Question 1
Tilly Brown aged 5 years has had a runny nose for the last two days and today she is wheezy and needs to take extra breaths when she talks. On examination her tympanic temperature is 36.1°C, heart rate 120/min regular, respiratory rate 28/min, and oxygen saturation 93% on room air. When Tilly breathes in, her nares flare, and there is intercostal recession. Chest auscultation reveals bilateral expiratory wheeze. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Adrenaline 0.1% (1:1000 1 mg/mL) solution 5 mL by inhalation via nebuliser
B. Ipratropium metered dose inhaler 21 mcg/inhalation with four inhalations via a spacer
C. Oxygen face mask applied with oxygen titrated to ensure SpO2 > 93%
D. Prednisolone 2 mg/kg orally stat
E. Salbutamol metered dose inhaler 100 mcg/inhalation with six inhalations via spacer
Correct Answer: E. Salbutamol metered dose inhaler 100 mcg/inhalation with six inhalations via spacer
Question 2
Valeria Lopez aged 32 years has had increasing fatigue over the past six months since contracting an upper respiratory tract infection. She works full-time as a lawyer and is completing her master’s degree, which requires several hours of study each evening. She is finding it increasingly difficult to study in the evenings as her eyelids become ‘droopy and heavy’ and her vision is blurry. She has stopped going to the gym after work as her muscles feel tired and she feels clumsy. Valeria is sleeping well and feels refreshed in the mornings.
What investigation is MOST appropriate to confirm your provisional diagnosis?
A. Acetylcholine receptor antibodies
B. Adrenocorticotropic hormone levels
C. Angiotensin converting enzyme levels
D. Combined aldosterone and renin levels
E. Epstein–Barr virus serology
F. Gastrin levels
G. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
H. Morning cortisol assay
I. Serum ferritin
J. Tissue transglutaminase antibodies
K. Urine drug screen
Correct Answer: A. Acetylcholine receptor antibodies
Question 3
Evan Edmunds aged 86 years, a resident at the local residential aged care facility, has become increasingly confused over the past week. Evan suffers from early dementia and has a neurodegenerative disease with muscle atrophy and dysphagia. On examination his tympanic temperature is 37.8°C, heart rate 88/min regular, blood pressure 132/78 mmHg, and respiratory rate 25/min. On auscultation of his right lower chest, there are inspiratory crackles, bronchial breath sounds, and a pleural rub. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
What is the MOST appropriate diagnosis?
A. Aspiration pneumonia
B. Bronchitis
C. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
D. Influenza
E. Legionnaires’ disease
F. Lung abscess
G. Mycoplasma pneumonia
H. Pleurisy
I. Tuberculosis
Correct Answer: A. Aspiration pneumonia
Question 4
Sandy White aged 25 years has noticed increased hair loss when washing her hair and on her hairbrush over the past three months. She worries a lot about her appearance. She is caring for her first child who is aged three months. She has attempted to reduce hair loss by using a thick-toothed brush. Recent full blood examination and iron studies were unremarkable. On examination, there is generalized hair thinning across her entire scalp. A gentle hair pull test produces five hairs.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Biotin 1.25 mg orally daily
B. Calcipotriol-betamethasone dipropionate 50 mcg/500 mcg topically at night for four weeks
C. Prednisolone 25 mg orally daily for seven days
D. Reassurance condition will self-resolve
E. Spironolactone 100 mg orally daily for one month
Correct Answer: D. Reassurance condition will self-resolve
Question 5
Joe Paton aged 42 years has had flu-like symptoms for the last four weeks associated with intermittent palpitations and a mild tremor in his hands. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 36.9°C, heart rate 80/min regular, and blood pressure 135/85 mmHg. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded. An electrocardiogram is normal and his thyroid function tests are as follows:
| Test | Result | Normal Range |
|---|---|---|
| Free thyroxine | 45* pmol/L | 9 – 25 |
| Free triiodothyronine | 6.9* pmol/L | 3.5 – 6.5 |
| Thyroid stimulating hormone | < 0.02* mIU/L | 0.35 – 5.5 |
| Thyroid peroxidase antibody | 27 IU/mL | < 35 |
| Thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor binding inhibitor immunoglobulin (TBII)/TRAb | 12* IU/L | < 1.75 |
You initiate an appropriate low-dose beta-blocker.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Carbimazole 10 mg orally twice daily
B. Indomethacin 50 mg orally twice daily for 14 days
C. Potassium iodine 250 mg orally three times daily
D. Prednisolone 37.5 mg orally daily for 10 days
E. Thyroxine 50 mcg orally daily
Correct Answer: A. Carbimazole 10 mg orally twice daily
Question 6
Laura Robinson aged 43 years has had two months of intermittent burning epigastric pain and underwent an endoscopy showing a small shallow peptic ulcer. Biopsies performed at the time of endoscopy confirmed Helicobacter pylori infection and she completed a course of esomeprazole 20 mg orally twice daily, amoxicillin 1 g orally twice daily, and clarithromycin 500 mg orally twice daily for seven days. Laura returns for review after completing her seven-day course and her symptoms have resolved.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Continue pantoprazole 40 mg orally daily for 12 weeks and then review symptoms
B. Helicobacter pylori serology four weeks after completion of treatment
C. No further investigations or treatment is required
D. Refer for follow-up endoscopy
E. Urea breath test four weeks after completion of treatment
Correct Answer: E. Urea breath test four weeks after completion of treatment
Question 7
Sandra Lion aged 52 years requests a ‘check-up’. Her mother developed bowel cancer at age 61 years and her grandmother developed ovarian cancer at age 68 years. She exercises regularly, has a good diet, and does not smoke cigarettes or drink alcohol. Sandra has no symptoms of medical illness. On examination, her blood pressure is 140/79 mmHg and her body mass index is 22 kg/m². Her last mammogram was last year and was normal; a faecal occult blood test last year was normal, and a cervical screening test this year detected no human-papilloma virus. Sandra is keen to reduce her risk of dying of cancer and asks whether there is anything she should do.
What is the MOST appropriate intervention to recommend to Sandra to reduce her risk of dying of cancer?
A. Annual skin examination
B. Chest X-ray every two years
C. Colonoscopy every three years
D. Fish oil 3 g orally daily for five years
E. Low-dose aspirin for at least two-and-a-half years
F. Pelvic ultrasound every five years
G. Regular breast examination by her general practitioner
H. Saw palmetto supplement daily for three years
I. Vitamin D 1000 IU daily long term
J. Yearly cervical screening test
Correct Answer: E. Low-dose aspirin for at least two-and-a-half years
Question 8
Alexandra Carter aged 37 years has bilateral cracked heels (see image). They are not painful but she is unhappy with their appearance. This has been a problem for several months. She has tried many moisturisers but they have not helped.
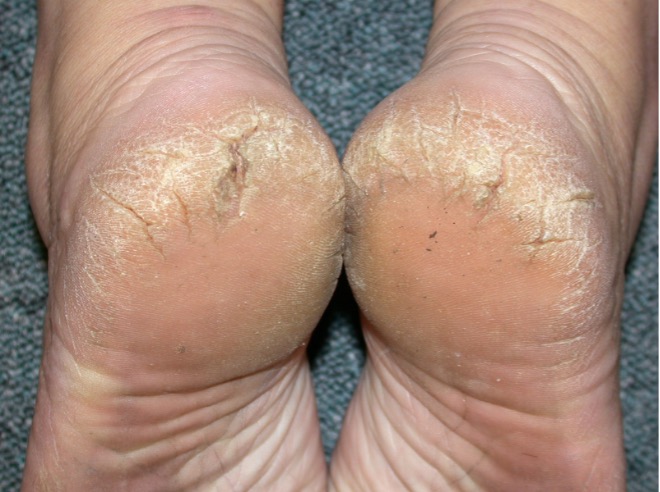
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Clotrimazole 1% cream topically twice daily for two weeks
B. Mometasone 0.1% ointment topically twice daily for up to two weeks
C. Mupirocin 2% ointment topically three times daily for 10 days
D. Urea 10% cream topically twice daily for two weeks
E. Wear open footwear when possible
Correct Answer: D. Urea 10% cream topically twice daily for two weeks
Question 9
Peter Butler aged 28 years returns for results of a recent sexual health check-up. He identifies as homosexual and has sex with men. He informs you that his regular sexual partner recently had an anal ulcer and was diagnosed with primary syphilis. Peter is asymptomatic. Peter’s syphilis results performed last week are as follows:
| Test | Result |
|---|---|
| Treponema pallidum immunoglobulin G | Negative |
| Treponema pallidum particle agglutination assay | Negative |
| Rapid plasma reagin antibody titre | Non-reactive |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise Peter not to have sex and repeat syphilis serology in one month
B. Reassure Peter that his syphilis serology is negative; therefore, no treatment is required
C. Treat Peter today with 2.4 million units benzathine penicillin intramuscularly stat
D. Treat Peter today with ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly and azithromycin 1 g orally stat
E. Treat Peter today with phenoxymethylpenicillin 500 mg orally twice daily for 10 days
Correct Answer: C. Treat Peter today with 2.4 million units benzathine penicillin intramuscularly stat
Question 10
Felicity Bragg aged 21 years has been tired for several months and now has an itchy rash on her buttocks and knees (see image). She has been using over-the-counter hydrocortisone 1% cream topically three times daily for the past week without significant improvement. She has a history of Hashimoto disease and takes thyroxine 50 mcg orally daily. Thyroid function testing performed last week was normal.

What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Antinuclear antibody
B. Cephalexin 500 mg orally four times daily for five days
C. Clotrimazole 1% cream topically twice daily for 14 days
D. Famciclovir 500 mg orally twice daily for seven days
E. IgA tissue transglutaminase antibody and deamidated gliadin peptide antibody
F. Increase thyroxine dose to 100 mcg orally daily
G. Permethrin 5% cream topically from the neck down and leave for eight hours
H. Prednisolone 25 mg orally daily tapering over one month
Correct Answer: E. IgA tissue transglutaminase antibody and deamidated gliadin peptide antibody
Question 11
Ian McCarthy aged 25 years has had persistent nausea over the last 10 days. He was diagnosed with major depression two weeks ago and commenced on fluoxetine 20 mg orally daily. His symptoms of depression are improving, but he is concerned about the nausea.
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Advise he likely has an allergy to fluoxetine
B. Advise Ian to take his medication with food
C. Advise regular aperients
D. Arrange upper abdominal ultrasound
E. Cease fluoxetine and review in one week
F. Change fluoxetine to paroxetine 10 mg orally daily
G. Initiate a proton pump inhibitor
H. Refer to gastroenterologist for consideration of endoscopy
Correct Answer: B. Advise Ian to take his medication with food
Question 12
Monique Letts aged 44 years has multiple sclerosis and since diagnosis has had increasing problems with urination. She needs to urinate frequently and only passes a small amount of urine each time. She lost control of her bladder recently when she arrived home from work. She is doing pelvic floor exercises regularly. Her only regular medication is glatiramer acetate 40 mg subcutaneously three times weekly. Urine microscopy and culture, renal ultrasound, and blood tests are normal.
What is the MOST appropriate pharmacological management?
A. Amitriptyline 10 mg orally nocte
B. Desmopressin 0.05 mg orally twice daily
C. Macrogol 13.12 g sachet orally daily
D. Oestriol pessary 500 mcg intravaginally at bedtime
E. Oxybutynin 3.9 mg transdermally twice weekly
Correct Answer: E. Oxybutynin 3.9 mg transdermally twice weekly
Question 13
David Wesley aged 20 years requires a pre-employment medical assessment for a mining contractor position. The assessment includes an audiogram. The results indicate an asymmetric hearing loss affecting his left ear. Further history reveals David has frequent episodes of otitis externa. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 36.7°C. Otoscopy on the right appears normal. Otoscopy of his left ear is as shown (see image).
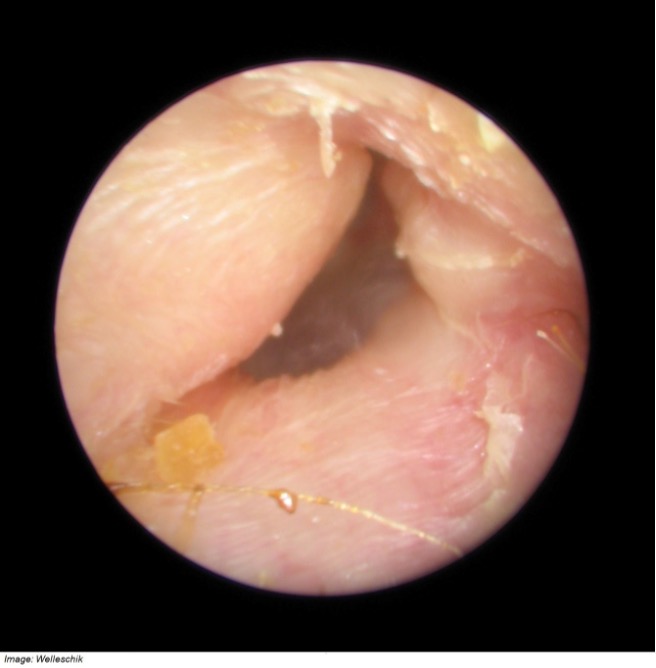
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Ciprofloxacin-hydrocortisone 0.2%/1% ear drops three drops into left ear twice daily for seven days
B. Clindamycin 450 mg orally three times daily for five days
C. Computed tomography brain and internal auditory meatus
D. Dicloxacillin 500 mg orally four times daily for five days
E. Flumethasone-clioquinol 0.02%/1% ear drops three drops into left ear twice daily for seven days
F. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
G. Magnetic resonance imaging vestibulocochlear nerve
H. Prednisolone 50 mg orally daily for three days then dose tapering over 14 days
I. Referral to audiologist for hearing aid assessment
J. Referral to ear nose and throat surgeon for consideration of surgical intervention
K. Repeat audiogram in two weeks
L. Saline irrigation of the external ear canal
Correct Answer: J. Referral to ear nose and throat surgeon for consideration of surgical intervention
Question 14
Sandra Gresham aged 84 years, a resident of your local aged care facility, has not used her bowels for the past five days. She has advanced Alzheimer dementia. She has difficulty swallowing and eats a pureed diet. On examination, her abdomen is mildly distended but nontender with active bowel sounds. On per-rectum examination, there is a large volume of hard faeces palpable within the rectum. She was commenced on poloxamer drops (Coloxyl) 100 mg/mL 2 mL orally daily two days ago.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Bisacodyl 10 mg rectally via suppository
B. Liquid paraffin 40 mL orally daily
C. Midazolam 5 mg subcutaneously followed by manual evacuation of the rectum
D. Plain abdominal X-ray
E. Psyllium husks two teaspoons orally daily
Correct Answer: A. Bisacodyl 10 mg rectally via suppository
Question 15
Leigh Miller aged 36 years has had pain in her left foot over the past six weeks. She has been training for a Masters athletics competition and is a sprint runner. Her foot was initially painful only during her morning run and was fine at rest. Recently the pain has become more persistent and severe and is now interfering with walking and activities of daily living. Two weeks ago, she had an X-ray which was reported as normal. On examination, she is tender on the top of her foot (see image).
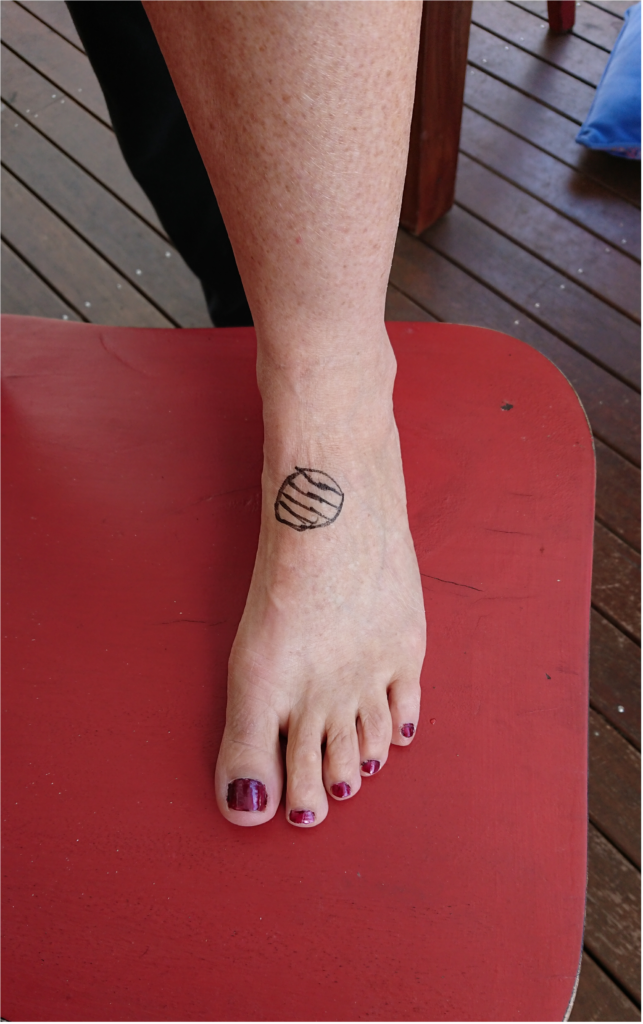
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Inferior tibio-fibular joint sprain
B. Navicular stress fracture
C. Pes anserine bursitis
D. Pseudogout
E. Tarsal tunnel syndrome
Correct Answer: B. Navicular stress fracture
Question 16
Samuel Stevens aged 65 years returns for his recent blood test results. Samuel had coronary artery bypass graft surgery 12 months ago following an anterior myocardial infarction. He has been asymptomatic since and is keen to reduce his medications. He has never smoked. On examination, his heart rate is 60/min regular, blood pressure 128/78 mmHg, and the rest of his cardiovascular examination is unremarkable. His current medications include aspirin 100 mg orally daily, clopidogrel 75 mg orally daily, atorvastatin 80 mg orally daily, metoprolol 100 mg orally twice daily, and telmisartan 40 mg orally daily.
| Test | Result | Desirable range (high risk) |
|---|---|---|
| Total cholesterol | 2.6 mmol/L | < 4.0 |
| Triglycerides | 1.9 mmol/L | < 2.0 |
| High-density lipoprotein (HDL) | 0.73* mmol/L | > 0.9 |
| Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) | 0.87 mmol/L | < 2.0 |
| Cholesterol:HDL ration | 3.6 | – |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Cease aspirin
B. Cease clopidogrel
C. Reduce atorvastatin to 40 mg orally daily
D. Reduce metoprolol to 50 mg orally twice daily
E. Reduce telmisartan to 20 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: B. Cease clopidogrel
Question 17
Amanpreet Kaur aged 50 years has had numbness in her right hand for the last 12 months. It is worse at night and when using a mobile phone. She has noticed weakness when she tries to grasp or pinch with that hand. She is right-handed, a non-smoker, and vegetarian. On examination, there is clawing in the fourth and fifth fingers, reduced sensation over the medial side of the hand, and weak abduction of the fifth finger. When Amanpreet grasps a piece of paper between her thumb and index finger, there is hyperflexion at the interphalangeal joint of her thumb (positive Froment sign).
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Carpal tunnel syndrome
B. Cubital tunnel syndrome
C. Dupuytren’s contracture
D. Herniated disc at C5/C6 level
E. Vitamin B12 deficiency
Correct Answer: B. Cubital tunnel syndrome
Question 18
Sean Smith aged 72 years has a severe headache over his left forehead and temporal region that radiates to the back of his head. He also has pain in his jaw on the left side, which is worse when he eats. The headache has been constant every day for the past 10 days and it is worse in the mornings. He also feels lethargic and has muscle aches. He has a history of hypertension and is prescribed perindopril 8 mg orally daily.
What is the MOST appropriate investigation to confirm your provisional diagnosis?
A. Antinuclear antibody test
B. C-reactive protein
C. Computed tomography brain
D. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
E. Full blood count
F. Human leukocyte antigen B27
G. Lumbar puncture
H. Magnetic resonance imaging brain
I. Rheumatoid factor
J. Temporal artery biopsy
Correct Answer: J. Temporal artery biopsy
Question 19
Grant Stinson aged 17 years injured his tongue today when he dropped a tyre he was changing and it rebounded and hit him on the jaw. On examination, there is an 8 mm linear laceration to the centre of the tongue with no current bleeding. It is not full thickness. You prescribe appropriate analgesia.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid 875 mg/125 mg orally twice daily for five days
B. Cauterise with silver nitrate stick
C. Reassurance that no active management is required
D. Refer to a tertiary hospital for plastic surgery review
E. Suture with absorbable sutures
Correct Answer: C. Reassurance that no active management is required
Question 20
Caroline Luck aged 19 years presents for results of tests ordered by one of your colleagues. She had diarrhoea and vomiting for a couple of days but her symptoms have now improved. On examination during acute illness, Caroline was noted to have slightly yellow skin. She reports ongoing mild fatigue, but repeat examination today is normal.
| Test | Result | Normal range |
|---|---|---|
| Full blood count | All values within normal range | |
| Bilirubin | 37* µmol/L | < 25 |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 52 U/L | 30 – 120 |
| Alanine aminotransferase | 24 U/L | < 41 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase | 32 U/L | < 41 |
| Gamma glutamyl transferase | 41 U/L | < 51 |
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Acute hepatitis A infection
B. Alcoholic cirrhosis
C. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
D. Anorexia nervosa
E. Chronic hepatitis C infection
F. Epstein–Barr virus infection
G. Gilbert syndrome
H. Haemochromatosis
I. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
J. Primary biliary cirrhosis
K. Wilson disease
Correct Answer: G. Gilbert syndrome
Question 21
Annette Dupont aged 46 years has had six months of worsening generalized pains associated with tiredness, poor sleep, and ‘brain fog’. Her pains are in her neck, shoulders, arms, and lower back. They are usually worst when she first gets up, improve a little in the middle of the day, but worsen again in the evening. For the past three weeks, she has tried paracetamol 665 mg two tablets orally three times daily with no improvement. Recent full blood examination, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, antinuclear antibodies, creatine kinase, and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels were normal. On examination, her heart rate is 75/min regular, blood pressure 110/80 mmHg, and body mass index 23 kg/m².
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Bone density scan
B. Diclofenac 50 mg orally twice daily
C. Magnetic resonance imaging brain
D. Prednisolone 15 mg orally daily
E. Referral for graded exercise program
F. Referral for sleep study
G. Rheumatoid factor
H. Sertraline 50 mg orally daily
I. Trial of menopause hormone therapy
J. X-ray cervical spine
Correct Answer: E. Referral for graded exercise program
Question 22
Bruce Loft aged 72 years is brought by ambulance to your small hospital after an episode of dizziness while shopping. Bruce still feels lightheaded and ‘queasy’. On examination, his heart rate is 42/min regular, blood pressure 80/55 mmHg, respiratory rate 18/min, and oxygen saturation 95% on room air. An electrocardiogram was taken by the ambulance officers (see image). They also administered aspirin 300 mg orally. Despite lying down, receiving oxygen, and elevating his legs, Bruce’s blood pressure remains low and he continues to feel lightheaded. You begin organizing transfer to your tertiary referral center.
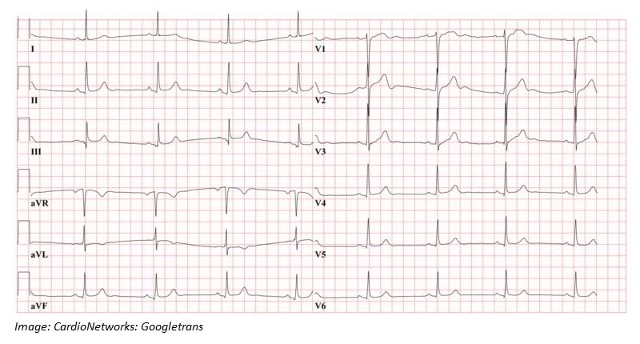
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Adenosine 6 mg intravenous bolus
B. Adrenaline 10 mcg/min intravenous infusion
C. Amiodarone 300 mg intravenous infusion
D. Atropine 0.5 mg intravenously
E. Flecainide 2 mg/kg (max 150 mg) intravenous infusion over 30 mins
F. Isoprenaline 10 mcg intravenously
G. Magnesium sulfate 50% solution 4 mL (2 g) intravenous infusion over 15 mins
H. Metoprolol tartrate 5 mg intravenously
I. Verapamil 1 mg/min (max 15 mg) intravenously
Correct Answer: D. Atropine 0.5 mg intravenously
Question 23
James Smith aged 45 years had a left ureteric stent inserted yesterday for management of a calculus. Since his procedure, he has been passing blood in his urine and feeling a frequent need to pass urine. James is taking paracetamol 1 g orally and ibuprofen 400 mg orally three times daily for pain management. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 36.8°C and blood pressure 125/75 mmHg. Abdominal examination reveals mild left loin tenderness with no masses. Dipstick urine reveals large blood and ketones.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Arrange urgent computed tomography kidneys ureters bladder
B. Oxycodone 5 mg orally four-hourly as required
C. Reassure that the symptoms should improve with time
D. Trimethoprim 300 mg orally at night for seven days
E. Urgent referral back to treating urologist to have stent removed
Correct Answer: C. Reassure that the symptoms should improve with time
Question 24
Lilly Tanner aged 11 months has a widespread rash. She became unwell three days ago with temperatures up to 40°C, a runny nose, and irritability. Today the fever has resolved and the rash appeared. On examination, there are rose pink blanching plaques on her trunk (see image). She also has some similar spots on her soft palate.
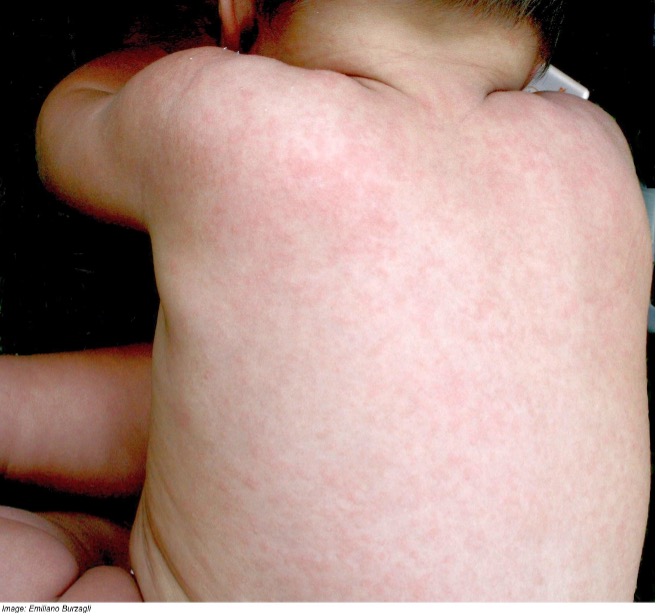
What is the MOST appropriate causative organism?
A. Coxsackie virus
B. Group A streptococcus
C. Human herpes virus 6B
D. Parvovirus B19
E. Measles virus
Correct Answer: C. Human herpes virus 6B
Question 25
Jean Simmonds, aged 71 years, has had a gradually worsening loss of appetite and nausea over the past three months. She has a history of hypertension and atrial fibrillation. She takes irbesartan 150 mg orally daily, hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg orally daily, metoprolol 50 mg orally twice daily, and digoxin 0.25 mg orally daily.
On examination, her heart rate is 60/min irregularly irregular, blood pressure 122/68 mmHg, and weight 51 kg.
| Test | Result | Normal range |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium | 138 mmol/L | 135 – 145 |
| Potassium | 5.8* mmol/L | 3.5 – 5.2 |
| Chloride | 98 mmol/L | 95 – 110 |
| Bicarbonate | 30 mmol/L | 22 – 32 |
| Urea | 6.7 mmol/L | 2.5 – 8.0 |
| Creatinine | 118* mmol/L | 45 – 90 |
| Estimated glomerular filtration rate | 50* mL/min/1.73m² | > 90 |
What is the MOST appropriate initial investigation to confirm your provisional diagnosis?
A. Computed tomography scan of brain
B. Faeces microscopy and culture
C. Fasting blood glucose
D. Gastroscopy
E. Serum calcium
F. Serum cortisol
G. Serum digoxin
H. Serum lipase
I. Urine microscopy and culture
Correct Answer: G. Serum digoxin
Question 26
Ronald Davis aged 70 years has had light-headedness and dizziness over recent weeks. His symptoms occur when he gets up from bed quite quickly, changes direction suddenly, or rolls over in bed. If he stays still, the symptoms settle down. His vision and hearing are normal.
What is the MOST appropriate examination to perform to support your provisional diagnosis?
A. Have patient stand quickly from a seated position and measure blood pressure three minutes later
B. Have patient stand with feet together and eyes closed for 30 seconds
C. Lower patient rapidly from sitting to supine position with their neck extended and rotated to one side
D. Rotate patient’s head from side to side in a sitting position over 30 seconds
E. Rotate supine patient with head turned to the side in 90-degree increments over two minutes
Correct Answer: C. Lower patient rapidly from sitting to supine position with their neck extended and rotated to one side
Question 27
Jenny Tran aged 47 years has had six weeks of pain and numbness in her right (dominant) hand. The pain is often aching and tingling and wakes her most nights. Lately, it has also occurred while typing. Her symptoms are partly relieved by shaking her hands in the air.
On examination of her right hand, she has no wasting or weakness of her hand muscles. She has decreased light touch sensation over the palmar aspect of the hand except for the fifth finger. Tinel’s sign at the wrist is negative. Phalen’s sign is positive.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Diagnostic wrist ultrasound
B. Diclofenac 50 mg orally twice daily for two weeks
C. Frusemide 20 mg orally daily
D. Nerve conduction studies
E. Nocturnal wrist splint
F. Physiotherapy for carpal bone mobilisation
G. Refer to hand surgeon for consideration of surgery
H. Steroid injection of the carpal tunnel
Correct Answer: E. Nocturnal wrist splint
Question 28
Rick McMahon aged 78 years moved to your town in North Queensland six months ago. He has been bothered by a red itchy rash on his back and chest since the move and is wondering if he is allergic to something (see image). He has tried fexofenadine 180 mg orally daily and betamethasone cream 0.02% topically twice daily for two weeks; however, there has been no significant improvement in his symptoms.
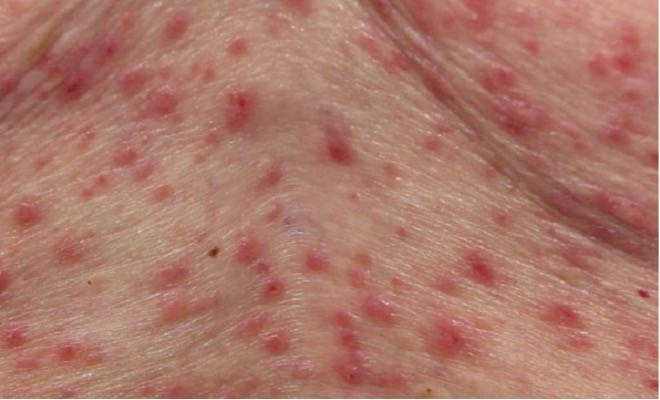
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Dermatitis herpetiformis
B. Folliculitis
C. Grover’s disease
D. Guttate psoriasis
E. Keratosis pilaris
F. Lichen planus
G. Nodular vasculitis
H. Pityriasis rosea
I. Scabies
J. Seborrhoeic dermatitis
Correct Answer: C. Grover’s disease
Question 29
John Leonard aged 78 years has had chronic back pain for over three years. Over the past eight months, he has had tingling pain and numbness around the buttock area and into both legs. Over the last three weeks, he has noticed increasing weakness in his lower legs and intermittent fecal incontinence. His pain is worse with walking and improves when he leans forward on a supportive device such as a shopping trolley. John takes paracetamol-codeine phosphate 500 mg/30 mg two tablets orally three times daily as required for pain relief. A plain X-ray performed 12 months ago revealed degenerative changes in John’s lumbar spine.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. C-reactive protein
B. Computed tomography of the lumbar spine
C. Human leukocyte antigen B27 levels
D. Nerve conduction studies
E. Nuclear bone scan of lumbar spine
F. Prostate-specific antigen
G. Refer to radiologist for lumbar sleeve root injection
H. Regular psyllium fiber supplement
I. Urgent Doppler ultrasound of both lower limb arteries
J. Urgent magnetic resonance imaging of lumbar spine
Correct Answer: J. Urgent magnetic resonance imaging of lumbar spine
Question 30
Jeremy Gloth aged 54 years is concerned because he coughed up blood last night. He reported seeing fresh blood mixed in with some clear sputum without any blood clots. Jeremy had a similar episode five weeks ago at the time of a mild respiratory infection. He does not feel like he has an infection today. Jeremy has a past history of hypertension treated with perindopril 5 mg orally daily. He has smoked a pack of cigarettes per day for 31 years and has not traveled outside Australia. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 37.2°C, heart rate 66/min regular, blood pressure 122/74 mmHg, and respiratory rate 24/min. Examination of the nose, throat, and chest is normal. A chest X-ray is reported as normal. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Computed tomography scan chest
B. Magnetic resonance imaging chest
C. Reassure Jeremy that no further investigation is required
D. Refer for urgent bronchoscopy
E. Send blood for coagulation studies
Correct Answer: A. Computed tomography scan chest
Question 31
Vanessa Day aged 26 years has had three months of increasing fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and memory lapses that are affecting her ability to care for her 2-year-old child. She has noticed a reduced appetite, menstrual irregularities, and a lower mood. One year ago, she was diagnosed with borderline personality disorder and has found psychological therapy very helpful. On examination, her temperature is 36.2°C, heart rate 56/min regular, blood pressure 120/94 mmHg, and a random finger-prick blood glucose level is 6.2 mmol/L (normal range 3.0 – 6.9).
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Full blood examination
B. Magnetic resonance imaging of her head
C. Morning serum cortisol level
D. Olanzapine 10 mg orally daily
E. Refer her for psychiatry review
F. Refer her to alternative psychologist for a second opinion
G. Sertraline 50 mg orally daily
H. Serum electrolytes
I. Thyroid stimulating hormone level
J. Topiramate 25 mg orally twice daily
Correct Answer: I. Thyroid stimulating hormone level
Question 32
James Windsor aged 52 years has had a painful left knee for the past two days. The pain is continuous but worse with movement of the joint. He does not recall any trauma. He had a large amount of alcohol and became quite intoxicated at a party four days ago. He has had similar episodes of this pain in the past which improved over time. He has hypertension treated with ramipril 5 mg orally daily and atenolol 25 mg orally daily. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 37.3°C, heart rate 98/min regular, blood pressure 132/88 mmHg, body mass index 33.1 kg/m². His left knee is swollen with a visible effusion and the skin appears intact. It is tender to palpation globally around the knee. He has a full range of motion of the knee with some tightness at full flexion.
What investigation is MOST likely to confirm your suspected provisional diagnosis?
A. Aspiration of synovial fluid for polarised light microscopy
B. Blood culture
C. C-reactive protein
D. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
E. Magnetic resonance imaging knee
F. Microscopy culture and sensitivity of synovial fluid
G. Serum urate level
H. White cell count
I. X-ray of the knee
Correct Answer: A. Aspiration of synovial fluid for polarised light microscopy
Question 33
Jessica Nathan aged 33 years, an Aboriginal woman, comes to see you as she is planning her first pregnancy. She is taking a pregnancy multivitamin as well as metformin extended-release 1 g orally daily for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Her most recent HbA1c was 6%. On examination, her body mass index is 23 kg/m² and blood pressure 130/85 mmHg. She has an appointment to see her endocrinologist in two weeks.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in pharmacological management?
A. Add folic acid 5 mg orally daily
B. Add methyldopa 125 mg orally twice daily
C. Add ferrous sulfate 270 mg orally daily
D. Change metformin to gliclazide modified-release 30 mg orally daily
E. Reduce metformin dose to metformin extended-release 500 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: A. Add folic acid 5 mg orally daily
Question 34
Stanley Spencer aged 67 years returns for results of blood tests completed two days ago. He was discharged last week from the local mental health facility after a two-week admission for severe agitated depression and suicidal ideation. He remains moderately depressed but has no further suicidal ideation. Before this admission, Stanley had no prior psychiatric history.
Medications that were initiated in hospital include sertraline 100 mg orally daily, lithium 250 mg orally twice daily, and quetiapine 100 mg orally twice daily. He has also continued to take perindopril 5 mg orally daily and amlodipine 5 mg orally daily for longstanding hypertension.
| Test | Two days ago | Four weeks ago | Normal range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum lithium | 1.0 mEq/L | N/A | 0.6 – 1.2 |
| Sodium | 139 mmol/L | 141 mmol/L | 135 – 145 |
| Potassium | 3.9 mmol/L | 3.8 mmol/L | 3.5 – 5.2 |
| Chloride | 102 mmol/L | 100 mmol/L | 95 – 110 |
| Urea | 17* mmol/L | 9.5 mmol/L | 2.5 – 8.0 |
| Creatinine | 162* mmol/L | 101 mmol/L | 45 – 90 |
| Estimated glomerular filtration rate | 36* ml/min/1.73m² | 78* ml/min/1.73m² | > 90 |
Which medication is MOST likely to have caused the abnormal test results?
A. Amlodipine
B. Lithium
C. Perindopril
D. Quetiapine
E. Sertraline
Correct Answer: B. Lithium
Question 35
Doris Bottari aged 84 years was travelling overseas and one month ago sustained a left distal radius fracture when she fell on her outstretched hand. She presented to the local emergency department, and a plaster back-slab was applied to the undisplaced fracture. She presents for follow-up. When the back-slab is removed, she has persistent pain and swelling within her wrist and tingling within her fingers.
What is the MOST appropriate next investigation?
A. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scan
B. Magnetic resonance imaging left wrist
C. Nerve conduction study left upper limb
D. Serum calcium
E. X-ray left wrist
Correct Answer: E. X-ray left wrist
Question 36
Amrita Sun aged 22 years is a child care worker who has had five days of malaise, headache, myalgia, nausea, and rhinorrhoea. Since yesterday, she has also had a rash on her arms and legs and aching, swollen hands and feet. Amrita is 11 weeks pregnant with her first child, and her pregnancy has been uneventful to date.
On examination, her tympanic temperature is 37.0°C and blood pressure 118/67 mmHg. The joints in her hands and feet are mildly swollen and tender on palpation. She has an erythematous rash on her arms and legs (see image). COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.

What is the MOST appropriate investigation to confirm your provisional diagnosis?
A. Measles serology
B. Parvovirus serology
C. Syphilis serology
D. Toxoplasmosis serology
E. Varicella serology
Correct Answer: B. Parvovirus serology
Question 37
Charmaine Coleman aged 65 years has had worsening of her usual cough for the past two months. She has seen another general practitioner on two occasions, but her symptoms have not improved. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded. Two months ago, she took a course of amoxicillin 500 mg orally three times daily for seven days. She returned last week and was sent for a chest X-ray which was reported as normal. She was then prescribed prednisolone 50 mg orally daily for five days and advised to increase her salbutamol to four puffs every four hours. She was diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease eight years ago and takes fluticasone-umeclidinium-vilanterol 100 mcg/62.5 mcg/25 mcg one puff daily. She stopped smoking five years ago after smoking 25 cigarettes a day for 40 years.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid 500 mg/125 mg orally twice daily for five days
B. Computed tomography scan chest with contrast
C. Refer to respiratory physician
D. Spirometry pre and post salbutamol
E. Sputum microscopy culture and sensitivities
Correct Answer: B. Computed tomography scan chest with contrast.
Question 38
Margie Visser aged 21 years returns for results of tests you ordered last week. She has had a chronic vaginal itch and white discharge for the past four months. Prior to seeing you she thought that she had ‘thrush’ which she tried to treat with over-the-counter fluconazole 150 mg orally stat and clotrimazole 1% intra-vaginal cream at night for six days. She has also been taking an oral probiotic but her symptoms have not improved.
Investigation results are as follows:
Endocervical swab chlamydia and gonorrhoea nucleic acid amplification test – Not detected
High vaginal swab microscopy culture and sensitivities – Candida glabrata ++
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Azithromycin 1 g orally stat
B. Boric acid 600 mg capsule intravaginally at night for 14 days
C. Clindamycin 2% vaginal cream one applicator intravaginally at night for seven days
D. Fluconazole 50 mg orally daily until symptoms resolve then twice weekly for two months
E. Miconazole 2% vaginal cream one applicator intravaginally at night for seven days
Correct Answer: B. Boric acid 600 mg capsule intravaginally at night for 14 days
Question 39
Terry Jones aged 65 years has recently been treated for a urinary tract infection and has returned to discuss the result of his renal ultrasound. He has made a full recovery from his urinary tract infection and otherwise feels well. The ultrasound report states that his infra-renal abdominal aortic artery has a diameter of 3.8 cm. Terry has a history of mild hypertension well controlled with perindopril 4 mg orally daily. He is an ex-smoker of 20 pack years.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Computed tomography scan abdomen in six months
B. Magnetic resonance imaging scan of the aorta
C. Reassure no further investigation is required
D. Repeat abdominal ultrasound in three years
E. Urgent referral to vascular surgeon
Correct Answer: D. Repeat abdominal ultrasound in three years
Question 40
Briar Roberts aged 87 years has a painful left shoulder after she tripped on the footpath and fell. On examination active shoulder abduction is restricted by pain to 100 degrees but passively she can extend her arm over her head. After administering 1 g of paracetamol you arrange a shoulder X-ray which demonstrates changes of osteoarthritis. Her shoulder ultrasound demonstrates an acute on chronic full thickness tear of the supraspinatus tendon.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Collar and cuff for two weeks
B. Ibuprofen 400 mg orally three times daily as required
C. Physiotherapy for graded exercise and activity modification
D. Refer to orthopaedic surgeon for surgical repair
E. Subacromial glucocorticoid injection
Correct Answer: C. Physiotherapy for graded exercise and activity modification
Question 41
Adam Tran aged 27 years has had recurrent feelings of anxiety after being assaulted one month ago at his workplace. He works as a prison guard and sustained multiple injuries during a prison riot. He has been off work for a number of weeks. Activities such as going shopping are causing panic attacks which he has never experienced before. He is having trouble sleeping and checks the locks on his windows and doors multiple times a day. He had anxiety when he was a teenager and was trialled on sertraline 50 mg orally daily. At that time it caused such severe nausea that he stopped it. He has been seeing a psychologist regularly for cognitive behavioural therapy.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in pharmacological management?
A. Amitriptyline 25 mg orally nocte
B. Clomipramine 25 mg orally daily
C. Diazepam 5 mg orally three times daily as required
D. Mirtazapine 15 mg orally daily
E. Paroxetine 10 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: E. Paroxetine 10 mg orally daily
Question 42
Elsie Smith aged 8 days is an Aboriginal child who presents with her mother Sally to the Aboriginal Medical Service for Elsie’s routine postnatal check-up. Elsie is Sally’s first child and was born via normal vaginal delivery at the local hospital. Her family live in a remote community and Sally had received limited antenatal care. Elsie is fully breastfed. Sally reports Elsie has had a ‘weepy’ right eye for the past few days. On examination Elsie has a purulent discharge from her right eye with clear sclera. She is otherwise developing normally and gaining adequate weight.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise Sally to clean the eye frequently with expressed breast milk
B. Instill tropicamide 1% drops for dilated fundus examination
C. Perform an additional eye swab for chlamydia polymerase chain reaction
D. Refer to ophthalmologist for probing of the nasolacrimal duct
E. Regular massage of nasolacrimal region
Correct Answer: C. Perform an additional eye swab for chlamydia polymerase chain reaction
Question 43
Bethany Nawes aged 42 years has been feeling tired and weak for seven weeks. Her muscles are ‘cramping’ and she has had difficulty hanging her washing up due to pain in her shoulders. Her hair is brittle and has started to thin in places. She has been taking ibuprofen 400 mg orally three times daily for the past three days without significant improvement in her pain. On examination she has no obvious muscle wasting. She has generalised reduction in active range of motion in both shoulders and her upper limb strength is mildly reduced.
What is the MOST appropriate next investigation to confirm your suspected provisional diagnosis?
A. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody
B. Bilateral shoulder ultrasound
C. Human leucocyte antigen B27
D. Serum ferritin
E. Thyroid stimulating hormone
Correct Answer: E. Thyroid stimulating hormone
Question 44
Georgie Disick aged 34 years and her partner Dave aged 27 years would like to discuss Georgie’s possible exposure to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Georgie and Dave had unprotected sex last night. Dave was diagnosed with HIV infection at age 22 years. His HIV viral load has been undetectable since he started daily antiretroviral medications five years ago at the time of his HIV diagnosis. His most recent viral load was done last week. Georgie and Dave have been together in a monogamous relationship for four years. They usually use condoms but last night did not. Georgie is concerned about her risk of contracting HIV.
What is the MOST appropriate advice?
A. Offer Georgie a blood test for HIV antigen/antibody to be performed in three months time
B. Offer Georgie a blood test for HIV antigen/antibody to be performed today
C. Offer pre-exposure prophylaxis to Georgie to reduce her risk of contracting HIV
D. Reassure Georgie that she is not currently at risk of contracting HIV as Dave has an undetectable HIV viral load
E. Refer Georgie to the emergency department for HIV post exposure prophylaxis
Correct Answer: D. Reassure Georgie that she is not currently at risk of contracting HIV as Dave has an undetectable HIV viral load
Question 45
Zara Bates aged 19 years is brought in by her father Greg. She returned home yesterday after studying in China for six months. Yesterday she started to feel anxious and nauseated. She was drinking up to eight standard alcoholic drinks daily while abroad but wants to start a ‘cleanse’ now that she is home. She had hepatitis A and typhoid vaccination prior to departure on her trip. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded. On examination Zara appears sweaty and has a slight tremor. Her temperature is 37.2 °C heart rate 98/min regular and blood pressure 138/90 mmHg. You prescribe thiamine.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Acamprosate 666 mg orally three times daily
B. Advise that her alcohol consumption is within safe limits
C. Arrange admission to specialist alcohol treatment facility
D. Diazepam 10 mg orally every six hours with sliding scale dosing
E. Disulfiram 100 mg orally daily
F. Naltrexone 50 mg orally daily
G. Reassurance that her symptoms will resolve over the next 72 hours
H. Seroquel 50 mg orally nocte
Correct Answer: D. Diazepam 10 mg orally every six hours with sliding scale dosing
Question 46
Serena Buchanan aged 31 years is a dermatology registrar who acquired hepatitis C 12 months ago following a needlestick injury. Assessment before beginning therapy showed no evidence of cirrhosis and she was treated with an appropriate course of antiviral medication. Blood tests taken 12 weeks after completing treatment show:
Liver function tests normal.
HIV antibodies negative.
Hepatitis A Immunoglobulin G antibodies (HAV IgG) Positive*
Immunoglobulin M antibodies (HAV IgM) Negative
Hepatitis B Surface antigen (HBsAg) Negative
Surface antibody (anti-HBs) Positive*
Core antibody (anti-HBc) Negative
Hepatitis C Hepatitis C antibodies (anti-HCV) Positive*
RNA (HCV-RNA) Undetectable
What is the MOST appropriate follow-up regime?
A. Alpha fetoprotein annually
B. Computed tomography scan abdomen annually
C. Fibroscan annually
D. Hepatitis A vaccine now and repeat dose in six months
E. Hepatitis B vaccine now with repeat doses in one month and six months
F. Hepatitis C virus RNA annually
G. Hepatitis C virus serology annually
H. Liver function test annually
I. No specific follow-up required
J. Upper abdominal ultrasound annually
Correct Answer: I. No specific follow-up required
Question 47
Paul Fletcher aged 26 years returns for a repeat prescription. Your colleague started him on phentermine 40 mg orally daily nearly two months ago in addition to advice about diet and exercise modification. He is pleased with weight loss of 7 kg during this time. Prior to starting phentermine he had tried many diets and exercise programs without success. He now wishes to continue the medication. He is a non-smoker. On examination his heart rate is 72 /min regular blood pressure 120/75 mmHg weight 100 kg height 175 cm and body mass index 32.7 kg/m².
What is the MOST appropriate next step regarding phentermine prescription?
A. Advise that diet and lifestyle changes alone would be more effective for Paul
B. Cease phentermine due to Paul’s cardiovascular disease risk factors
C. Provide a repeat prescription with regular review of weight loss
D. Recommend ceasing phentermine due to Paul’s risk of addiction
E. Refer to an endocrinologist for ongoing prescriptions
Correct Answer: C. Provide a repeat prescription with regular review of weight loss
Question 48
Jayden Holden aged 3 years, an Aboriginal boy, is brought to see you by his mother for a review of his ear. He saw you 10 days ago with his first middle ear infection and you prescribed a course of amoxicillin. His fevers have resolved but he occasionally says his ear is sore at night.
What examination finding is MOST consistent with your provisional diagnosis?
A. A hole in the tympanic membrane
B. A retracted tympanic membrane with pink edges
C. A scarred tympanic membrane
D. Blood vessels on a shiny tympanic membrane
E. Bulging red tympanic membrane
Correct Answer: B. A retracted tympanic membrane with pink edges
Question 49
Ivy Ward aged 82 years returns for results of her echocardiogram which was ordered to investigate cardiomegaly seen on a recent chest X-ray. Her echocardiogram shows an ejection fraction of 38%. She is asymptomatic. She has a history of hypertension and chronic kidney disease and is taking ramipril 5 mg orally daily. On examination her heart rate is 86/min regular and blood pressure 135/85 mmHg. She has no ankle oedema and her lungs are clear. Results from yesterday are as follows:
| Test | Result | Normal range |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium | 138 mmol/L | 135 – 145 |
| Potassium | 5.4* mmol/L | 3.5 – 5.2 |
| Chloride | 100 mmol/L | 95 – 110 |
| Urea | 7.5 mmol/L | 2.5 – 8.0 |
| Creatinine | 87 mmol/L | 45 – 90 |
| Estimated glomerular filtration rate | 52* ml/min/1.73m² | > 90 |
Which is the MOST appropriate adjustment to her medication regime?
A. Change ramipril to sacubitril-valsartan 24 mg/26 mg orally twice daily
B. Commence bisoprolol 1.25 mg orally daily
C. Commence hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg orally daily
D. Commence spironolactone 25 mg orally daily
E. Increase ramipril to 10 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: B. Commence bisoprolol 1.25 mg orally daily
Question 50
Ron Byzart aged 69 years is brought in by his daughter Sarah as he has become confused. Sarah says that over the past two weeks Ron has been tired and has had nausea. He has been drinking more water than usual and has complained of bad breath. He has had type 2 diabetes for eight years and hypertension for five years. His regular medications include metformin modified-release 2 g orally daily, dapagliflozin 10 mg orally daily, atorvastatin 40 mg orally daily, and irbesartan 300 mg orally daily. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 36.5 °C, heart rate 69/min regular, blood pressure 140/85 mmHg, respiratory rate 32/min, and body mass index 30 kg/m².
Cardiovascular and abdominal examination is normal. His random blood glucose is 11.8 mmol/L.
What is the MOST appropriate investigation to support your provisional diagnosis?
A. Electrocardiograph
B. Full blood examination
C. Serum sodium level
D. Upper abdominal ultrasound
E. Urine dipstick for ketones
