Case 1: Yaku Tanaka
Yaku Tanaka, aged five months, is brought in by his father, Mo. Mo says that Yaku has been unwell for two days with a mild runny nose, has felt hot and has not been drinking as much as normal. Today Mo has noticed that Yaku has been increasingly distressed and looks like he is having trouble breathing. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded. Yaku has no significant past medical history, takes no regular medications and has no known allergies. His immunisations are up to date. He was born at term, had no complications at birth and is meeting appropriate developmental milestones. He is exclusively breastfed (including bottles of expressed breastmilk) and is growing on the 50th centile. Yaku usually attends daycare three days a week. Mo has a history of asthma and smokes 20 cigarettes per day.
Question 1
What additional specific physical examination findings would indicate that Yaku requires admission to hospital? Write four (4) specific physical examination findings.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 2
Yaku’s parents return to see you one week later. They explain that Yaku deteriorated after seeing you and has been in hospital for the last five days. He required oxygen for the first three days but has not required supplemental oxygen since. They are unsure of any follow-up or further management required for Yaku. The results of Yaku’s nasopharyngeal swab performed in hospital are as follows:
| Pathogen | Result |
|---|---|
| Influenza A virus | Negative |
| Influenza B virus | Negative |
| Parainfluenza virus | Negative |
| Adenovirus | Negative |
| Respiratory syncytial virus | Positive* |
| Bordetella pertussis | Negative |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Negative |
What specific advice is appropriate? Write four (4) specific pieces of advice.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 3
Yaku is brought back to see you six weeks later by his distressed maternal grandmother, Miyu. Miyu says that Yaku’s mother and father have had a big argument and that they left Yaku with her. She has been unable to contact them. She shows you multiple bruises upon his arms and torso. Miyu lives locally and has previously regularly looked after Yaku while his parents were working.
What immediate management actions are appropriate? Write three (3) immediate management actions.
- …
- …
- …
Case 2: Jack Sie
Jack Sie, aged 39 years, comes in holding his left shoulder. Four hours ago he was playing football when he was hit on the back of his left shoulder and felt sudden sharp pain and his shoulder ‘popped’. Since then, he has had an ongoing ache and difficulty moving his shoulder. Jack has no significant past medical history, takes no regular medications and has no known allergies. He does not smoke and drinks two standard drinks of alcohol three nights per week. On examination, Jack looks uncomfortable. His temperature is 36.8 °C, blood pressure is 131/87 mmHg, heart rate 65/min regular and body mass index is 24.5 kg/m2.
Question 4
What specific examination findings would help to confirm the most likely diagnosis? Write three (3) specific examination findings.
- …
- …
- …
Question 5
A few months later, Jack returns with ongoing shoulder pain. He has been seeing a physiotherapist for conservative management of his shoulder pain but has not had significant improvement. An ultrasound arranged by the physiotherapist shows a large subacromial/subdeltoid effusion with bunching on abduction. His physiotherapist has suggested a subacromial steroid injection. Jack asks you to explain the possible risks of a subacromial steroid injection.
What specific risks of a subacromial steroid injection are appropriate to discuss with Jack? Write four (4) specific risks.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 6
Jack returns to see you one week later. He is extremely upset and explains that the doctor who performed his injection was very rude and dismissive. He says the procedure was very painful and he thinks the needle was the same one used on the patient before him. He says that he has tried to contact the doctor concerned and has also written a letter to the practice but has not heard back. He asks for your help to make a ‘formal complaint’.
What management actions are appropriate? Write three (3) management actions.
- …
- …
- …
Case 3: Kimberley Bradford
Kimberly Bradford, aged 47 years, is a regular patient of your practice. Her usual GP is on leave and cannot be contacted. Kimberly requests a prescription for clonidine. She says that she has been on clonidine for the last three years. Her GP prescribed it for her difficulty in getting to sleep and nightmares. The nightmares began after Kimberly was in a car crash in which her friend died. Kimberly denies low mood or thoughts of self-harm. She has not tried any other treatments. Kimberly’s past medical history includes post-traumatic stress disorder, psoriasis, chronic low back pain and previous opioid dependence for which she is prescribed clonidine 600 mcg orally at night, naproxen 500 mg orally twice daily as required and oxycodone 2.5 mg orally daily as required. She has no known allergies. Kimberly’s back pain has been present for two years and she has previously seen a multidisciplinary pain clinic. No underlying pathology has been found for her back pain. On examination, Kimberly looks well though drowsy and has constricted pupils. Her temperature is 37.2 °C, blood pressure is 108/66 mmHg, heart rate is 50/min regular and body mass index is 24.5 kg/m2. Her electrocardiogram is as shown below (see image).
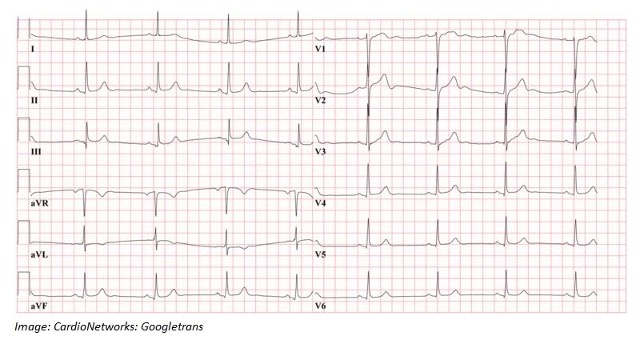
What is the single most likely diagnosis to account for the findings shown on the electrocardiogram? Write one (1) diagnosis.
- …
Question 8
What management actions are appropriate? Write two (2) management actions.
- …
- …
Question 9
Kimberly asks for a repeat script of oxycodone. She says that her prescribed dose has been insufficient and that she has been using oxycodone 10 mg orally twice per day for the last few weeks.
What non-pharmacological management actions are appropriate? Write four (4) nonpharmacological management actions.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 10
Kimberly returns to the practice one month later. She describes worsening sleep difficulties, nightmares and increasing anxiety. Kimberly has been unable to attend work due to her anxiety.
She asks if she would be eligible for a Centrelink disability pension.
What specific advice is appropriate regarding eligibility for a Centrelink disability pension? Write three (3) specific pieces of advice.
- …
- …
- …
Case 4: Jake Stevens
Jake Stevens, aged 12 months, presents as a new patient for his 12-month immunisations with his mother and father, Tara and Cayle. Tara and Cayle are concerned about his measles, mumps and rubella vaccine and ask to receive the vaccine as separate vaccinations. Jake has no significant past medical history, takes no regular medications and has no known allergies. Jake was born via normal vaginal delivery at term. He is growing along the 50th centile and meeting appropriate developmental milestones. Jake’s immunisations are up to date, but Tara and Cayle tell you that they delayed each of his pneumococcal immunisations by one month as they were worried about Jake having too many immunisations at once. On examination, Jake looks well. His temperature is 36.9 °C, heart rate 120/min regular, weight is 9.6 kg, length is 76 cm and head circumference is 46 cm (50th centile). On examination of his scrotum, you find that neither of Jake’s testes are located in the scrotum. The testes are normal in size, palpable in the inguinal canal and cannot be palpated into the scrotum. The remainder of his examination is normal.
Question 11
What advice is appropriate regarding the request for single vaccinations? Write four (4) pieces of advice.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 12
What management actions are appropriate for the scrotal examination findings? Write two (2) management actions.
- …
- …
Question 13
What long term complications may arise as a consequence of the scrotal examination findings? Write two (2) long term complications.
- …
- …
Case 5: Anastacia Sanders
Anastacia Sanders, aged 28 years, presents after a positive home pregnancy test one week ago. She has a regular 28-day cycle and her last menstrual period was seven weeks ago. She feels tired but otherwise well. Anastacia has no significant past medical history and has no known allergies. She is taking a pre-natal vitamin supplement, but no other regular medications. She does not smoke, drink alcohol or use recreational drugs. Her cervical screening test is up to date. On examination Anastacia looks well. Her temperature is 36.7 °C, blood pressure is 115/65 mmHg, heart rate 72/min regular and body mass index is 20 kg/m2 . The remainder of her examination is normal.
Question 14
What investigations are appropriate? Select six (6) investigations from the following list.
- Cytomegalovirus serology
- First pass urine for gonorrhoea polymerase chain reaction
- Full blood count
- Glucose tolerance test
- Glycosylated haemoglobin
- Hepatitis B surface antibody
- Hepatitis B surface antigen
- Hepatitis C antibody
- Human immunodeficiency virus serology
- Iron studies
- Liver function tests
- Parvovirus serology
- Rubella immunoglobulin G
- Syphilis serology
- Thyroid stimulating hormone
- Toxoplasmosis serology
- Urea and electrolytes
- Urine for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
- Vaginal swab for group B streptococcus
- Varicella immunoglobulin G
- Vitamin D
Question 15
Anastacia’s investigations are normal. Her blood group is A negative. Anastacia presents two weeks later. She reports a single episode of vaginal spotting overnight. She has had no abdominal pain. On examination, Anastacia looks well. Her temperature is 36.9 °C, blood pressure is 118/70 mmHg and heart rate 70/min regular. Examination of her abdomen reveals no tenderness, masses or guarding. The remainder of her examination is normal.
What are the most likely differential diagnoses? Write three (3) differential diagnoses.
- …
- …
- …
Question 16
You arrange a pelvic ultrasound later that day to assess Anastacia’s episode of bleeding. The report is as follows: “A gestational sac is seen in the uterus with mean sac diameter of 28 mm but a fetal pole is not visible.”
You managed Anastacia appropriately and arrange a repeat pelvic ultrasound seven days later that reveals the same findings.
What immediate management options are appropriate? Write four (4) management actions.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Case 6: Shelby Hope
Shelby Hope, aged 25 years, reports a two-day history of lower abdominal pain. The pain developed over a few hours. It is a cramping pain. She rates the pain 4 out of 10 and explains it is mainly on the right lower side of her abdomen. Shelby had her period when due last week and it was very painful. Her periods have become increasingly painful and longer in duration over the last few years. Shelby has no significant past medical history, takes no regular medications and has no known allergies. She does not smoke, drink alcohol or use recreational drugs.
On examination, Shelby looks well. Her temperature is 37.4 °C, blood pressure is 118/79 mmHg, heart rate 89/min regular, respiratory rate is 14/min and body mass index is 23 kg/m2 . Examination of her abdomen reveals mild tenderness on her right iliac fossa, with no guarding or rebound. The remainder of her examination is normal. A home urine pregnancy test is negative.
Question 17
What are the most likely differential diagnoses? Write five (5) differential diagnoses.
- …
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 18
What initial investigations are appropriate? Select five (5) investigations from the following list.
- Cancer antigen 125
- Coeliac serology
- Colonoscopy
- Computed tomography scan of abdomen
- Faecal calprotectin
- Faeces for microscopy, culture, and sensitivities
- Faeces ova, cysts and parasites
- First pass urine for chlamydia polymerase chain reaction
- First pass urine for gonorrhoea polymerase chain reaction
- Follicle stimulating hormone
- Free androgen index
- Full blood count
- Human immunodeficiency virus serology
- Iron studies
- Luteinizing hormone
- Serum beta human-chorionic gonadotrophin
- Serum testosterone
- Syphilis serology
- Thyroid stimulating hormone
- Ultrasound scan of abdomen
- Ultrasound scan of kidneys, ureters and bladder
- Ultrasound scan of pelvis
- Urea and electrolytes
- Urine for microscopy, culture, and sensitivity
Question 19
Shelby is managed appropriately and makes a full recovery. Shelby returns to see you six months later. She has always had significant pain with penetrative sex and finds it difficult to insert a tampon. She is very distressed by her symptoms. Shelby does not consent to a physical examination.
What non-pharmacological management actions are appropriate? Write four (4) nonpharmacological management actions.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Case 7: Jennifer Symonds
Jennifer Symonds, aged 77 years, presents to your remote clinic with a painful and swollen left wrist. She tripped when walking her dog earlier this morning. Her husband drove her to the appointment as she was in too much pain to drive. She did not sustain any other injuries. Jennifer’s past medical history includes gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, for which she takes omeprazole 20 mg orally daily. She has an allergy to opiate analgesia, which causes severe nausea and vomiting. Jennifer smokes six cigarettes per day and drinks three to four standard drinks of alcohol four nights per week.
On examination, Jennifer looks well. Her temperature is 36.5 °C, blood pressure is 132/92 mmHg, heart rate 82/min regular and body mass index is 23 kg/m2.
She has swelling and tenderness over her left distal forearm and wrist. She has limited movement of her wrist due to pain and her grip strength is reduced. The remainder of her examination is normal. You arrange an X-ray of her left wrist (see image).
The nearest emergency department is 400 km away.
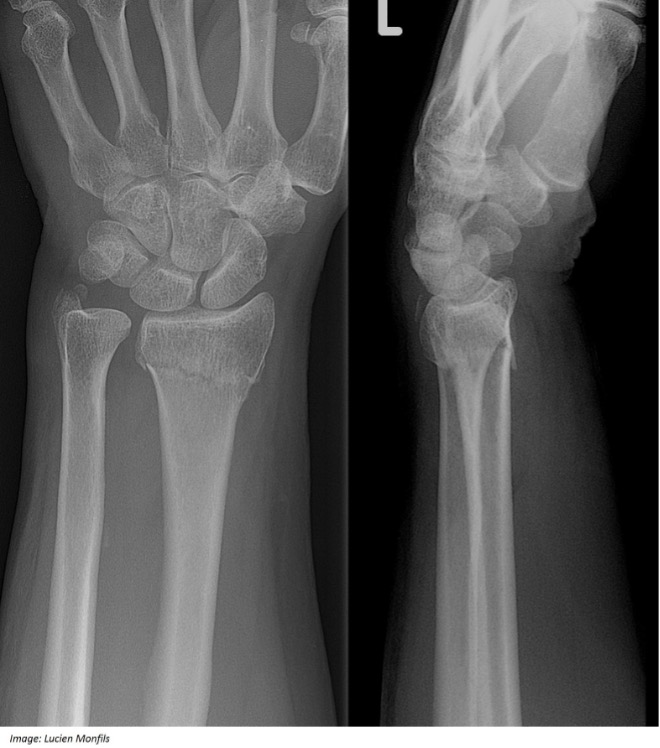
Question 20
What immediate management actions are appropriate? Write three (3) immediate management actions, including dosing where appropriate.
- …
- …
- …
of a Colles fracture?
Question 21
Jennifer returns for review six weeks after her injury. She has ongoing mild pain in her wrist and has been unable to resume some of her normal activities. On examination, she has residual swelling of her left wrist with persistent tenderness.
What immediate non-pharmacological management actions are appropriate? Write three (3) nonpharmacological management actions.
- …
- …
- …
Question 22
You see Jennifer again four months later and take the opportunity to discuss strategies to reduce her risk of a future fracture. What specific non-pharmacological management advice is appropriate?
Write four (4) specific pieces of non-pharmacological management advice.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 23
You arrange further investigations that confirm the most likely underlying diagnosis. You decide to commence pharmacological management to prevent further fractures.
What specific pharmacological management options are appropriate? Write three (3) specific pharmacological management options (dosing is not required).
- …
- …
- …
Case 8: Gideon Cohen
Gideon Cohen, aged 30 years, is a new patient. He requests a “general check-up” as he and his wife are planning to try to conceive their first child. Gideon has no significant past medical history, takes no regular medications and has no known allergies. He has never smoked and drinks three to four standard drinks of alcohol two days per week. He works as an accountant. Gideon’s father died six months ago from an acute myocardial infarct, aged 52 years, and his paternal uncle underwent coronary bypass surgery aged 54 years. He has two brothers aged 28 years and 24 years. On examination, Gideon looks well. His temperature is 37.1 °C, blood pressure is 128/83 mmHg, heart rate 71/min regular and body mass index is 22.5 kg/m2 .
You arrange fasting blood tests with results as follows:
Full blood count – Normal
Urea and electrolytes – Normal
Urate – Normal
Fasting glucose – Normal
Lipid studies (fasting)
| Test | Result | Normal Range |
|---|---|---|
| Total cholesterol | 7.6* mmol/L | < 5.6 |
| High-density lipoprotein | 0.8* mmol/L | > 1.0 |
| Low-density lipoprotein | 5.0* mmol/L | < 2.5 |
| Triglycerides | 2.3* mmol/L | < 1.5 |
| Non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol | 6.8* mmol/L | < 4.6 |
| Low-density lipoprotein: High-density lipoprotein ratio | 6.25* mmol/L | < 3.7 |
| Total cholesterol: High-density lipoprotein ratio | 9.5* mmol/L | < 0.45 |
Question 24
What is the most likely diagnosis? Write one (1) diagnosis.
- …
Question 25
What specific examination findings would help to confirm the most likely diagnosis? Write two(2) specific examination findings.
- …
- …
