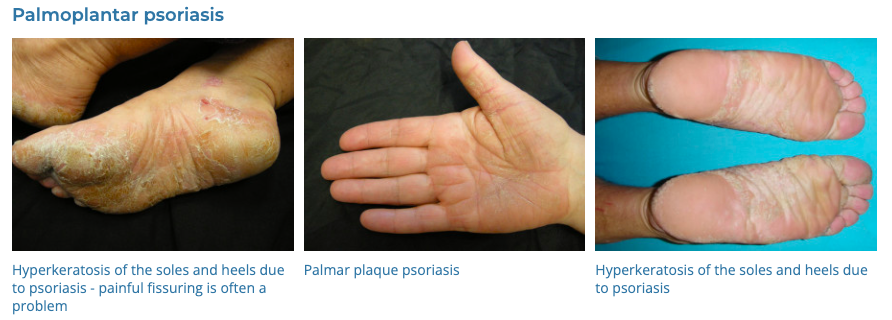
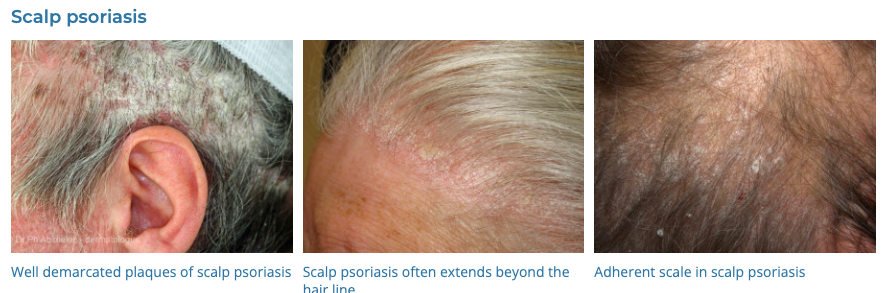
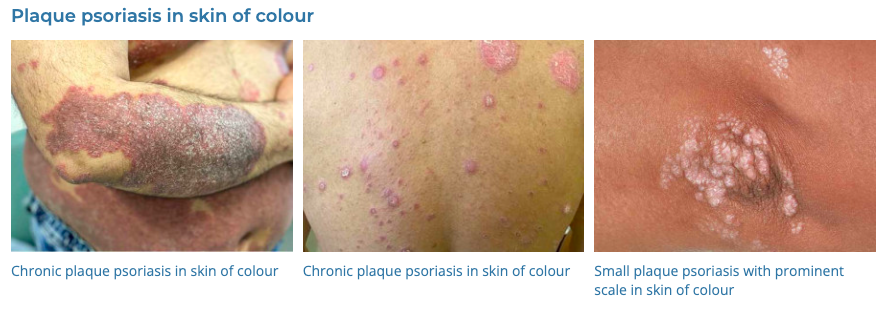
4. Psoriasis
- Description: Autoimmune disease that causes raised, red, scaly patches on the skin.
- Associations: Genetic predisposition, triggers include stress, infection, medications.
- Management: Topical treatments (steroids, vitamin D analogues), phototherapy, systemic medications for severe cases.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/psoriasis
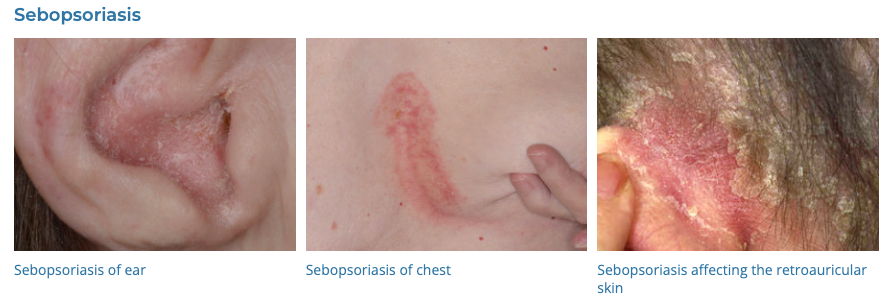
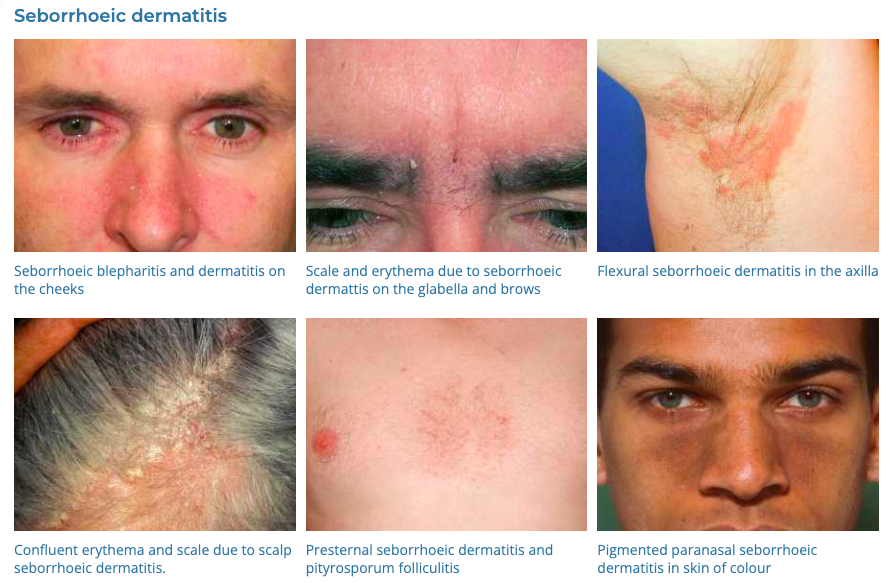
5. Seborrheic Dermatitis
- Description: Skin condition causing scaly patches, red skin, and stubborn dandruff.
- Associations: It’s more common in oily skin, stress, cold, dry weather.
- Management: Antifungal creams or shampoos, topical corticosteroids, calcineurin inhibitors.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/seborrhoeic-dermatitis
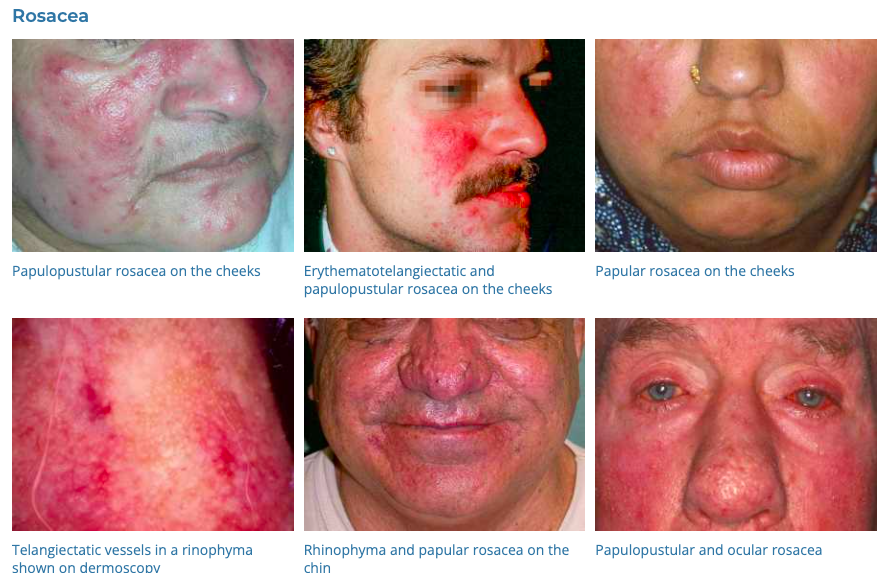
6. Rosacea
- Description: Chronic skin condition causing flushing, redness, pimples, and visible blood vessels, usually on the face.
- Associations: Fair skin, family history, age between 30 and 50.
- Management: Avoiding triggers, topical and oral antibiotics, laser therapy, managing lifestyle factors.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/rosacea
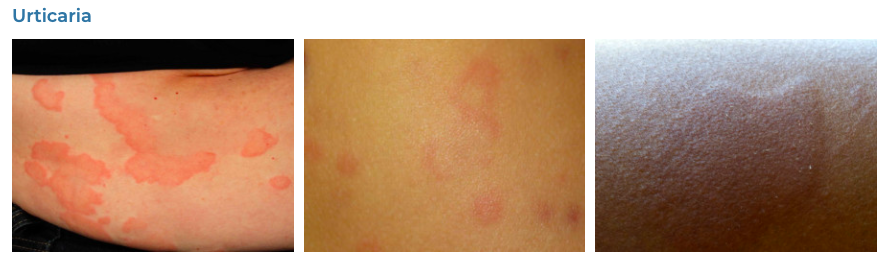
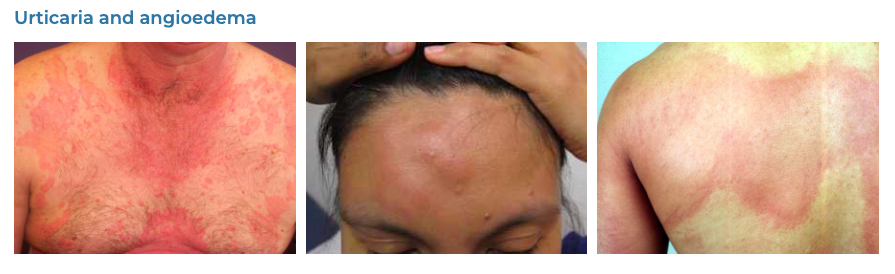
7. Urticaria
- Description: Sudden outbreak of swollen, pale red bumps or plaques on the skin.
- Associations: Allergic reactions, infections, stress, exposure to cold or heat.
- Management: Oral antihistamines, avoiding known triggers, corticosteroids for severe cases.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/urticaria-an-overview
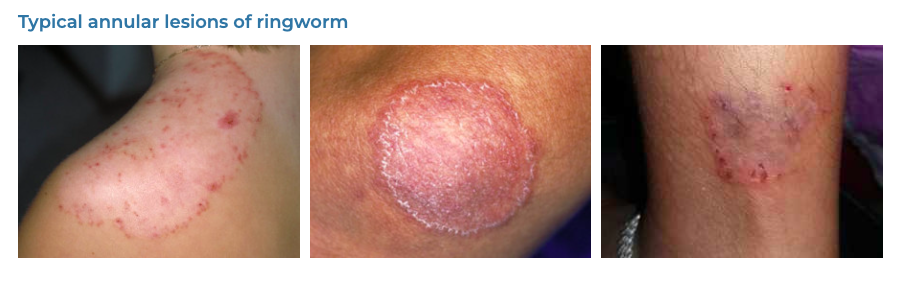
8. Tinea
- Description: Fungal infection of the skin, scalp, or nails presenting as a red, itchy, scaly ring-shaped rash.
- Associations: Warm, moist environments; close contact with infected individuals or animals.
- Management: Antifungal creams, shampoos, or oral medications, keeping the affected area clean and dry.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/tinea-corporis
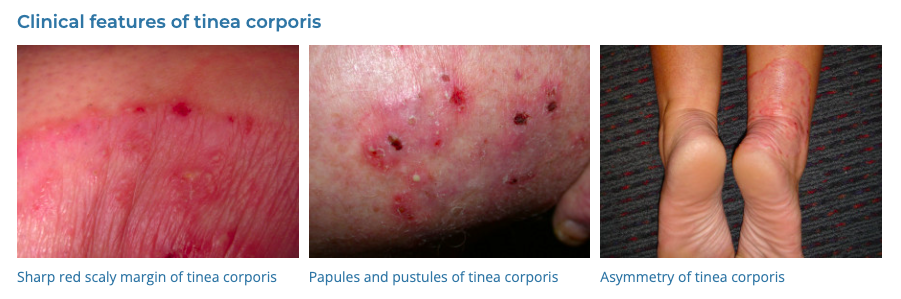
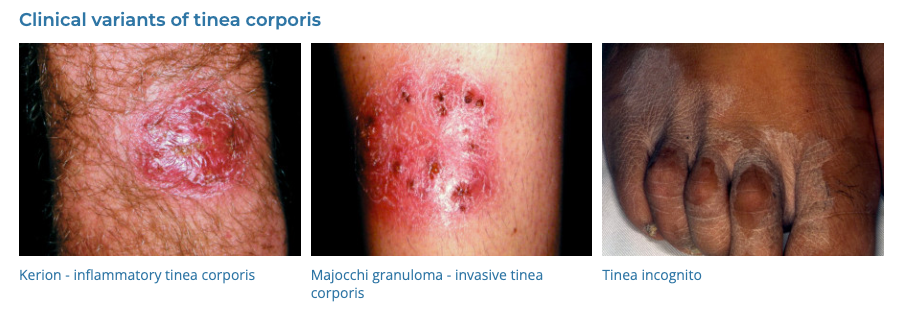
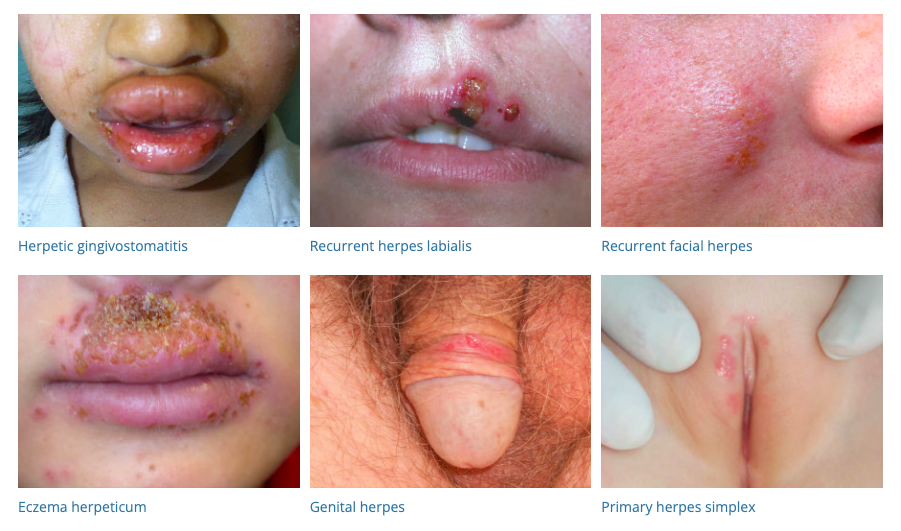
9. Herpes Simplex
- Description: Viral infection causing blisters and sores, usually on the mouth or genitals.
- Associations: HSV-1 and HSV-2 viruses, stress, sunlight, fever, weakened immune system.
- Management: Antiviral medications (topical or oral), pain relief measures, avoiding triggering factors.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/cme/viral-infections/herpes-simplex
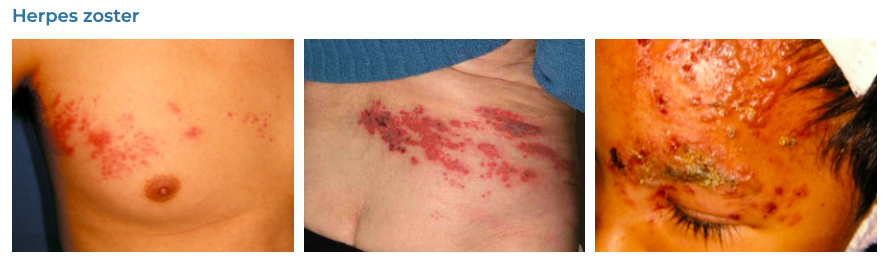
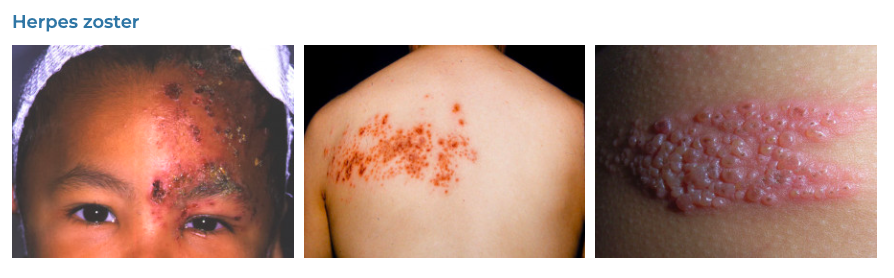
10. Varicella-Zoster
- Description: Chickenpox causes itchy, blister-like rash; shingles causes painful rash, often with blisters.
- Associations: Initial infection with the varicella-zoster virus (chickenpox); shingles occurs from reactivation of the virus.
- Management: Vaccination for prevention; antiviral drugs, pain management, and itch relief for active cases.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/herpes-zoster
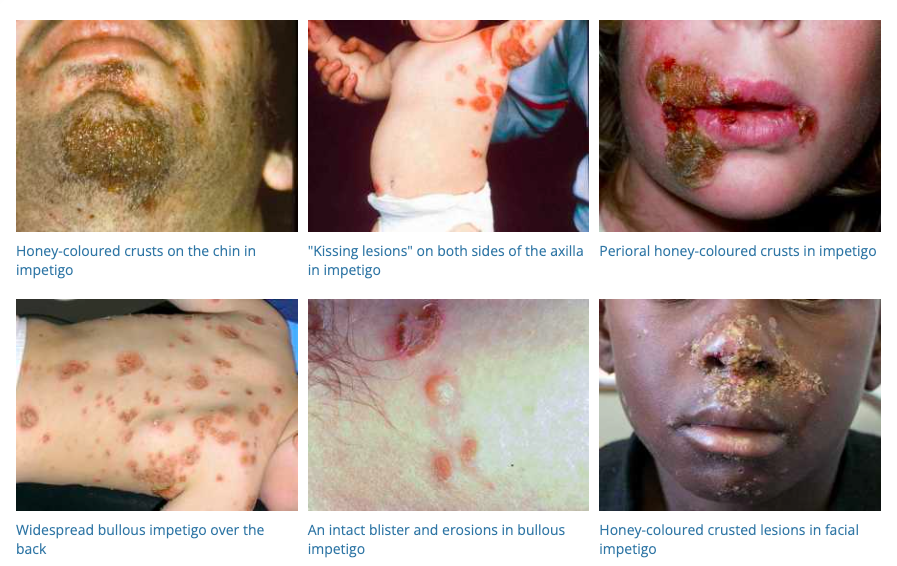
11. Impetigo
- Description: Highly contagious bacterial skin infection, causing red sores that can rupture, ooze fluid, and form a yellow-brown crust.
- Associations: Common in children, direct contact with infected person, or with items they’ve touched.
- Management: Topical or oral antibiotics, keeping the skin clean, avoiding scratching.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/impetigo
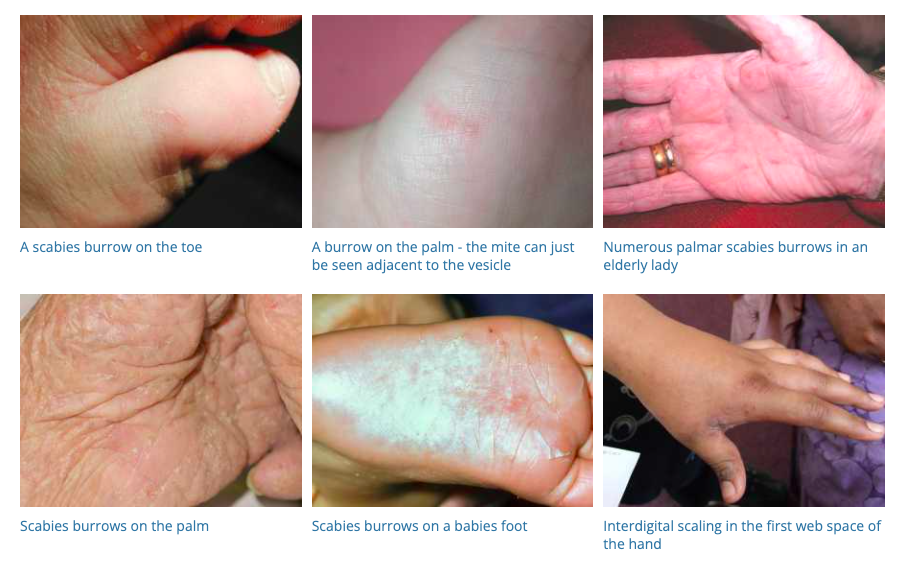
12. Scabies
- Description: Skin infestation by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei, causing intense itching and a pimple-like skin rash.
- Associations: Close physical contact, crowded conditions, compromised immune system.
- Management: Prescription scabicidal lotions or creams, washing clothes and bedding in hot water.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/scabies
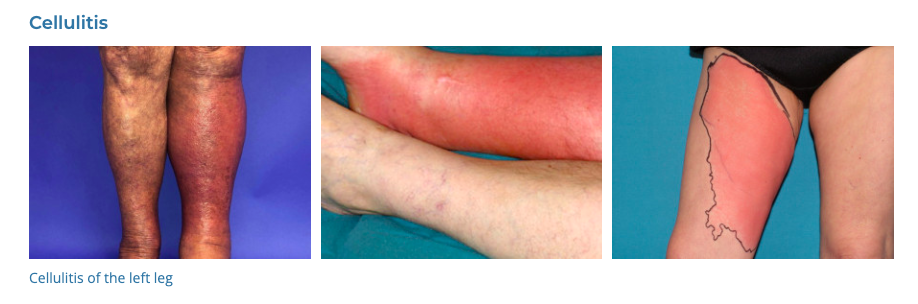
13. Cellulitis
- Description: Bacterial skin infection causing red, swollen, and painful skin, often with fever.
- Associations: Breaks in the skin, chronic skin conditions, weakened immune system.
- Management: Oral or intravenous antibiotics, rest, elevation of the affected area.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/cellulitis
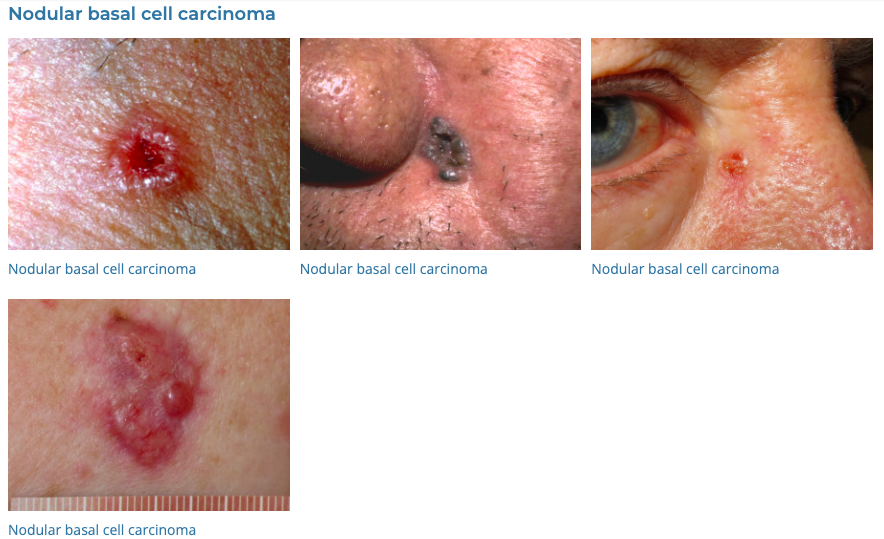
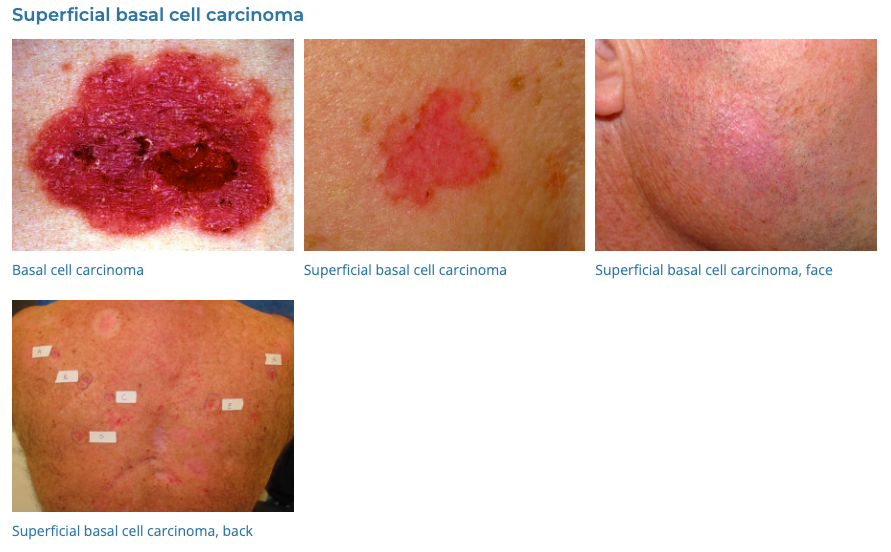
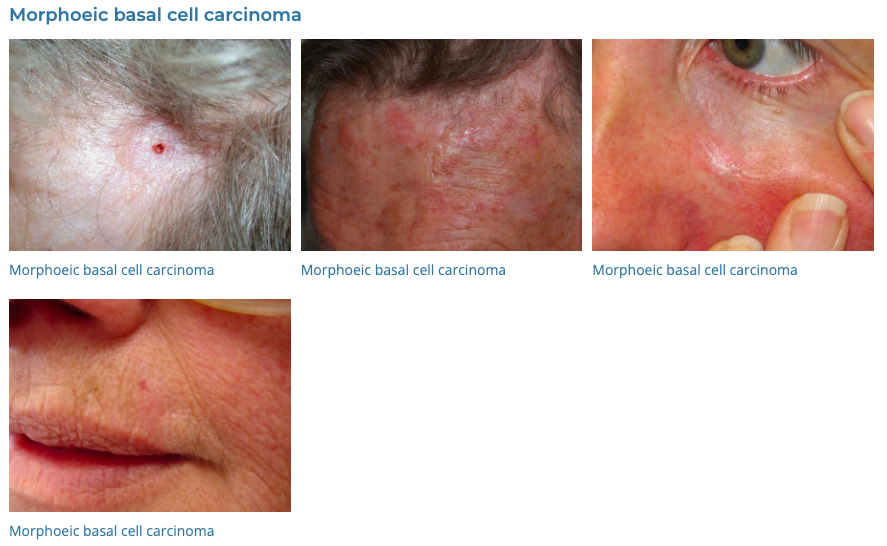
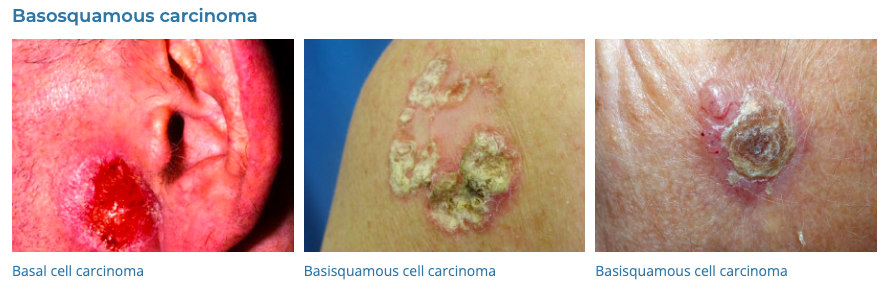
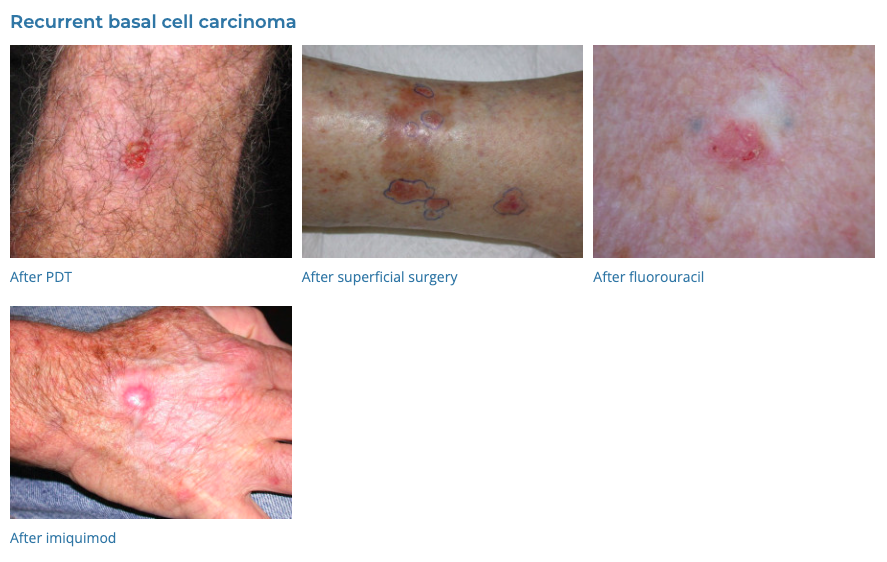
14. Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Description: Type of skin cancer featuring lesions or nodules on sun-exposed areas.
- Associations: Long-term sun exposure, fair skin.
- Management: Surgical removal, cryotherapy, topical treatments for early stages, radiation therapy.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/basal-cell-carcinoma
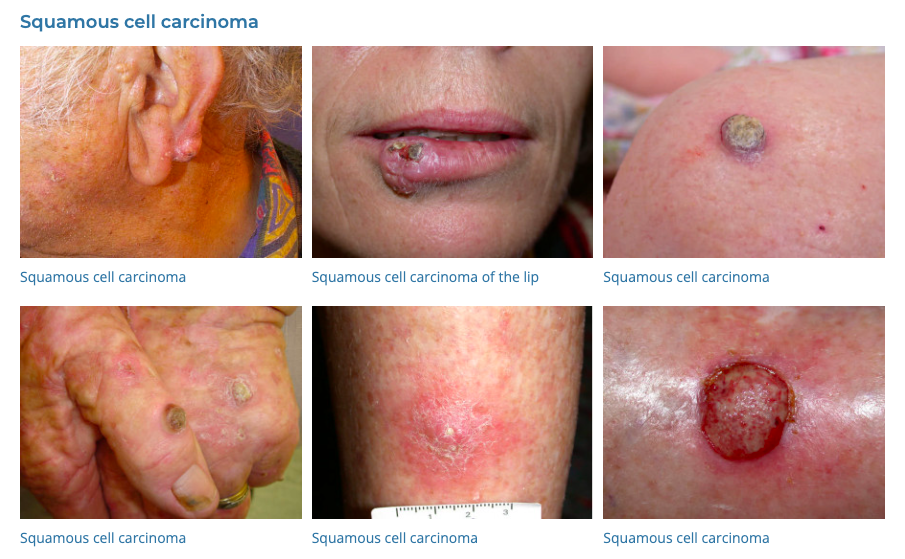
15. Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Description: Type of skin cancer causing firm, red nodules or flat sores with a scaly crust.
- Associations: UV exposure, fair skin, history of sunburns.
- Management: Surgical removal, radiation therapy, cryotherapy.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/cme/lesions/squamous-cell-carcinoma
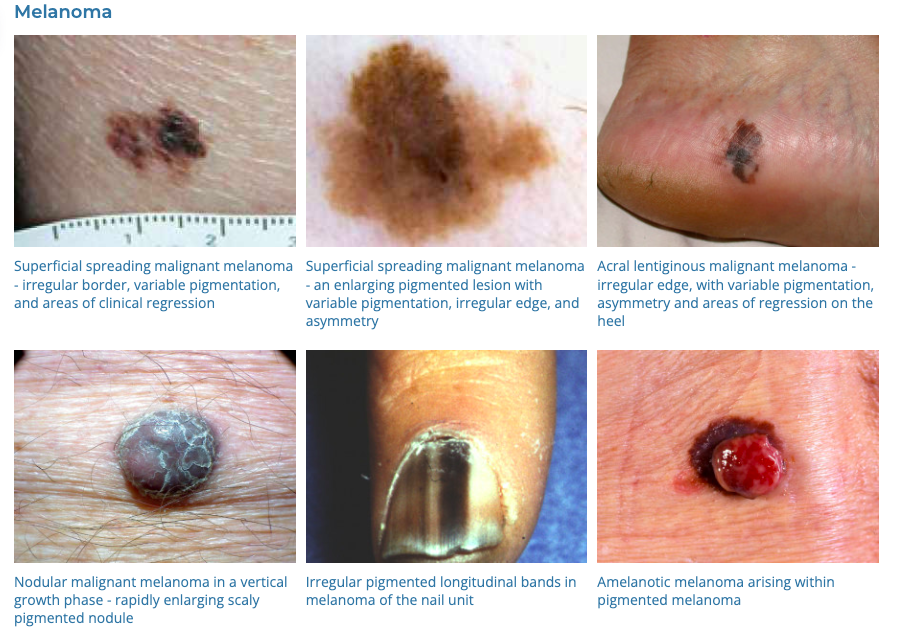
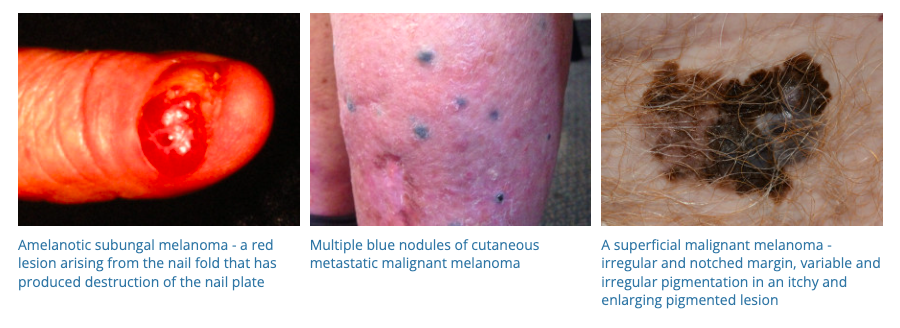
16. Melanoma
- Description: The most serious type of skin cancer, often resembling moles or developing from them.
- Associations: Intense UV exposure, fair skin, genetics, having many moles.
- Management: Surgical removal, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/melanoma
- Lentigo Maligna (Hutchinsons Melanotic Freckle)
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/lentigo-maligna-and-lentigo-maligna-melanoma
- Lentigo maligna has a 3-10% chance of malignant transformation flagged by rapid change – thickness, pigment…
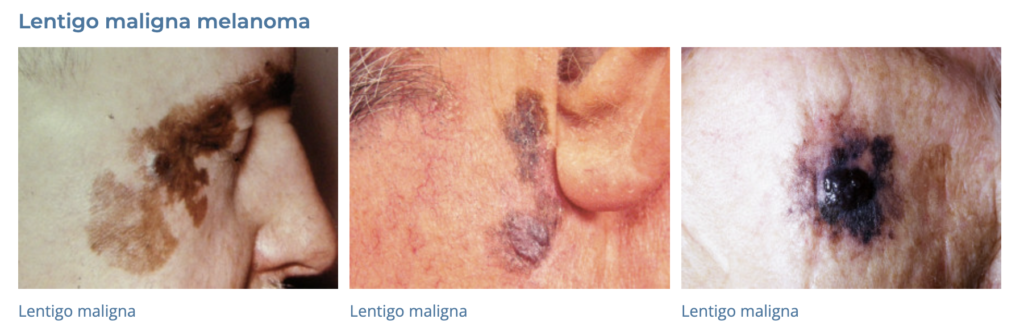
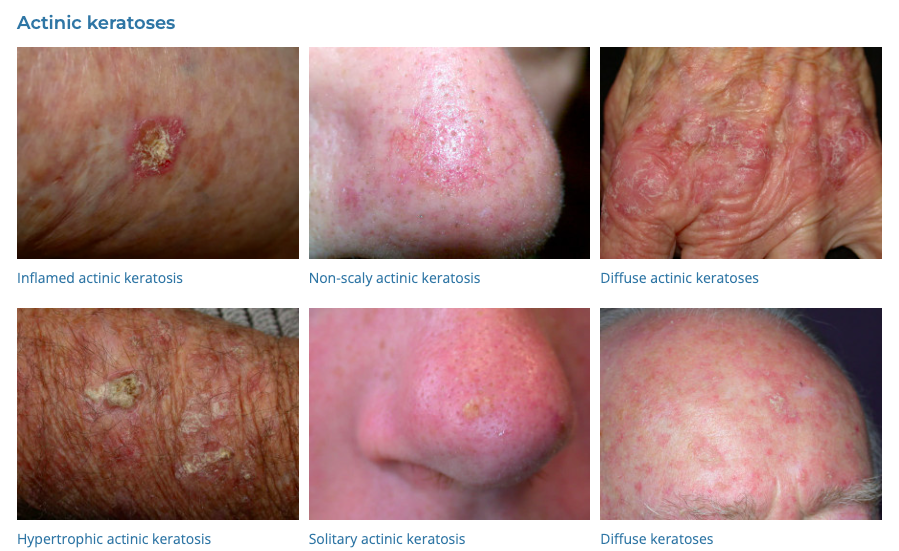
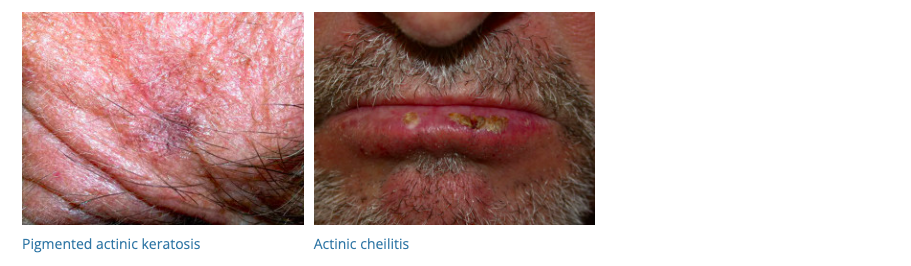
17. Actinic Keratosis
- Description: Rough, scaly patches on sun-exposed skin, potentially precancerous.
- Associations: Long-term sun exposure, older age, fair skin.
- Management: Cryotherapy, topical chemotherapy, photodynamic therapy.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/actinic-keratosis
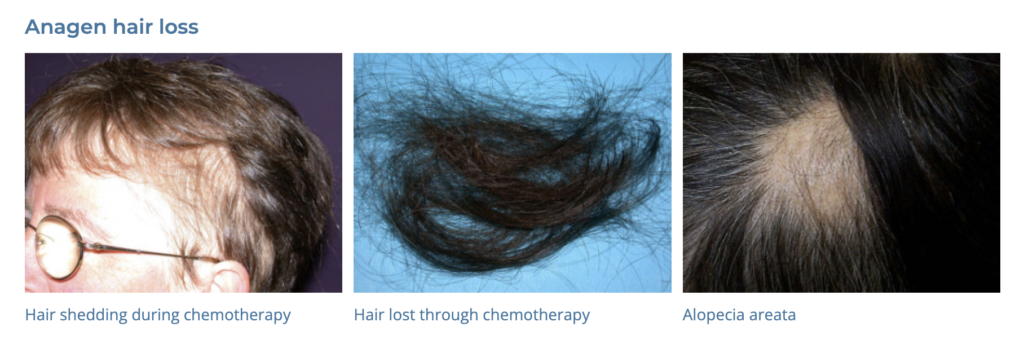
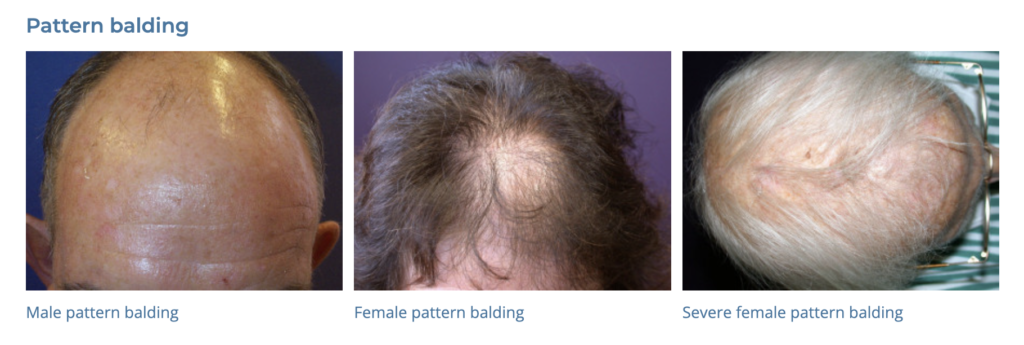
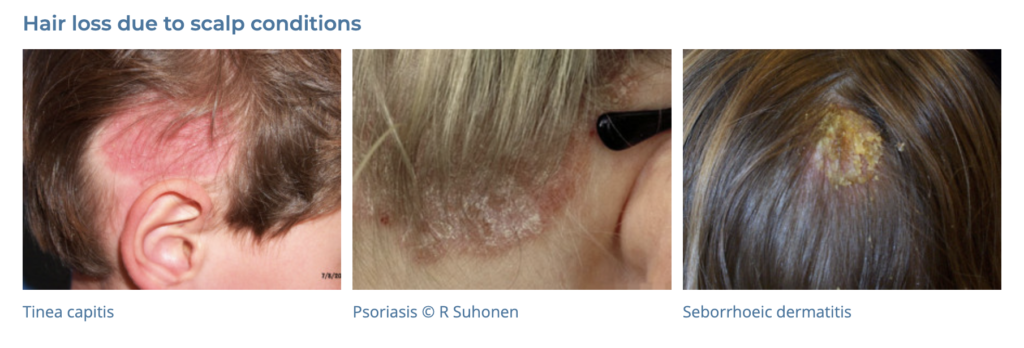
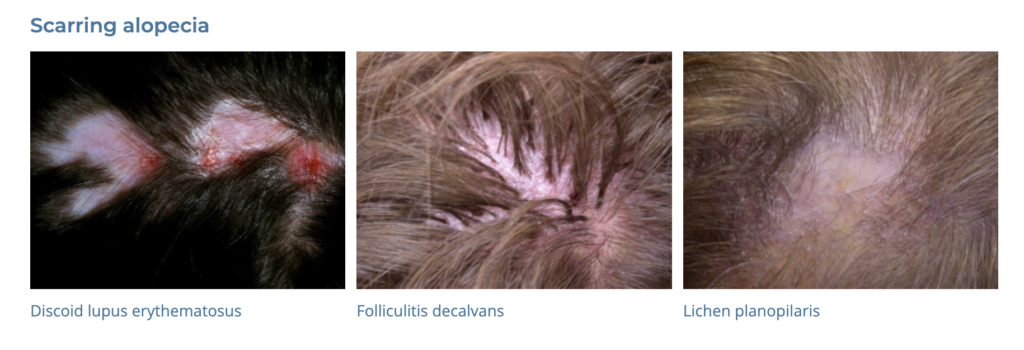
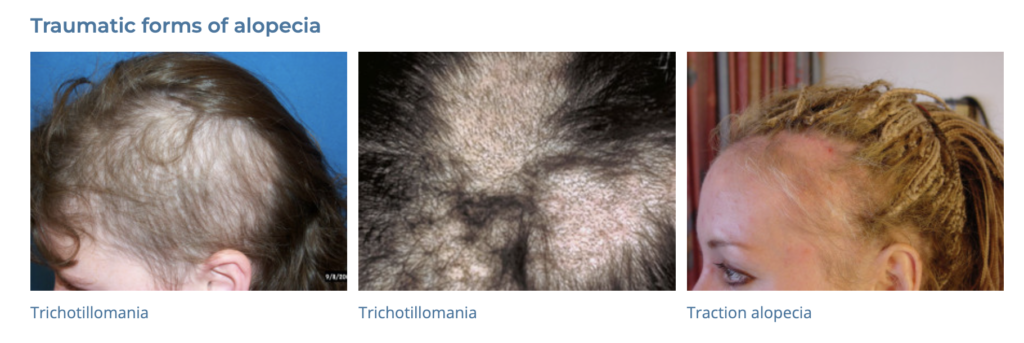
18. Alopecia
- Description: Loss of hair from the scalp or body, which can be temporary or permanent.
- Associations: Genetics, autoimmune conditions, certain medications, stress.
- Management: Topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, corticosteroids, hair transplant surgery.
- Exclamation mark hairs -> alopecia areata
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/hair-loss
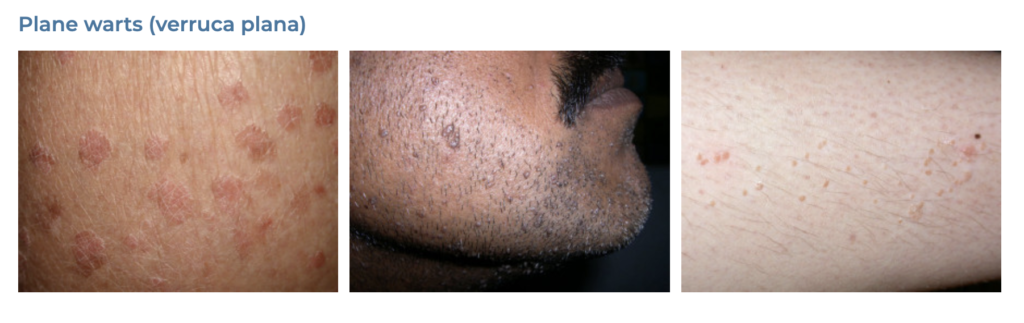
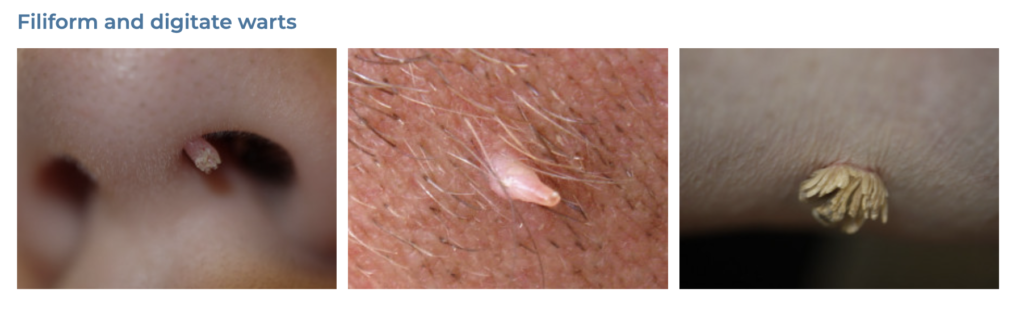
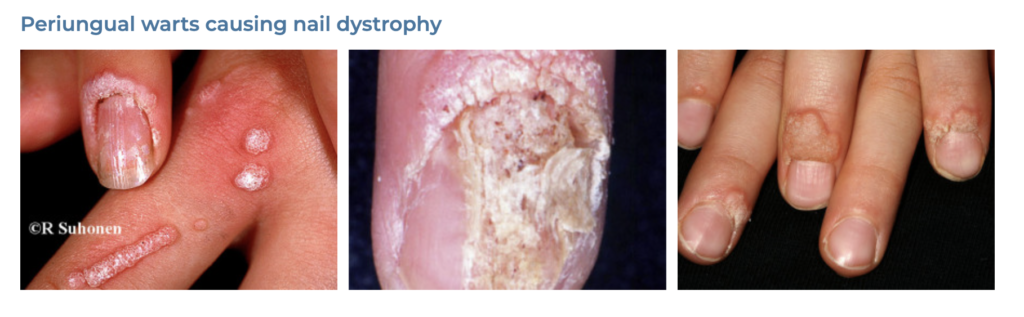
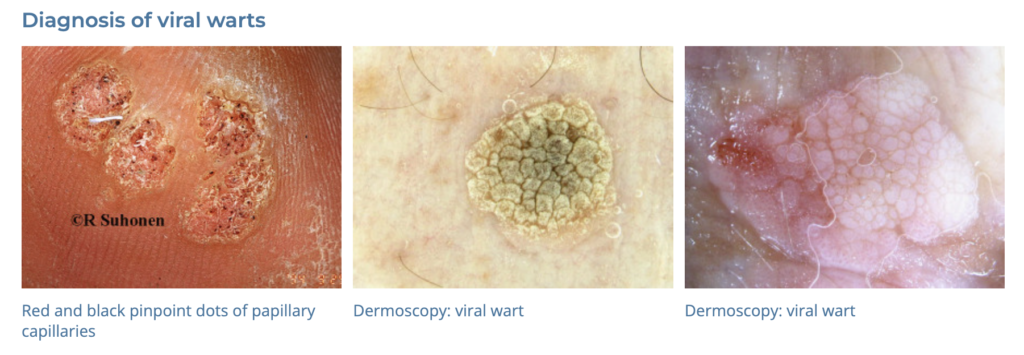
19. Warts
- Description: Small, grainy skin growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV).
- Associations: HPV infection, cuts or damage to the skin.
- Management: Cryotherapy, salicylic acid treatments, laser treatment, surgical removal.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/viral-wart
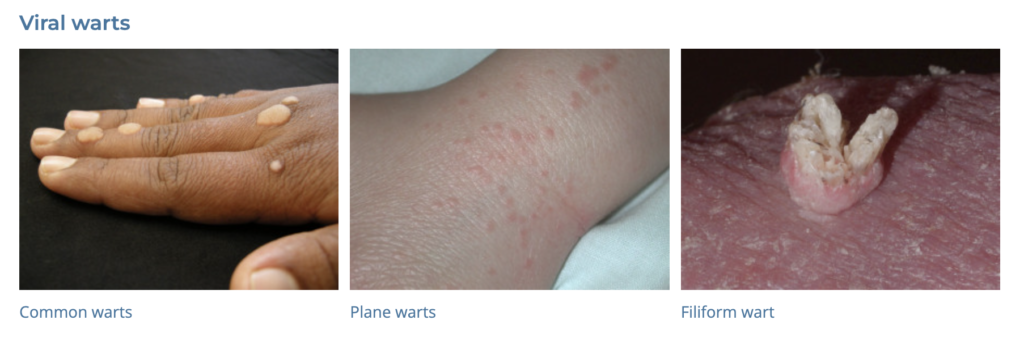
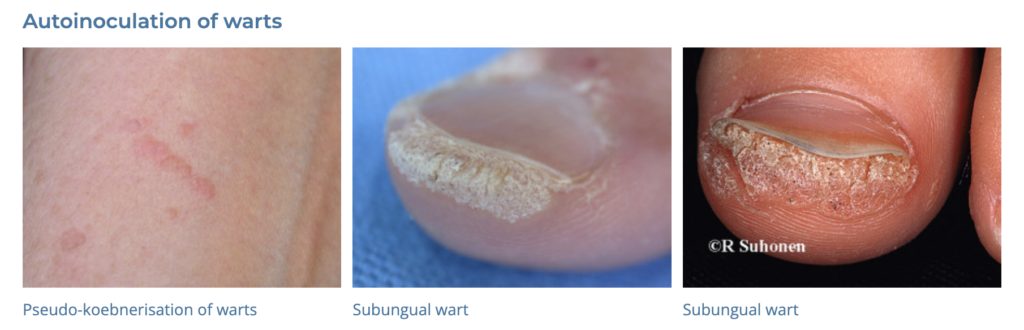
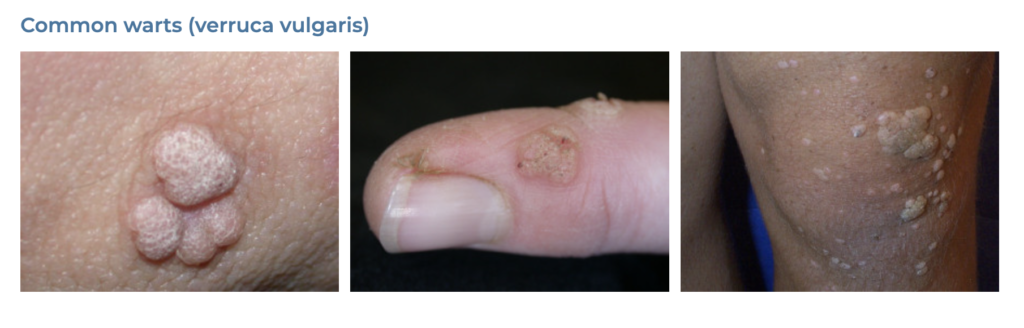
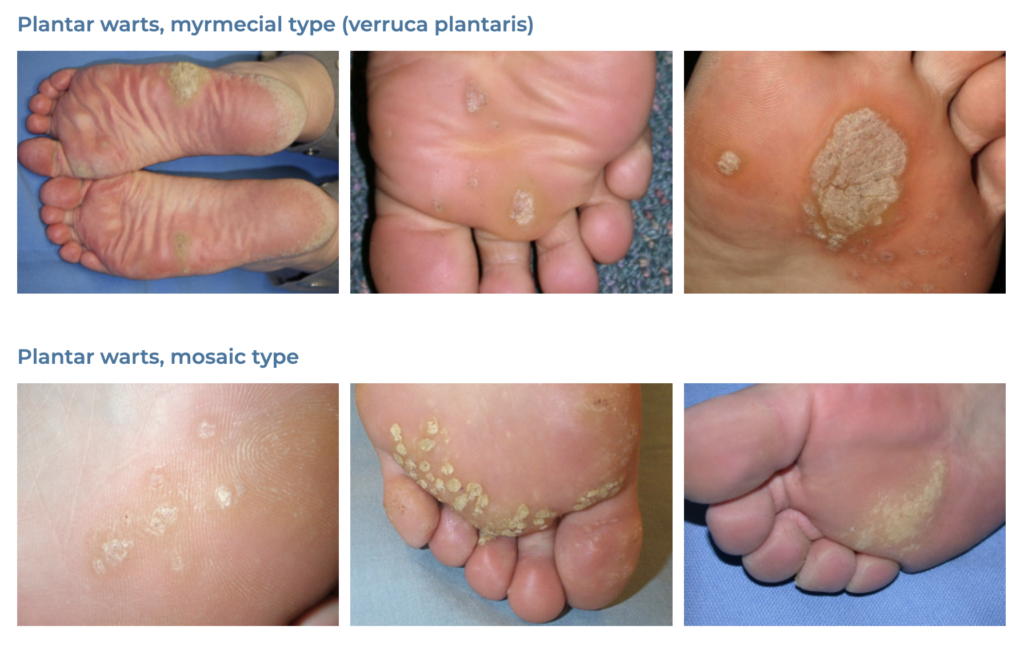
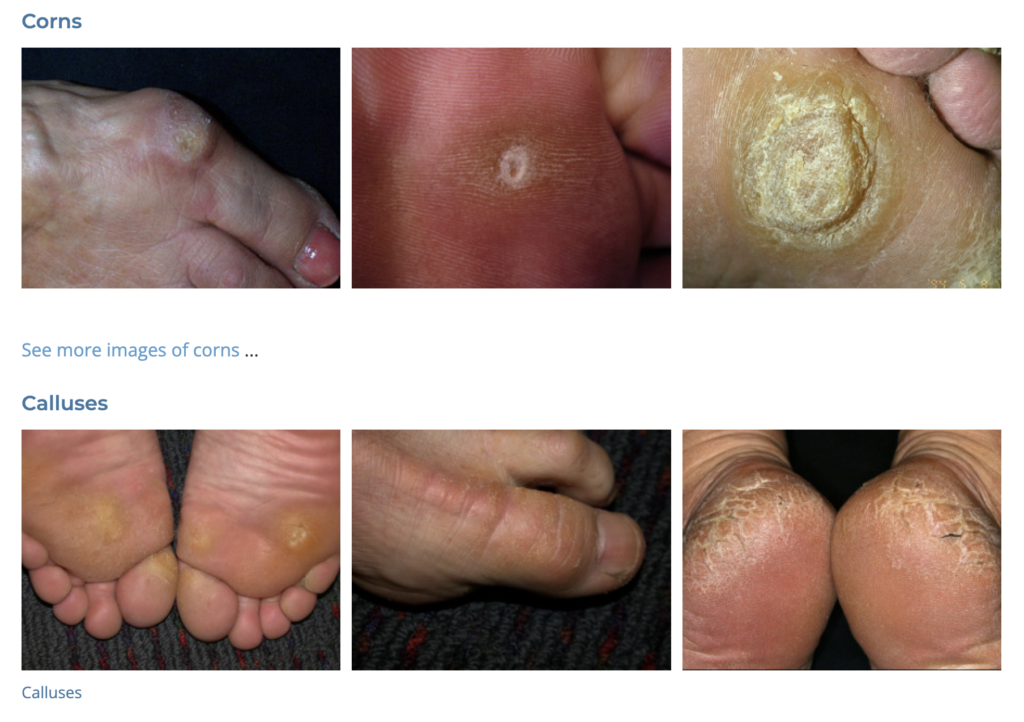
20. Corns and Calluses
- Description: Thickened skin areas formed due to repeated pressure or friction.
- Associations: Ill-fitting shoes, repetitive actions.
- Management: Protective pads, changing footwear, paring down thickened skin, orthotics.
- Dermnet: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/corn-callus