Question 1
Lucy Schumann aged 28 years presents to your clinic in a remote town in significant distress. She has been extremely agitated and has not slept well for weeks. She feels exhausted and finds concentrating on work difficult. She hears voices every day that tell her negative things about a termination of pregnancy she had several years ago. She has no suicidal thoughts or plans. She used cocaine and methamphetamines recreationally three months ago but has not used any recently. On examination, her speech is rapid, and she appears highly anxious. She does not appear to be in immediate danger, and you determine she can be managed as an outpatient safely. You also arrange an outpatient psychiatry appointment, but it is not for another three days.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Agomelatine 25 mg orally nocte
B. Amitriptyline 25 mg orally nocte
C. Diazepam 10 mg orally nocte and 4 hourly as needed
D. Melatonin controlled release 2 mg orally nocte
E. Mirtazapine 15 mg orally nocte
F. Olanzapine 5 mg orally nocte
G. Referral to a psychologist for cognitive behavioural therapy
H. Referral to a psychologist for dialectical behavioural therapy
I. Sertraline 25 mg orally mane
J. Venlafaxine 37.5 mg orally mane
Correct Answer: C. Diazepam 10 mg orally nocte and 4 hourly as needed
Question 2
Emily Black aged 18 years is concerned about her eating behaviours. For the last three years, she has bought large amounts of ‘junk food’ which she eats alone in her room. She is not able to stop eating until she has finished all of the food and then goes to the bathroom and forces herself to vomit. This now occurs five days a week. Emily eats two standard meals a day with her family and goes to the gym twice a week. She does not use laxatives and has regular periods. She has just finished year 12 and has been under a lot of stress this year. On examination, her heart rate is 72/min regular, blood pressure 110/60 mmHg (sitting) and 118/64 mmHg (standing), weight 68 kg, and body mass index 22.3 kg/m². Electrocardiogram shows no abnormalities. You arrange appropriate blood tests.
What electrolyte abnormality would be MOST likely to be associated with Emily’s presentation?
A. Elevated creatinine
B. Hyperchloraemia
C. Hyperglycaemia
D. Hypermagnesaemia
E. Hypokalemia
F. Hypophosphataemia
G. Hypouricaemia
H. Metabolic acidosis
Correct Answer: E. Hypokalemia
Question 3
Yasmin Stevens aged 31 years is an Aboriginal woman who lives in a remote Aboriginal community. Your nurse has performed a urine pregnancy test as Yasmin suspected she may be pregnant after missing her period last month. The pregnancy test is positive. Yasmin has had significant nausea with vomiting over the last week. She is not eating much food but is tolerating regular sips of water. This is her second pregnancy and she has a healthy 2-year-old who weighed 5.1 kg at birth. On examination, her body mass index is 35 kg/m² and she is clinically euvolaemic. You arrange standard antenatal screening tests.
Which additional antenatal test is MOST appropriate to include at this stage?
A. HbA1c
B. High vaginal swab for trichomoniasis testing
C. Thyroid autoantibodies
D. Urinary dipstick for ketones
E. Vitamin B12
Correct Answer: A. HbA1c
Question 4
Paul Smith aged 55 years asks whether he should be changed to a new antihypertensive medication which he had read about on the internet. He shows you the results of a meta-analysis which pools the results of four randomized controlled trials comparing a new medication, Newpril, with his current medication, Oldpril. The pooled results of the main outcome measured mean systolic blood pressure at three months are summarized in a forest plot (see image). There was no difference in side effects or safety profile between the two drugs.
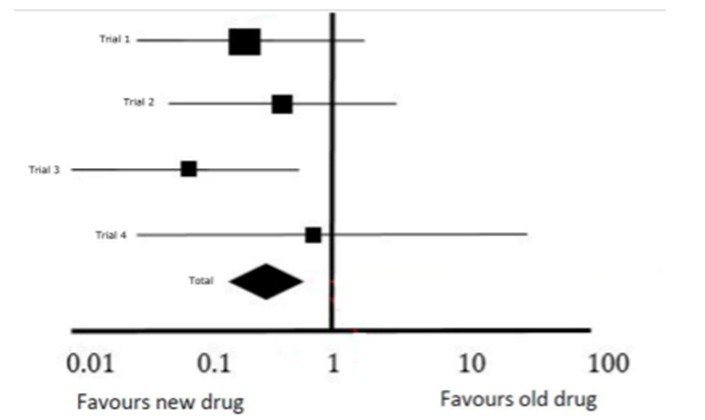
What is the MOST appropriate advice to give Paul based on the results of the meta-analysis?
A. The evidence is not strong enough to allow a recommendation
B. He should change to Newpril
C. He should stay on Oldpril
D. A larger study is needed before a recommendation can be made
E. There is no difference between Newpril and Oldpril
Correct Answer: B. He should change to Newpril
Question 5
Samuel Newton aged 32 years has had 12 hours of sweats, headache, muscle pain, and cough. Samuel has Down syndrome and lives with his mother Sarah. Sarah has had similar symptoms for two days, and today Sarah’s swab results have come back as positive for influenza A and negative for COVID-19. On examination, Samuel’s tympanic temperature is 38.3°C, heart rate 96/min regular, blood pressure 115/70 mmHg, respiratory rate 16/min, and oxygen saturation 97% on room air. Chest examination is normal. You collect swabs from him for influenza A and COVID-19 and recommend appropriate self-isolation.
What is the MOST appropriate next step for Samuel?
A. Amoxicillin 500 mg orally three times daily for seven days
B. Chest X-ray
C. Dexamethasone 6 mg orally daily for 10 days
D. Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for 10 days
E. Full blood examination
F. Influenza vaccination
G. Oseltamivir 75 mg orally twice daily for five days
H. Refer to emergency department for consideration of hospital admission
I. Sputum microscopy and culture
J. Symptomatic treatment only with paracetamol and oral fluids until swab results are available
Correct Answer: G. Oseltamivir 75 mg orally twice daily for five days
Question 6
Benny Smith aged 65 years has pain in his left shoulder and neck. He had been chopping wood in his backyard when the pain started. He describes the pain as constant and severe. He has a history of hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, and moderate renal impairment. His current medications are irbesartan 300 mg orally daily and atorvastatin 40 mg orally daily. On examination, he is sweaty and distressed. His temperature is 36.7°C, heart rate 98/min regular, blood pressure 85/62 mmHg, and oxygen saturation 96% on room air. An electrocardiogram is performed (see image). You ask for an ambulance to be called and administer aspirin 300 mg orally stat.
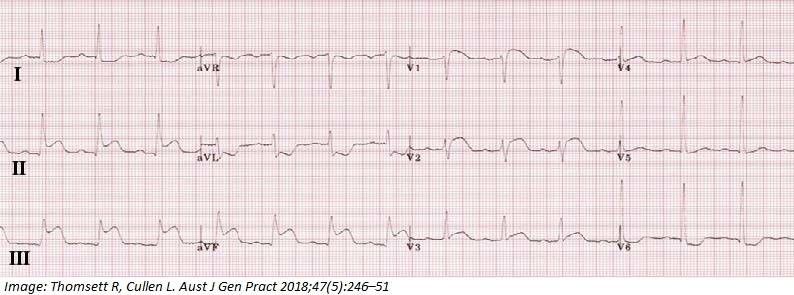
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Fentanyl 50 mcg intramuscularly
B. Glyceryl trinitrate spray 400 mcg sublingually
C. Morphine 2.5 mg intravenously
D. Start supplemental oxygen
E. Take blood for troponin
Correct Answer: C. Morphine 2.5 mg intravenously
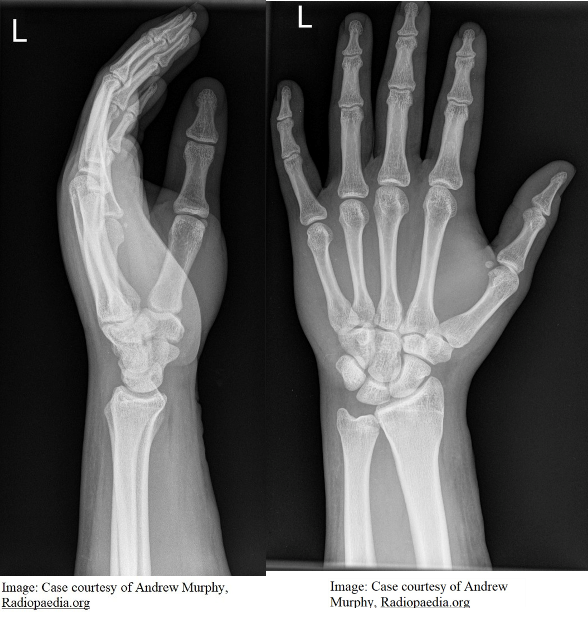
Question 7
Harry Hunter aged 5 years is brought in by his mother following a fall off his bicycle the day before. Since the accident, he has had a sore left shoulder and has been unable to lift his left arm above shoulder height. His mother has administered paracetamol 15 mg/kg orally earlier today. On examination, he is tender in the left mid-clavicular region and demonstrates limited range of movement of his left shoulder due to pain. X-rays are performed (see images).
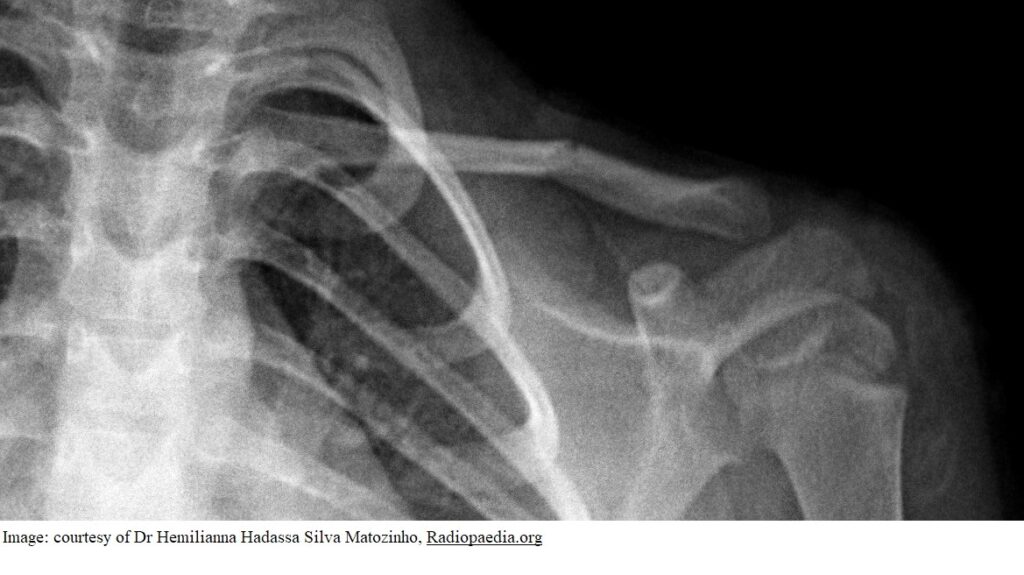
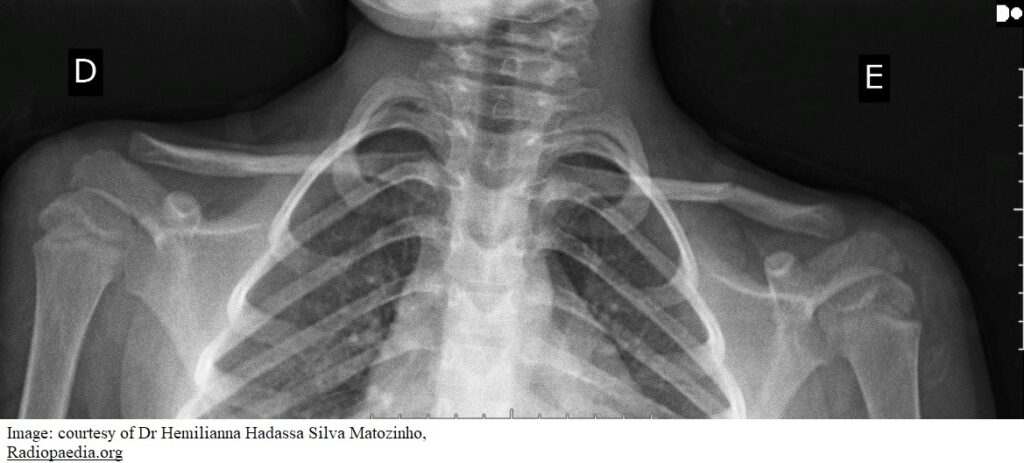
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Broad arm sling to support left arm for two to three weeks
B. Codeine 1 mg/kg/dose (max 30 mg) orally every four hours as needed
C. Computed tomography scan left clavicle
D. Recommend regular shoulder range of motion exercises
E. Refer to orthopaedic surgeon for open reduction and internal fixation
Correct Answer: A. Broad arm sling to support left arm for two to three weeks
Question 8
Barbara Davis aged 65 years has been increasingly short of breath and ‘wheezy’ during the past six months when she goes for her daily walk. She had moderately severe childhood asthma and still uses salbutamol 100 mcg two puffs as required. She smoked 20 cigarettes per day for 20 years before quitting 15 years ago.
Spirometry results are as follows:
| Test | Predicted Value | Actual (Pre-Bronchodilator) | % Predicted (Pre-Bronchodilator) | Actual (Post-Bronchodilator) | % Change (Post-Bronchodilator) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forced expiratory volume in 1 sec (FEV1) (L) | 3.29 | 2.18 | 64 | 2.83 | 30 |
| Forced vital capacity (FVC) (L) | 4.22 | 3.19 | 78 | 3.99 | 25 |
| FEV1/FVC (%) | 80 | 68 | 85 | 70 | 4 |
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Add ciclesonide 80 mcg inhaled daily
B. Add indacaterol 150 mcg inhaled daily
C. Add tiotropium 18 mcg inhaled daily
D. Change salbutamol to ipratropium 21 mcg two inhalations as required
E. Prednisolone 50 mg orally daily for five days
Correct Answer: A. Add ciclesonide 80 mcg inhaled daily
Question 9
Alice Harper aged 74 years would like to know if she requires a cervical screening test after reading an article about the new program. She had regular Pap smears under the previous National Screening Program and never had an abnormal smear. Her last Pap smear was five years ago and was normal. She was advised at that time that no further Pap smears were required. Alice is asymptomatic. Her husband passed away last year, and she has not been sexually active since.
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Advise no further cervical screening is required
B. Perform co-test
C. Perform cervical screening test
D. Prescribe vaginal oestrogen for two weeks then review for cervical screening test
E. Recommend self-collected human papillomavirus test in 12 months
Correct Answer: A. Advise no further cervical screening is required
Question 10
Rafaela Garcia aged 2 years is brought in by her mother Maria for review. You last saw Rafaela five weeks earlier and you diagnosed her with acute croup. She was prescribed a single dose of prednisolone 1 mg/kg orally. Maria reports she initially improved following this treatment; however, she has an ongoing ‘phlegmy’ cough and ‘rattly breathing’ which occurs throughout the day and keeps her awake at night. She has had no fevers and is eating and drinking normally. On examination, she is alert and interactive; her tympanic temperature is 36.7°C, heart rate is 110/min, and respiratory rate is 25/min. Ear, nose, and throat examination is unremarkable. A wet cough is observed; however, her chest is clear on auscultation. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Amoxicillin 15 mg/kg (max 500 mg orally) three times daily for five days
B. Amoxicillin–clavulanate 22.5 mg/3.2 mg/kg (max 875 mg/125 mg) orally twice daily for 14 days
C. Fluticasone inhaler 50 mcg twice daily via spacer and mask
D. Inhalation of humidified air or steam twice daily
E. Prednisolone 1 mg/kg (max 50 mg) orally daily for five days
F. Reassure Maria the cough will settle with time
G. Salbutamol inhaler 100 mcg 2–4 puffs as required via spacer and mask
H. Saline intranasal spray twice daily until symptoms resolve
Correct Answer: B. Amoxicillin–clavulanate 22.5 mg/3.2 mg/kg (max 875 mg/125 mg) orally twice daily for 14 days
Question 11
Christopher Walsh aged 28 years has come to see you at the insistence of his new partner Kate seeking assistance for his extreme shyness. Christopher recalls being very shy since childhood. He found adolescence very difficult due to poor self-esteem and fear of being ridiculed by his peers. He does not go to social gatherings because he feels that he is ‘hopeless’ in social situations and worries that people will not like him. He now works largely in isolation as a software developer. He dislikes face-to-face meetings as he is fearful of his work being criticised. He met Kate online, and she states he always has a ‘wall up’ and has difficulty talking about his feelings with her. Christopher feels he is sabotaging their relationship and is worried about how he would cope with the embarrassment if she broke up with him.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Agoraphobia
B. Avoidant personality disorder
C. Borderline personality disorder
D. Dependent personality disorder
E. Dysthymia
F. Histrionic personality disorder
G. Major depressive disorder
H. Narcissistic personality disorder
I. Paranoid personality disorder
J. Schizoaffective disorder
Correct Answer: B. Avoidant personality disorder
Question 12
David Buchanan aged 45 years is frustrated by frequent episodes of abdominal bloating and diarrhoea. The episodes have been occurring for many years. Six months earlier, he underwent investigations including blood tests, stool tests, colonoscopy, and endoscopy. The results of these investigations were normal. He has previously tried several over-the-counter and prescribed medications, but nothing has been helpful in alleviating his symptoms. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 36.5°C, and blood pressure is 125/88 mmHg. Abdominal examination reveals mild generalised tenderness on palpation.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Faecal transplantation
B. Hypnotherapy
C. Lactose-free diet
D. Loperamide 2 mg orally after each bowel motion
E. Low FODMAP diet
F. Maxolon 10 mg orally three times daily as required
G. Metronidazole 400 mg orally three times daily for five days
H. Milk of magnesia 10 mL orally after each bowel motion
I. Omeprazole 20 mg orally daily
J. Referral to gastroenterologist
Correct Answer: E. Low FODMAP diet
Question 13
Hugh Forester aged 60 years is having difficulty sleeping. He works in the local coalmine and feels he is not adjusting to the constant change from night shift to day shift like he did when he was younger. It takes him a few hours to fall asleep, but then he is able to sleep through the night. He is frustrated by being sleepy during the day, which is problematic for his employment as his supervisor has commented on his grumpy behaviour. He has excellent sleep hygiene. Your colleague referred him for cognitive behavioural therapy sessions to address his sleep issue, but after three sessions, he has not noticed any improvement.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Continued cognitive behavioural therapy sessions
B. Melatonin 2 mg orally before bed
C. Mirtazapine 15 mg orally before bed
D. Promethazine 25 mg orally before bed
E. Suvorexant 20 mg orally before bed
Correct Answer: B. Melatonin 2 mg orally before bed
Question 14
Rayna Hart aged 6 years is brought in by her mother Kylie with three weeks of intermittent abdominal pain. The pain is there most days but does not limit her activities. The pain does not change with position. Rayna is well and has met all of her developmental milestones. She recently received a new tablet device for her birthday and will often spend hours playing educational games. Kylie is uncertain about Rayna’s toileting as Rayna closes the door and does not let her in. On examination, Rayna is tracking on the 60th centile for height and weight. She has mild tenderness in the left lower quadrant of her abdomen with no guarding.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Coeliac serology
B. Faeces microscopy culture and sensitivities
C. Macrogol 3350 one sachet orally daily
D. Ultrasound abdomen
E. X-ray abdomen
Correct Answer: C. Macrogol 3350 one sachet orally daily
Question 15
Michael Matthews aged 60 years has experienced two episodes of palpitations in the past month. The episodes have lasted for up to 30 minutes, and there is no clear trigger. However, he has been very stressed at work recently, has not been sleeping well, and has been drinking large amounts of alcohol. Recent blood tests, including full blood examination, renal and liver function, and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels, were within normal limits. An electrocardiogram is performed while he is experiencing the palpitations (see image).
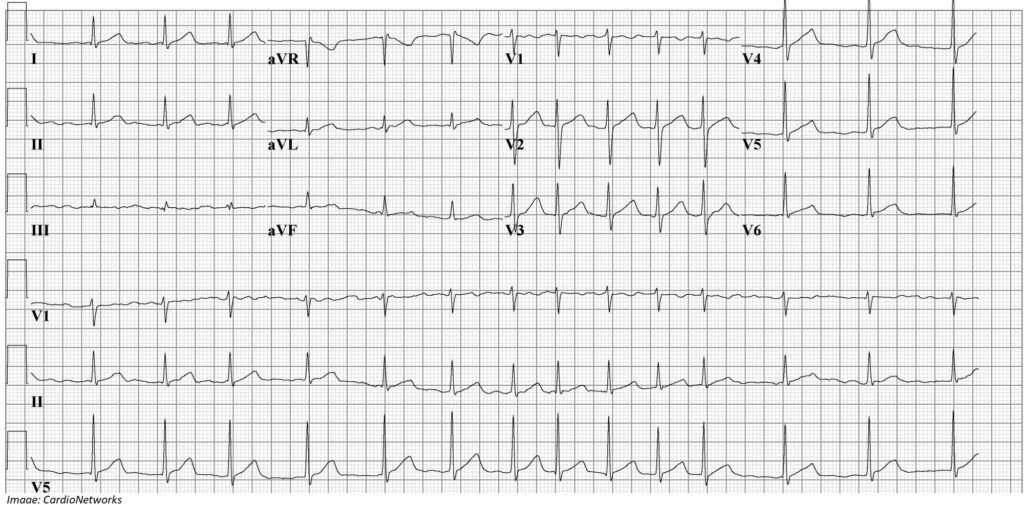
You discuss the importance of adequate sleep and reducing alcohol intake.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise that anticoagulation is not required at this stage
B. Aspirin 100 mg orally daily
C. Clopidogrel 75 mg orally daily
D. Rivaroxaban 20 mg orally daily
E. Warfarin orally daily with dose adjusted according to international normalised ratio
Correct Answer: A. Advise that anticoagulation is not required at this stage
Question 16
Anne Ober aged 45 years comes to see you to discuss medications to assist with weight loss. Over the past six months, she has been exercising for 30 minutes daily and has reduced her caloric intake with the assistance of a dietician; however, she is very despondent because of her inability to lose weight. She takes olmesartan 20 mg orally daily and felodipine 5 mg orally daily for hypertension. She sees a psychologist for management of major depressive disorder. On examination, her blood pressure is 150/96 mmHg, and her body mass index is 30 kg/m². Recent blood tests, including full blood examination, urea and electrolytes, liver function tests, thyroid-stimulating hormone, and lipid profile, were within normal ranges.
What is the MOST appropriate pharmacological management?
A. Liraglutide 0.6 mg subcutaneously daily
B. Metformin extended release 500 mg orally daily
C. Naltrexone–bupropion 8 mg/90 mg orally daily
D. Phentermine 30 mg orally daily
E. Topiramate 12.5 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: A. Liraglutide 0.6 mg subcutaneously daily
Question 17
Rebecca Wagner aged 52 years has had dizziness and vomiting for the past four hours. She feels unsteady on her feet and has had difficulty walking. For the past three days, her right ear has felt blocked and her nose has been runny. She describes a sensation that the room is spinning. On examination, her temperature is 36.8°C, blood pressure is 130/70 mmHg, and heart rate is 85/min. Her neurological examination shows a unidirectional mixed horizontal and torsional nystagmus, and the result of her head impulse test is positive. Rinne test shows air conduction is greater than bone conduction bilaterally, and Weber test localises to both ears equally.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Acoustic neuroma
B. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
C. Eustachian tube dysfunction
D. Intracerebral tumour
E. Meniere’s disease
F. Perilymphatic fistula
G. Ramsay Hunt syndrome
H. Transient ischaemic attack
I. Vestibular neuronitis
Correct Answer: I. Vestibular neuronitis
Question 18
Tenae Thomas aged 21 years has had right lateral knee pain for the past month. She plays rugby league for her local club but does not recall a specific injury. The pain is aggravated the longer she spends on the field but eventually settles with rest. Strapping the knee has not helped, and she has recently had to stop her training due to the pain. On examination, there is no swelling, but there is focal tenderness over the right lateral condyle. Her pain is reproduced when pressure is placed over the lateral condyle and the knee is moved through 30 degrees of flexion.
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Advise to refrain from playing rugby league for three months
B. Magnetic resonance imaging right knee
C. Referral to orthopaedic surgeon for arthroscopy
D. Steroid injection to the lateral femoral condyle
E. Stretching and active rehabilitation program
Correct Answer: E. Stretching and active rehabilitation program
Question 19
Adam Peters aged 26 years has painful lesions in his groin. He has sex with men and has multiple sexual partners. He first noticed a small painless lump on his penis three weeks earlier, which resolved spontaneously after a few days. One week ago, he felt painful lumps in his left groin, and in the past two days, some of the lumps have ruptured to form ulcers. On examination, his left inguinal lymph nodes are enlarged and tender. There is a 2 cm fluctuant mass in the left inguinal region with surrounding ulcers. He agrees to testing for sexually transmissible infections and you arrange blood tests, urine collection, and swabs of the ulcers.
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Aciclovir 400 mg orally three times daily for 10 days
B. Azithromycin 1 g orally as a single dose
C. Benzylpenicillin 2.4 million units intramuscularly
D. Ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly
E. Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for 21 days
Correct Answer: E. Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for 21 days
Question 20
Vova Lima aged 7 years presents with his mother Wendy because Vova still needs to wear nappies at night. Vova is upset because his younger sister aged 4 years is now dry overnight, and he has become embarrassed about still needing nappies. Vova was successfully trained to use a toilet during the day when he was 3 years old. He has a dry overnight nappy approximately once per week. He has regular soft bowel motions each day. An appropriate physical examination and evaluation of his developmental milestones are normal. Urine dipstick results are normal.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Cease use of overnight nappies and encourage Vova to change his own wet bedding
B. Macrogol 3350 one sachet orally daily
C. Micturating cystourethrogram
D. Prescribe desmopressin 120 mcg intranasally at bedtime
E. Recommend fluid restriction in the evening
F. Recommend use of a bedwetting (pad and bell) alarm
G. Refer to a psychologist for cognitive behavioural therapy
H. Ultrasound kidneys ureters and bladder
Correct Answer: F. Recommend use of a bedwetting (pad and bell) alarm
Question 21
Martina Woods aged 19 years has had heavy vaginal discharge since yesterday. She has been living in Bali and returned to Australia yesterday. Four days earlier, she had unprotected sex with a local man in Bali. She has an etonogestrel 68 mg implant in situ. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 36.1°C, and heart rate is 72/min. Her abdomen is soft and nontender. Bimanual pelvic examination reveals no cervical excitation. Speculum examination shows inflammation of the cervix and a profuse cream-coloured discharge. You perform vaginal swabs for microscopy culture and nucleic acid amplification testing. Results confirm your provisional diagnosis.
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Amoxicillin–clavulanate 875 mg/125 mg orally twice daily for 14 days
B. Ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly and azithromycin 1 g orally stat
C. Clindamycin 2% cream intravaginally one applicatorful at night for seven days
D. Metronidazole 400 mg orally twice daily for five days
E. Ultrasound pelvis
Correct Answer: B. Ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly and azithromycin 1 g orally stat
Question 22
Mitchell Stevenson aged 21 years presents on a Friday afternoon requesting a medical certificate for university. He states he has been unable to attend compulsory classes since Tuesday as he has been unwell. He asks you to date the certificate from Tuesday as he does not want to be penalised for his absence. An appropriate history and physical examination is performed, and you are satisfied he has not been able to attend university since Tuesday.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Certify that Mitchell is unable to attend university today and date the certificate today
B. Contact Mitchell’s university lecturer directly to discuss his illness
C. Document that Mitchell has been unable to attend university since Tuesday and date the certificate with Tuesday’s date
D. Record Mitchell’s diagnosis on the medical certificate to justify that he has been unable to attend since Tuesday and date the certificate today
E. State that Mitchell has been unable to attend university from Tuesday but date the certificate today
Correct Answer: E. State that Mitchell has been unable to attend university from Tuesday but date the certificate today
Question 23
Slavka Petrovic aged 68 years has been experiencing shortness of breath when walking on flat ground or when carrying out activities of daily living such as hanging out the washing for the past few months. She was previously prescribed salbutamol 100 mcg 4–6 inhalations as required but has been needing it more in the past six weeks. She is a smoker and has a 20 pack-year smoking history. You discuss smoking cessation and appropriate lifestyle changes.
Her spirometry results are shown below:
| Test | Predicted Value | Actual (Pre-Bronchodilator) | % Predicted (Pre-Bronchodilator) | Actual (Post-Bronchodilator) | % Change (Post-Bronchodilator) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forced expiratory volume in 1 sec (FEV1) (L) | 2.32 | 1.28 | 55 | 1.36 | 6 |
| Forced vital capacity (FVC) (L) | 2.96 | 2.1 | 71 | 2.18 | 4 |
| FEV1/FVC (%) | 76 | 60 | 77 | 61 | 2 |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Add fluticasone furoate–umeclidinium–vilanterol 100 mcg/62.5 mcg/25 mcg one inhalation daily
B. Add fluticasone propionate–salmeterol 125 mcg/25 mcg two inhalations twice daily
C. Add tiotropium 18 mcg inhaled daily
D. Change salbutamol to ipratropium 21 mcg two inhalations every four hours as required
E. Computed tomography scan chest
Correct Answer: C. Add tiotropium 18 mcg inhaled daily
Question 24
Maria Santos aged 32 years has been coughing up blood-stained mucus for the past two months. She has also been experiencing excessive sweating at night and has unintentionally lost 6 kg over the past three months. She has never smoked. She immigrated from the Philippines six months ago. Her physical examination today is normal. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
What is the MOST appropriate investigation to confirm your provisional diagnosis?
A. Bronchoscopy
B. Chest X-ray
C. Computed tomography pulmonary angiogram
D. High-resolution computed tomography scan chest
E. Interferon-gamma release assay
F. Lung function testing
G. Spirometry
H. Sputum for acid-fast bacilli stain and culture
I. Tuberculin skin test
Correct Answer: H. Sputum for acid-fast bacilli stain and culture
Question 25
Damien Dixon aged 75 years is requesting a referral to a new gastroenterologist as he is due for his colonoscopy. Damien is a new patient to your practice and has just moved from interstate. He has been having a colonoscopy every five years since he turned 50 years old as his father was diagnosed with colon cancer at 54 years of age. A review of his previous colonoscopy reports shows he has had a total of four polyps removed. The polyps were all hyperplastic with no evidence of dysplasia. No polyps were found in his last two colonoscopies. He has type 2 diabetes, atrial fibrillation, and moderate chronic kidney disease. His medications include metformin 1000 mg orally daily, ramipril 5 mg orally daily, and rivaroxaban 20 mg orally daily.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise that he does not need any further bowel cancer screening
B. Commence aspirin 100 mg orally daily
C. Recommend a faecal occult blood test every two years instead of colonoscopy
D. Refer him for colonoscopy
E. Refer him for flexible sigmoidoscopy
Correct Answer: A. Advise that he does not need any further bowel cancer screening
Question 26
Jimmy McKenzie aged 5 weeks is brought in by his mother Brittany due to feeding concerns. He is exclusively breastfed. Brittany reports that Jimmy has had frequent vomiting after feeds from two weeks of age, which has become more frequent and forceful. She has noticed some flecks of blood in Jimmy’s vomit this morning, and he has been lethargic today. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 36.8°C, heart rate is 150/min (normal range: 120–185), respiratory rate is 40/min (normal range: 25–60), and capillary refill time is 3 seconds with mottled skin. A mass is palpable in his right upper quadrant.
What is the MOST likely finding on initial investigation?
A. Elevated bile acids
B. Elevated galactose-1 phosphate
C. Hyperchloraemia
D. Hyperglycaemia
E. Hyperphosphataemia
F. Hypokalaemia
G. Hypothyroidism
H. Phenylketonuria
Correct Answer: F. Hypokalaemia
Question 27
Karen Jameson aged 67 years is concerned about a rash on her shins that has been present for the past six months. Karen is new to your practice and states she has not had a general check-up in several years. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 36.7°C, heart rate is 75/min, and blood pressure is 130/95 mmHg. Her body mass index is 31 kg/m². You perform a skin biopsy, and the results show necrobiosis lipoidica.
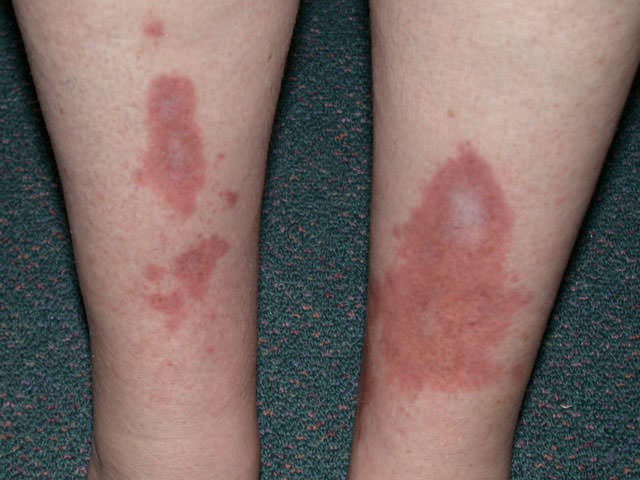
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise gentle sunshine exposure to affected areas
B. Arterial duplex ultrasonography lower limbs
C. Calcipotriol–betamethasone dipropionate 50 mcg/500 mcg/g ointment topically daily until skin is clear
D. Dicloxacillin 500 mg orally four times daily for five days
E. Glycated haemoglobin testing
F. LPC–salicylic acid 6%/3% in a cream base topically twice daily for one month
G. Recommend graduated compression stockings
H. Serum vitamin B12 levels
I. Terbinafine 1% cream topically twice daily for 14 days
J. Transglutaminase and deamidated gliadin peptide antibody tests
Correct Answer: E. Glycated haemoglobin testing
Question 28
Michelle Stevenson aged 58 years has been advised by her dentist that she requires a dental extraction prior to upcoming dental implant surgery. She has come to discuss with you whether she requires antibiotics for the procedures as she has a heart murmur. Review of her records shows she has a moderate mitral valve prolapse which is under regular surveillance with a cardiologist.
What is the MOST appropriate advice regarding antibiotic use?
A. Amoxicillin 2 g orally 60 minutes before the procedure
B. Amoxicillin 500 mg orally three times daily for five days following the procedure
C. Antibiotic prophylaxis is not recommended
D. Cefalexin 2 g orally 60 minutes before the procedure
E. Clindamycin 600 mg orally 120 minutes before the procedure
Correct Answer: C. Antibiotic prophylaxis is not recommended
Question 29
Jill Rockling aged 56 years is embarrassed by her fingernails. She works as a swimming instructor and has noticed that her nails have become discoloured and brittle over the past 12 months. She has a history of Crohn’s disease and is prescribed infliximab by her gastroenterologist. On examination, you note all nails have a similar appearance (see image).
You arrange nail clippings, and the results are as follows:
Mycological examination:
- Specimen: Nail
- Site: Nail
- Microscopy: Fungal elements seen on direct microscopy.
- Culture: Candida species +
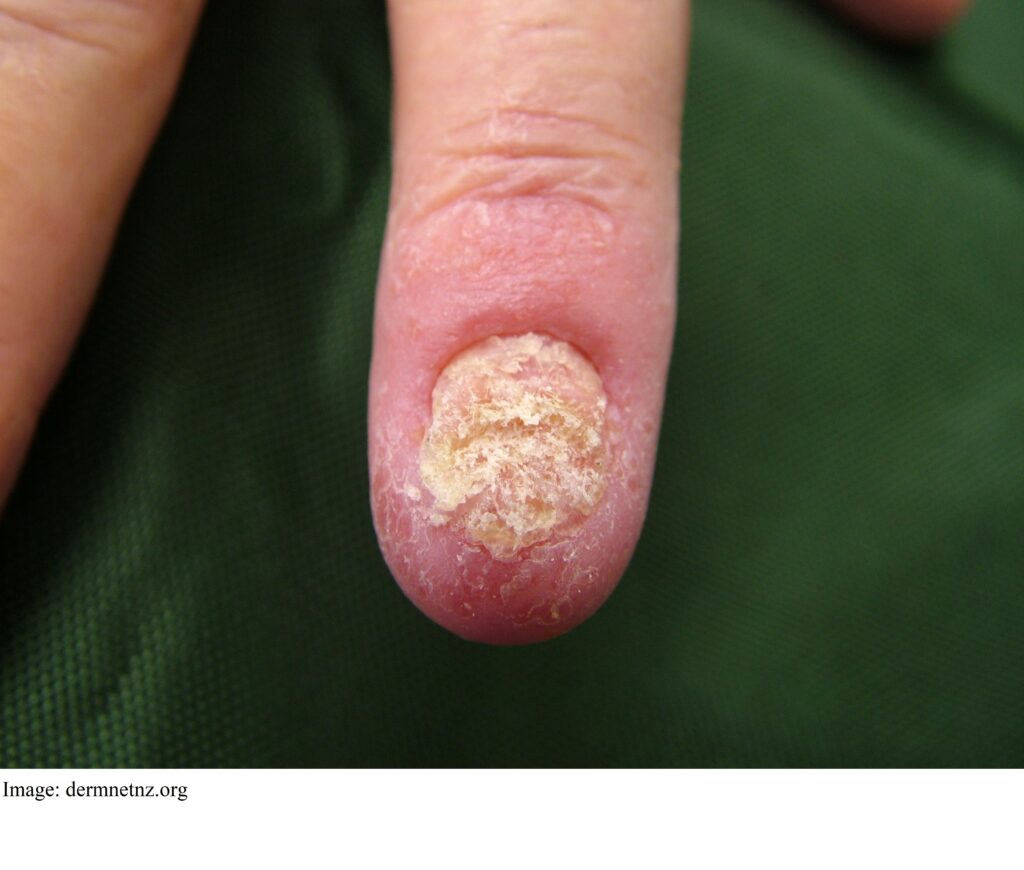
What is the MOST appropriate treatment?
A. Amorolfine 5% nail lacquer topically twice per week for 3–6 months
B. Diode laser therapy over three sessions
C. Fluconazole 150 mg orally weekly for 12–24 weeks
D. Griseofulvin 500 mg orally daily for 12–20 weeks
E. Iontophoresis
Correct Answer: C. Fluconazole 150 mg orally weekly for 12–24 weeks
Question 30
Annabel Han aged 31 years presents to your rural emergency department. She is 30 weeks pregnant and has had four hours of painless vaginal spotting. Due to her nomadic lifestyle, she is yet to receive any antenatal care. She does not know her blood type. She denies recent trauma or sexual intercourse. She reports normal fetal movements. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 37.1°C, heart rate is 84/min, and blood pressure is 105/70 mmHg. Her abdomen is soft and non-tender. Speculum examination is unremarkable. Fetal heart rate is 140/min.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Administer anti-D immunoglobulin
B. Perform bimanual pelvic examination
C. Reassurance and continuation of normal antenatal care
D. Urgent cardiotocography
E. Urgent obstetric ultrasound
Correct Answer: E. Urgent obstetric ultrasound
Question 31
Jackie Sanchez aged 42 years presents for the results of a blood test you performed two days earlier. She had presented with a three-week history of a dry mouth and increased thirst resulting in her drinking up to 5L of water per day. She has been frequently going to the toilet during the day and 3–4 times overnight. Her current medications include telmisartan 40 mg orally daily, hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg orally daily, lithium 250 mg orally twice per day, and sertraline 100 mg orally daily. On examination, her heart rate is 74/min, blood pressure is 142/84 mmHg, and body mass index is 32 kg/m². Examination is otherwise unremarkable.
Her blood test results are as follows:
| Test | Result | Normal range |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium | 148* mmol/L | 135 – 145 |
| Potassium | 3.8 mmol/L | 3.5 – 5.2 |
| Chloride | 106 mmol/L | 95 – 110 |
| Bicarbonate | 28 mmol/L | 22 – 32 |
| Anion gap | 18* mmol/L | 7 – 17 |
| Glucose | 5.5 mmol/L | 3.2 – 5.5 |
| Urea | 5.4 mmol/L | 2.7 – 8.0 |
| Creatinine | 99* umol/L | 45 – 90 |
| Estimated glomerular filtration rate | 51* mL/min/1.73m² | > 90 |
| Urate | 0.40 mmol/L | 0.15 – 0.45 |
| Corrected calcium | 2.49 mmol/L | 2.10 – 2.60 |
| Ionised calcium | 1.23 mmol/L | 1.10 – 1.30 |
| Phosphate | 0.83 mmol/L | 0.75 – 1.50 |
| Plasma osmolality | 321* mmol/kg | 275 – 295 |
| Urine osmolality | 22* mmol/kg | 50 – 1200 |
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Minimal change disease
B. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
C. Psychogenic polydipsia
D. Sjogren’s syndrome
E. Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion
F. Systemic lupus erythematosus
G. Type 2 diabetes
H. Urinary tract infection
Correct Answer: B. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
Question 32
James Glasson aged 52 years wishes to discuss prostate cancer screening. His brother-in-law was recently diagnosed with prostate cancer at 58 years of age. James is asymptomatic. After obtaining informed consent, he proceeds to prostate-specific antigen testing, and his results are as follows:
| Test | Result | Normal range (age-dependent) |
|---|---|---|
| Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) | 3.4 ug/L | < 50 years: < 2.5, < 60 years: < 3.5, < 70 years: < 4.5, > 70 years: < 6.5 |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise James that no further screening is required
B. Arrange prostate-specific antigen test at age 70 years
C. Perform digital rectal examination
D. Recommend prostate-specific antigen testing every two years
E. Repeat prostate-specific antigen test and free-to-total prostate-specific antigen percentage in three months
Correct Answer: E. Repeat prostate-specific antigen test and free-to-total prostate-specific antigen percentage in three months
Question 33
Ryan Baker, aged 45 years, comes to you for advice to relieve itching from a partial thickness burn (see image). The burn occurred 10 days earlier from direct contact with a hot cooking pot to his right forearm. It epithelialised well with dressings over seven days. The itch is keeping him awake at night, and he is concerned that scratching it will cause further damage.
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Apply warm compresses regularly
B. Hydrocortisone 1% cream topically three times daily
C. Mineral oil topically as required
D. Mupirocin 2% ointment topically three times daily
E. Water-based emollient topically regularly
Correct Answer: E. Water-based emollient topically regularly
Question 34
Tamara Devitt aged 22 years has had worsening asthma over the past 12 months since she started working as a landscape gardener. She has had increased symptoms at night and daytime symptoms now occurring with physical work. She is currently taking beclomethasone diproprionate 100 mcg via inhalation twice daily with salbutamol 100 mcg via inhalation two puffs as required. Today her forced expiratory volume in one second is 75% of the predicted value.
What is the MOST appropriate pharmacological management?
A. Change beclomethasone to beclometasone–formoterol 100 mcg/6 mcg inhaled twice daily
B. Change beclomethasone to eformoterol 12 mcg inhaled twice daily
C. Change beclomethasone to fluticasone furoate 100 mcg inhaled twice daily
D. Change beclomethasone to montelukast 10 mg orally at night
E. Increase beclomethasone to 200 mcg inhaled twice daily
Correct Answer: A. Change beclomethasone to beclometasone–formoterol 100 mcg/6 mcg inhaled twice daily
Question 35
Janine Bryce aged 72 years has had a painful right foot for the past two days (see image). She had the same problem last year but the pain settled without treatment. She is due to leave for a holiday in two days and is concerned about her ability to do the walking required on tour. She takes perindopril 8 mg orally daily and verapamil extended release 240 mg orally daily for hypertension. She has chronic renal failure, and her most recent estimated glomerular filtration rate was 29* mL/min/1.73m² (normal range: >90). On examination, her tympanic temperature is 36.8°C. The first metatarsophalangeal joint of her right foot is extremely tender to touch.
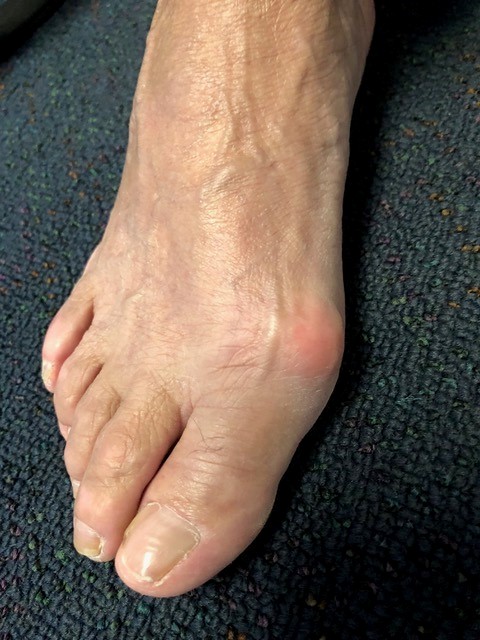
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Allopurinol 50 mg orally daily for four weeks
B. Cefalexin 500 mg orally four times daily for five days
C. Colchicine 1 mg orally stat then 500 mcg one hour later
D. Indomethacin 50 mg orally three times daily for five days
E. Triamcinolone acetonide (10 mg/mL) 1 mL via intraarticular injection
Correct Answer: E. Triamcinolone acetonide (10 mg/mL) 1 mL via intraarticular injection
Question 36
Colin Webster aged 50 years has had moderate diarrhoea for two months. Colin has type 2 diabetes which was diagnosed three years earlier. He takes metformin extended-release tablet 2000 mg orally daily and glibenclamide 5 mg orally daily. His glycated haemoglobin last month was 6.5% (target range: < 7) and screening faecal occult blood test four months ago was negative. On examination, his weight is 68 kg and body mass index is 24.5 kg/m² (no change from six months ago). Abdominal examination is normal. Rectal examination is also normal with soft yellow faeces and no blood on the examination glove.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Change glibenclamide 5 mg orally daily to sitagliptin 100 mg orally daily
B. Coeliac antibodies
C. Faecal calprotectin
D. Refer for colonoscopy
E. Withhold extended-release metformin and review in three weeks
Correct Answer: E. Withhold extended-release metformin and review in three weeks
Question 37
Serena Moore aged 15 years is extremely frustrated by her irregular periods. Her last period was six weeks ago. Her periods started at age 13 years and her cycles can be 30–45 days long. She does not have bleeding between her periods. She is not sexually active. She currently uses benzoyl peroxide–adapalene 2.5%/0.1% topically daily for mild acne. On examination, her blood pressure is 115/75 mmHg and body mass index is 28.6 kg/m². You discuss appropriate lifestyle changes.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Ethinylestradiol–levonorgestrel 30 mcg/150 mcg orally daily
B. Medroxyprogesterone acetate 10 mg orally daily for 12 days per month
C. Serum follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinising hormone, and oestradiol
D. Thyroid function test
E. Ultrasound pelvis
Correct Answer: A. Ethinylestradiol–levonorgestrel 30 mcg/150 mcg orally daily
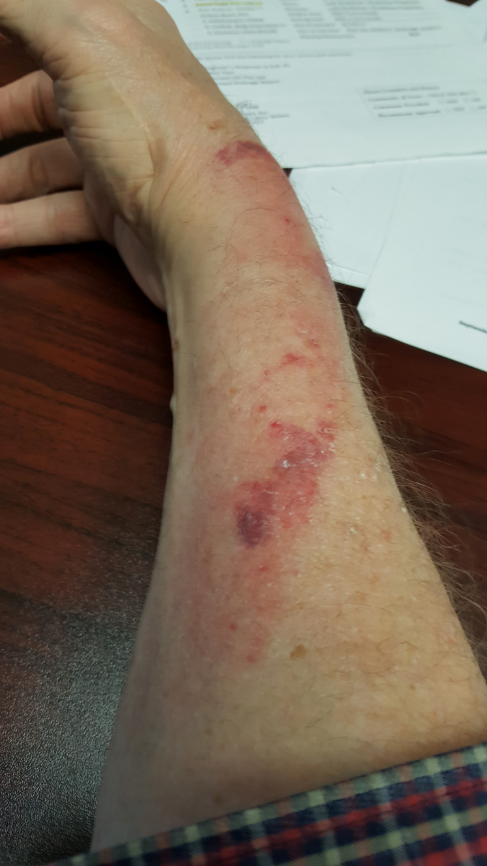
Question 38
Andy Kim aged 45 years presents to your remote health service for wound care. He lives on a property two hours away. He cut his left foot while repairing a fence two weeks earlier. He was initially managed at the local hospital. He has completed a course of antibiotics and a dressing was applied, which fell off yesterday. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 36.8°C, heart rate is 72/min, and blood pressure is 129/76 mmHg. There is a 4 cm wound on the dorsum of his foot with multiple areas of granulation tissue which bleeds with contact.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Hydrogel dressing and review in three days
B. Mupirocin 2% ointment topically three times daily for seven days
C. Silver foam dressing and review within two weeks
D. Soak wound in chlorhexidine four times daily
E. X-ray left foot
Correct Answer: C. Silver foam dressing and review within two weeks
Question 39
Bhavita Dinesh aged 36 years has been feeling unwell for the past four weeks. She reports feeling lightheaded and generally tired and weak. At times she is nauseated, and she has not felt as hungry as usual. She has found that eating salty crackers has made her feel a bit better. She thought she might be pregnant, but her home pregnancy test was negative. On examination, her heart rate is 95/min, blood pressure is 105/65 mmHg (seated) and 85/55 mmHg (standing). Her weight is 58 kg, and she reports that this is 3 kg less than her usual weight. The result of a random finger-prick blood glucose test is 4 mmol/L.
Which initial investigation is MOST appropriate to support your provisional diagnosis?
A. Acetylcholine receptor antibody titre
B. Antinuclear antibody titre
C. Fasting blood glucose level
D. Iron studies
E. Serum electrolytes
F. Thyroid-stimulating hormone
G. Tissue transglutaminase antibodies
H. Vitamin B12 level
Correct Answer: E. Serum electrolytes
Question 40
James Bradbury aged 31 years is embarrassed about his enlarging breasts. James has been overweight since puberty and has gained a further 6 kg in the past 18 months. On examination, his height is 181 cm, weight is 99 kg, body mass index is 30.2 kg/m², and waist circumference is 98.5 cm. He has moderate gynaecomastia, sparse body hair, and symmetrical firm testes (approximately 3 mL each). Relevant investigations are shown below:
| Test | Result | Normal range |
|---|---|---|
| Total cholesterol | 5.9* mmol/L | < 5.5 |
| Triglycerides | 2.9* mmol/L | < 2.0 |
| Follicle-stimulating hormone | 29* IU/L | 1 – 8 |
| Luteinising hormone | 21* IU/L | 1 – 8 |
| Serum total testosterone | 7.1* nmol/L | 9 – 29 |
| Karyotype | 47 XXY |
What is the MOST appropriate further investigation to recommend?
A. Bone densitometry
B. Computed tomography scan pituitary fossa
C. Glycated haemoglobin
D. Iron studies
E. Serum thyroxine
Correct Answer: A. Bone densitometry
Question 41
Alice Hodge aged 42 years presents with pain under her left heel. The pain started two months earlier when she took a job as a parking inspector and has gradually worsened. The pain is worse when she gets out of bed in the morning and improves over the day. On examination, her body mass index is 28.2 kg/m². Pain can be reproduced with firm palpation of the medial plantar region of her left heel.
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Controlled ankle movement walker for four weeks
B. Corticosteroid injection into affected area
C. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy
D. Program of strapping, stretching, and strengthening exercises
E. Refer to orthopaedic surgeon for surgical management
Correct Answer: D. Program of strapping, stretching, and strengthening exercises
Question 42
Colin O’Mahoney aged 63 years woke up with a painless ‘bloody’ eyeball this morning (see image). He takes candesartan 8 mg orally daily for hypertension. On examination, his blood pressure is 136/84 mmHg and heart rate is 94/min. Visual acuity is 6/12 in both eyes (uncorrected).
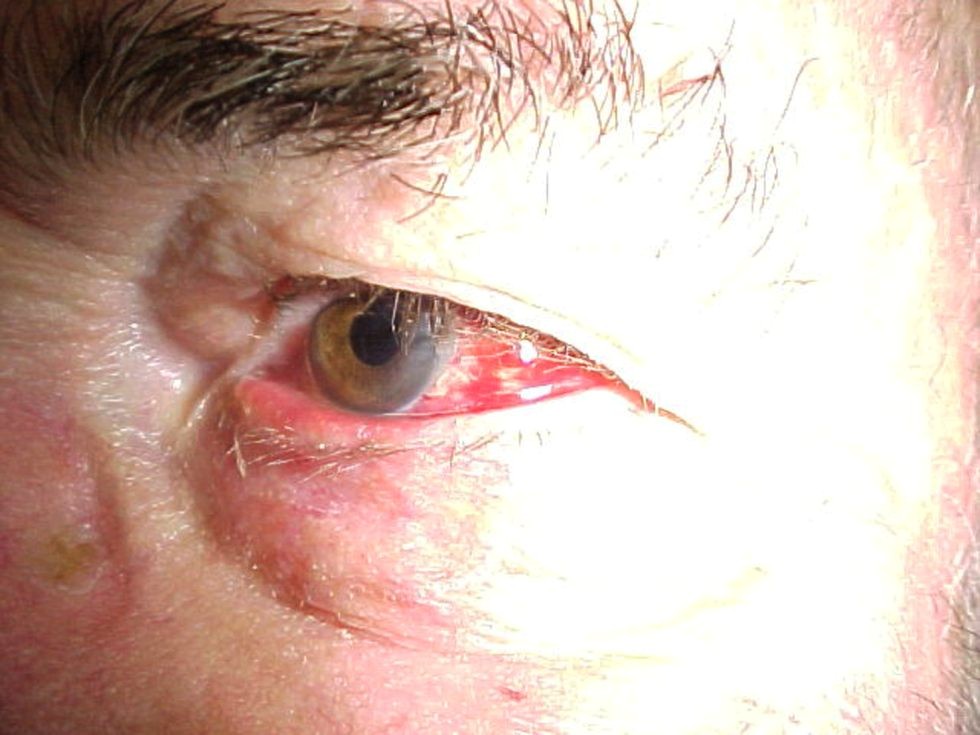
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Arrange emergency ophthalmology assessment
B. Bimatoprost–timolol 0.03% /0.5% eye drops topically daily for one week
C. Chloramphenicol 1% ointment topically twice daily for three days
D. Increase candesartan to 16 mg orally daily
E. Reassurance and review in one week
Correct Answer: E. Reassurance and review in one week
Question 43
Lucy Howie aged 33 years presents for postnatal review. Two weeks earlier she had a normal vaginal delivery at 38 weeks following induction due to gestational hypertension. Lucy is taking nifedipine extended release 30 mg orally twice daily. She is currently breastfeeding. On examination, her blood pressure is 135/86 mmHg on first measurement and 128/78 mmHg when repeated. Urinalysis is normal.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Arrange 24-hour blood pressure monitor
B. Cease nifedipine and commence perindopril 5 mg orally daily
C. Continue nifedipine 30 mg orally twice daily and review in four weeks
D. Fasting lipids
E. Reduce nifedipine to 30 mg orally daily and review in two weeks
Correct Answer: E. Reduce nifedipine to 30 mg orally daily and review in two weeks
Question 44
Molly Higgins aged 15 years has experienced two months of an intermittent dry cough since the weather has become colder. The cough occurs during the day about once per week. Twice a month she wakes at night with her cough and at those quiet times she can also hear herself making a ‘whistling’ sound. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded. You arrange spirometry with results as follows:
| Test | Predicted value | Actual (prebronchodilator) value | % Predicted (prebronchodilator) | Actual (postbronchodilator) value | % Change (postbronchodilator) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) (L) | 3.62 | 2.73 | 75 | 3.08 | 12.8 |
| Forced vital capacity (FVC) (L) | 3.97 | 3.86 | 97 | 3.94 | 2 |
| FEV1/FVC (%) | 89 | 70 | 79 | 85 | 22 |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Budesonide-formoterol 200 mcg/6 mcg inhaled as required
B. Chest X-ray
C. Esomeprazole 20 mg orally daily
D. Ipratropium 42 mcg inhaled as required
E. Montelukast 5 mg orally once daily
F. Pertussis serology
G. Promethazine 25 mg orally at night
H. Salbutamol 100 mcg two puffs inhaled as required
Correct Answer: A. Budesonide-formoterol 200 mcg/6 mcg inhaled as required
Question 45
Matthew Edmond aged 12 years presents with a three-day history of pain on the left side of his scrotum. On examination, he has a tender pea-sized swelling at the upper pole of his left testicle. The cremasteric reflex is present.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Epididymo-orchitis
B. Hydrocoele
C. Inguinoscrotal hernia
D. Sperm granuloma
E. Spermatocoele
F. Testicular cancer
G. Testicular haematoma
H. Torsion of appendix of Morgagni
I. Torsion of testis
J. Varicocoele
Correct Answer: H. Torsion of appendix of Morgagni
Question 46
Betty Phillips aged 89 years is brought in by her daughter Anne who is concerned about an extremely itchy rash on Betty’s hands that has been keeping her awake at night. Betty moved into a local residential aged care facility six weeks earlier. Anne purchased some soap-free cleanser and emollients for Betty to use, but despite this, the rash seems to be spreading. On examination, Betty has areas of excoriation on both of her palms and wrists (see image).
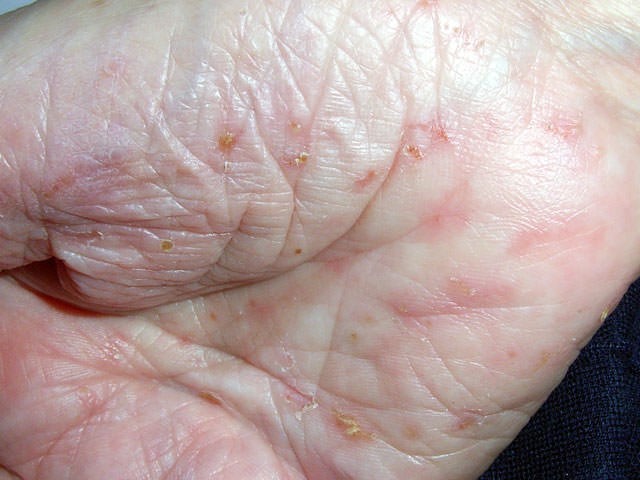
What is the MOST appropriate treatment?
A. Betamethasone valerate 0.1% ointment topically daily until skin is clear
B. Hydrocortisone–miconazole 1%/2% cream topically twice daily for two weeks
C. Mupirocin 2% ointment topically twice daily for five days
D. Permethrin 5% cream applied topically from the neck down for eight hours and repeated seven days later
E. Urea 10% cream topically twice daily
Correct Answer: D. Permethrin 5% cream applied topically from the neck down for eight hours and repeated seven days later
Question 47
Julia De Silva aged 17 years injured her left fifth finger in a netball game one hour earlier (see image 1). It is painful to move, and she is unable to extend the distal interphalangeal joint. Sensation is intact. You prescribe simple analgesia and advise her to apply ice. An X-ray is performed (see images 2 and 3).
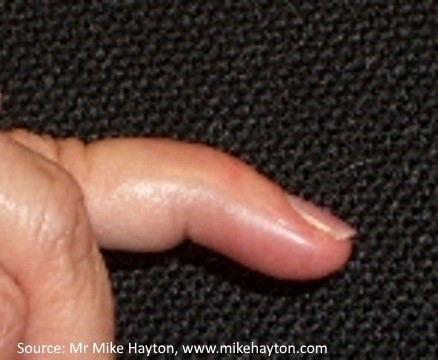
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Apply splint to maintain distal interphalangeal joint in full extension
B. Buddy strap to the fourth finger
C. Computed tomography scan left fifth finger
D. Passive stretching exercises four times per day
E. Relocation of subluxed joint
Correct Answer: A. Apply splint to maintain distal interphalangeal joint in full extension
Question 48
Micah Johnson aged 20 years injured his right knee one week earlier. He was at football training and attempted to change direction while running and felt a sudden ‘pop’ and pain in his knee. He now has pain in his knee with walking and is unable to run due to pain. On examination, when you rotate the right knee while the knee is at 90 degrees of flexion, there is pain with external tibial rotation which Micah says is worse on the inside of the knee.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Anterior cruciate ligament strain
B. Lateral collateral ligament tear
C. Lateral meniscal tear
D. Medial collateral ligament strain
E. Medial meniscal tear
Correct Answer: E. Medial meniscal tear
Question 49
Charmaine Lundy aged 65 years presents for her routine international normalised ratio test. She has been taking warfarin 5 mg orally daily for two years since receiving a mechanical mitral valve replacement. Charmaine has been on holiday, and it has been six weeks since her last international normalised ratio test. Her international normalised ratio today is 5.6* (normal range: 2.5–3.5). She is asymptomatic and denies any bleeding.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Arrange transfer to emergency department for intravenous fresh frozen plasma transfusion
B. Continue warfarin 5 mg orally and repeat international normalised ratio test tomorrow
C. Reduce warfarin to 2.5 mg orally daily and repeat international normalised ratio test tomorrow
D. Vitamin K 2 mg orally stat and repeat international normalised ratio test in 12 hours
E. Withhold warfarin today and repeat international normalised ratio test tomorrow
Correct Answer: E. Withhold warfarin today and repeat international normalised ratio test tomorrow
Question 50
Denise Dean aged 65 years has noticed swelling and redness of the skin near her left eye for the past three days (see image). She describes an initial tingling which has developed into a burning-type pain. She has not required any analgesic medication. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 37.0°C, and an appropriate examination of her conjunctiva and cornea does not reveal any abnormalities.
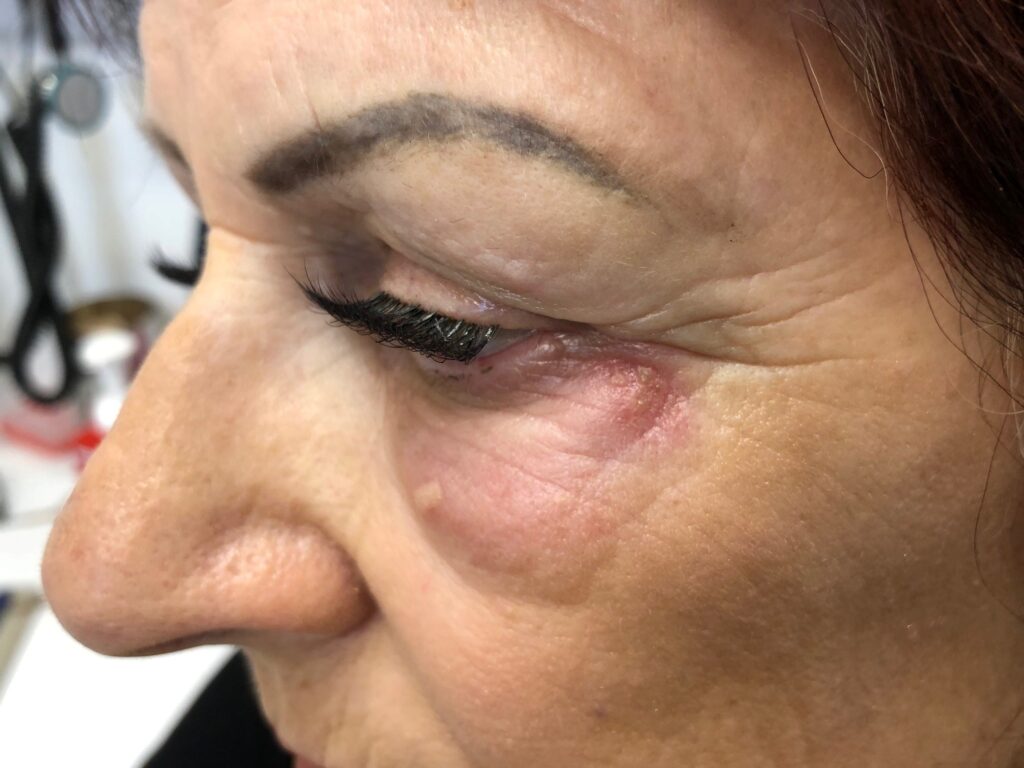
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Acyclovir 3% eye ointment topically five times daily
B. Cefalexin 500 mg orally four times daily
C. Cetirizine 10 mg orally daily
D. Chloramphenicol 0.5% eye ointment topically every three hours
E. Hydrocortisone 1% cream topically to affected skin twice daily
F. Mupirocin 2% cream topically to affected skin three times daily
G. Prednisolone 50 mg orally daily
H. Valaciclovir 1 g orally three times daily
