Question 1
Tamika Edwards, aged 23 years, has a four-day history of fevers, a runny nose, sore throat, and a cough. She has had difficulty completing her university assignment because she has felt so tired. She has tried taking some over-the-counter cold and flu medications, but this has not helped. She wants to know if she can get something “stronger” on prescription. She is a non-smoker, and her only medication is an etonorgestrel 68 mg implant. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 37.5°C, heart rate 80/min regular, and respiratory rate 20/min. She has clear rhinorrhoea, erythematous tympanic membranes bilaterally, and pharyngeal erythema, but her chest is clear with equal breath sounds.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Amoxicillin 500 mg orally three times daily for five days
B. Amoxicillin-clavulanate 875 mg/125 mg orally twice daily for five days
C. Chest X-ray
D. Fexofenadine 120 mg orally daily
E. Oseltamivir 75 mg orally twice daily for five days
F. Pseudoephedrine 60 mg orally up to four times daily
G. Rest, oral fluids, and paracetamol as required
H. Serology for Epstein–Barr virus
I. Throat swab for microscopy, culture, and sensitivities
Correct Answer: G. Rest, oral fluids, and paracetamol as required
Question 2
Annie Lim, aged 41 years, presents today for test results. For the past two weeks, she has had infrequent irregular heartbeats occurring at any time of the day. These heartbeats are associated with an uncomfortable sensation in her chest lasting one or two seconds. She has not felt lightheaded or breathless with these episodes. On examination, her heart rate is 72/min regular, blood pressure 122/78 mmHg, and cardiovascular examination is normal. Full blood examination, serum electrolytes, and thyroid function tests performed two days ago were normal. An echocardiogram is normal. An electrocardiogram is performed while she experiences the irregular heartbeat.
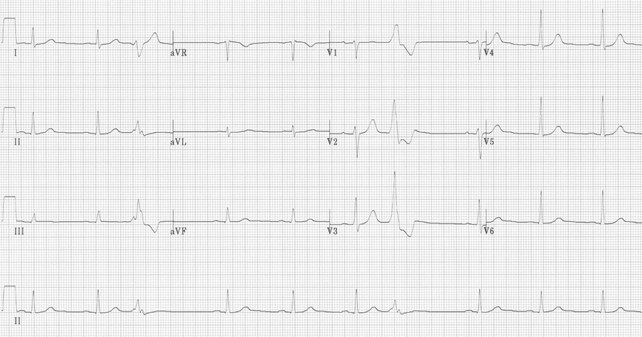
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Apixaban 5 mg orally twice daily
B. Aspirin 100 mg orally daily
C. Exercise stress test
D. Flecainide 50 mg orally twice daily
E. Metoprolol 25 mg orally twice daily
F. Reassure no further management required
G. Stress echocardiogram
H. Troponin
Correct Answer: F. Reassure no further management required
Question 3
Zach Bennett, aged 23 years, returned two days ago from a backpacking trip through Borneo. He has been unwell for the past three days with abdominal cramping, watery diarrhoea, and nausea. Zach has been taking loperamide and is tolerating an oral rehydration solution. This morning he noticed a small amount of blood in his stool. On examination, his temperature is 37.9°C, heart rate 82/min regular, blood pressure 110/65 mmHg lying and 108/60 mmHg standing, and his mucous membranes appear mildly dry. Zach’s abdomen is generally tender but soft with frequent bowel sounds. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Admit to hospital for intravenous rehydration
B. Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid 875 mg/125 mg orally twice daily for five days
C. Azithromycin 1 g orally initially then 500 mg orally daily for a further two days
D. Clindamycin 450 mg orally three times daily for five days
E. Continue current treatment
F. Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for seven days
G. Metronidazole 400 mg orally twice daily for five days
H. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole 160 mg/800 mg orally twice daily for five days
Correct Answer: C. Azithromycin 1 g orally initially then 500 mg orally daily for a further two days
Question 4
Emilia Urquijo, aged 3 weeks, is brought in by her parents who are concerned that her breathing sounds quite loud when she is lying on her back. Emilia has been feeding well and is gaining weight appropriately. On examination, she is alert and afebrile, her breathing is regular and relaxed, she has normal oxygen saturation, a normal-sounding cry, and her chest is clear to auscultation. During the examination, when she is lying flat on her back, you note a very soft high-pitched noise on inspiration.
What is the MOST appropriate diagnosis?
A. Bilateral vocal cord paralysis
B. Branchial cleft cyst
C. Croup
D. Foreign body aspiration
E. Laryngomalacia
F. Thyroid tumour
G. Tuberculosis
H. Vocal cord nodules
Correct Answer: E. Laryngomalacia
Question 5
Evelyn Kinston, aged 45 years, has a painful and swollen right ankle after “rolling” it while walking down a hill yesterday. She felt a “crunching” sensation when it occurred. The swelling has gradually increased overnight. On examination, she has an antalgic gait. The lateral side of her right ankle is visibly swollen and is tender to palpation, particularly over the distal margin of the lateral malleolus. Further examination of her foot is unremarkable. You refer her for an X-ray.
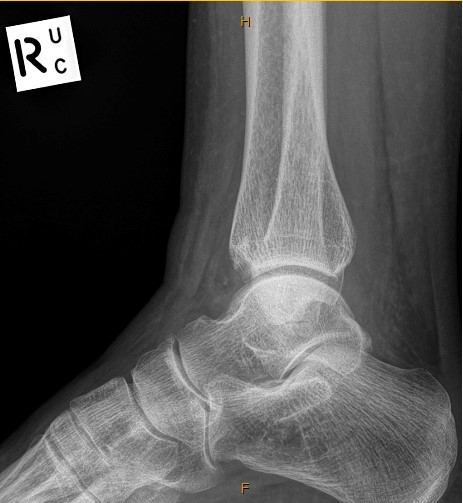
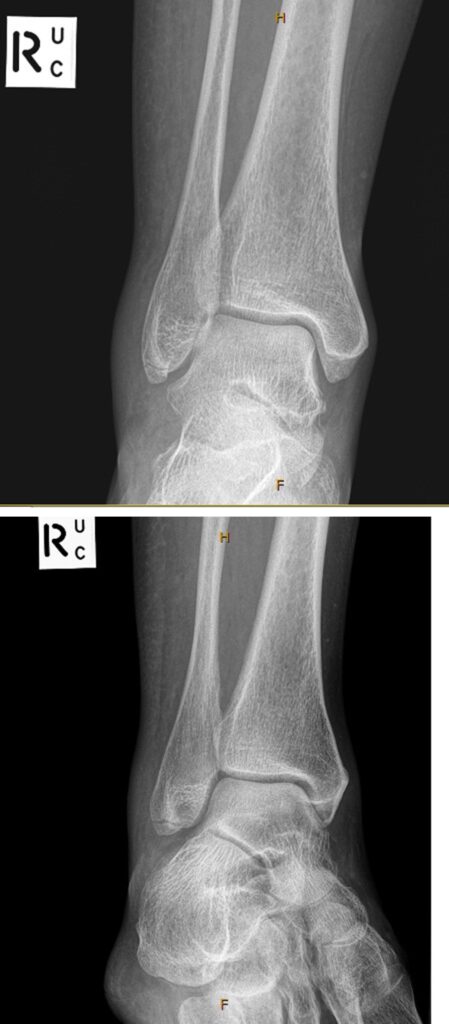
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Below-knee split plaster of Paris cast for six weeks
B. Computed tomography scan of the right foot
C. Controlled action motion walker (“moon boot”) for one to two weeks
D. Podiatry referral for stretching exercises
E. Urgent orthopaedics referral for operative management
Correct Answer: C. Controlled action motion walker (“moon boot”) for one to two weeks
Question 6
Jemima Holmes, aged 37 years, returns for the removal of sutures 10 days after a skin cancer excision from her left arm. The lesion was identified during a routine full-body skin examination and was excised with 5 mm surgical margins. Jemima’s histopathology report showed a superficial-spreading melanoma in situ, 5 mm in width. The lesion was removed with a minimum of 6 mm microscopic margins. Jemima asks what further management she requires.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Arrange recall in six to 12 months for a skin check
B. Chest X-ray
C. Organise a wider local excision with at least 10 mm margins
D. Refer for a sentinel node biopsy
E. Refer to an oncologist for consideration of a positron emission tomography scan
Correct Answer: A. Arrange recall in six to 12 months for a skin check
Question 7
Carol Ike, aged 68 years, developed streaks of light on the extreme left of her vision last night. She thinks she has seen little “spots” floating in her vision since that time. On examination, her visual acuity with glasses on is 6/6 in both eyes. Examination of her visual fields is normal.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Acute glaucoma
B. Amaurosis fugax
C. Central retinal artery occlusion
D. Occipital lobe tumour
E. Optic neuritis
F. Posterior vitreous detachment
G. Retinal detachment
H. Retinal migraine
I. Vertebrobasilar transient ischaemic attack
Correct Answer: F. Posterior vitreous detachment
Question 8
Georgia Yare, aged 12 years, presents to your clinic on her own. She asks for a medical certificate as she has not been to school for two days. She tells you she keeps hearing her grandfather’s voice telling her to do “nasty” things. She says her friends are “whispering behind her back.” She agrees that she might be depressed but does not want to see a psychiatrist. In your room, she avoids looking at your eyes, and her face is without emotion. She does not want you to talk to her parents. She does not have any current thoughts of self-harm.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Complete an involuntary treatment order and organise transfer to hospital for psychiatric assessment
B. Contact her parents to discuss Georgia’s ongoing care
C. Explain that she must complete a urine drug screen before leaving the premises
D. Fluoxetine 10 mg orally daily and review in two weeks
E. Provide her with a medical certificate and ask her to return next week for a mental health care plan
Correct Answer: B. Contact her parents to discuss Georgia’s ongoing care
Question 9
Natalie Elder, aged 32 years, is 11 weeks pregnant and returns for her blood test results. She has had mild nausea with occasional vomiting but is otherwise well. Her clinical examination is appropriate for her gestation, and her body mass index is 27.8 kg/m². She had an ultrasound scan last week; results were appropriate for gestational age. She does not want genetic screening. Natalie has a past history of long-term stable subclinical hypothyroidism that has not required medication. Blood test results completed yesterday are as follows:
- Thyroid stimulating hormone: 5.2 mIU/L (Normal range: 0.1 – 2.5 for first trimester)
- Free T4: 8 pmol/L (Normal range: 10 – 20)
- Anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies: 25 IU/mL (Normal range: < 60)
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Foetal growth scan at 14 weeks gestation
B. Increase dietary intake of iodine-rich foods
C. Nuclear thyroid scan
D. Reassure Natalie that she requires no further thyroid follow-up
E. Repeat Natalie’s thyroid studies today including T3
F. Repeat thyroid function tests in six weeks
G. Thyroxine 50 mcg orally daily
H. Ultrasound of the thyroid
Correct Answer: G. Thyroxine 50 mcg orally daily
Question 10
Thomas Englehart, aged 73 years, has a painful itchy rash on the sole of his left foot. It has worsened over the last few months. He has tried using over-the-counter hydrocortisone 1% cream and a four-week course of miconazole 2% ointment topically; however, the rash has not significantly improved. He usually plays golf often, but the pain is limiting his ability to play. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 36.2°C, and his foot is as shown.
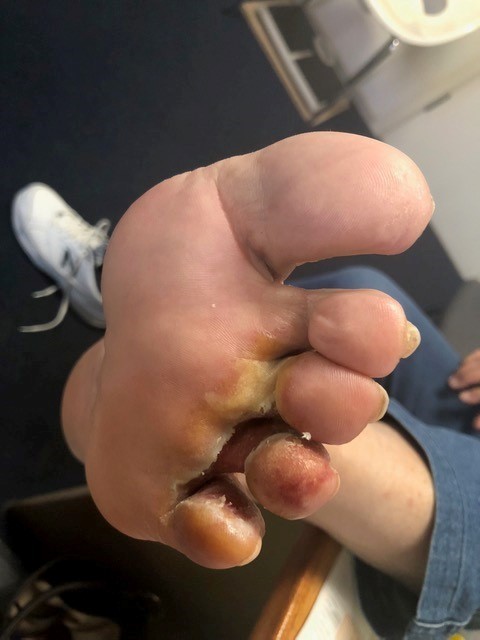
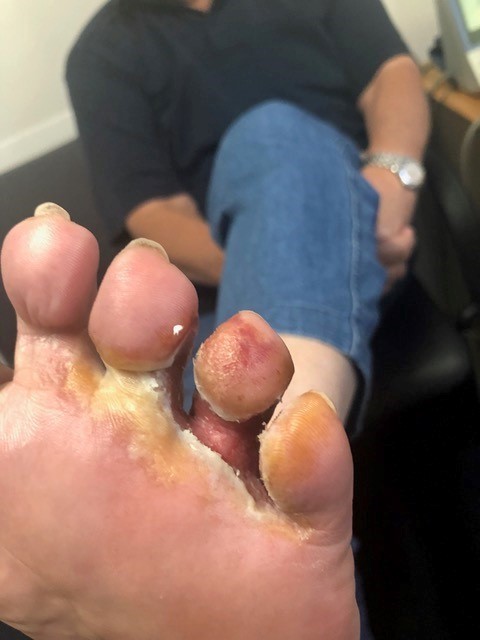
What is the MOST appropriate treatment?
A. Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid 875 mg/125 mg orally twice daily for 10 days
B. Betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% ointment topically twice daily for two weeks
C. Calcipotriol-betamethasone dipropionate 0.005%/0.05% ointment topically once daily for four weeks
D. Cephalexin 500 mg orally four times daily for 10 days
E. Erythromycin 400 mg orally four times daily for seven days
F. Famciclovir 250 mg orally three times daily for seven days
G. Hydrocortisone-clotrimazole 1%/1% cream topically twice daily for two weeks
H. Mupirocin 2% ointment topically three times daily for 10 days
I. Prednisolone 50 mg orally daily for seven days
J. Terbinafine 250 mg orally daily for two weeks
Correct Answer: J. Terbinafine 250 mg orally daily for two weeks
Question 11
Jacinta Hall, aged 48 years, is feeling flat and tired as she has not been sleeping well for the past two months. She has followed your recommendations regarding sleep hygiene, but her sleep remains very disturbed. She has been under stress at work but expects this to settle down in the next few weeks. She last had a light period three months ago. She has hot flushes at night, which interfere with her sleep. Jacinta has hypertension, which is well controlled with perindopril 5 mg orally daily, and she had a levonorgestrel-containing intrauterine device inserted 12 months ago for contraception.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Amitriptyline 10 mg orally at night
B. Diazepam 5 mg orally at night
C. Melatonin prolonged release 2 mg orally at night
D. Oestradiol 50 mcg 24-hour patch transdermally applied twice weekly
E. Tibolone 2.5 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: D. Oestradiol 50 mcg 24-hour patch transdermally applied twice weekly
Question 12
Shenayah Ah See, aged 12 years, an Aboriginal girl, is brought in by her mother. Shenayah has had fevers and a lumpy rash on her arms for one week. She has felt sore all over, especially in different joints. After a day or two, a joint feels better, but then the pain begins again in another joint. Shenayah is normally well, although she did have “school sores” a month ago which resolved without treatment. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 39.0°C. Her left knee and ankle are swollen and are tender when palpated. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
What is the MOST appropriate investigation to support your provisional diagnosis?
A. Dengue virus serology
B. Epstein–Barr virus serology
C. Joint aspiration of left knee
D. Serum antistreptolysin O titre
E. Serum rheumatoid factor
Correct Answer: D. Serum antistreptolysin O titre
Question 13
Gerald McMahon, aged 78 years, is brought in by his wife Mary who is concerned about Gerald’s increasing confusion over the past two days. He has been forgetting what day it is and has had difficulty finding his way around their home. He has also had “tingling” in his lips and hands and painful muscle cramps. You last saw Gerald four weeks ago for renewal of his regular prescriptions and administration of his six-monthly denosumab for osteoporosis. Gerald’s past history includes gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, hypertension, and mild renal impairment. He also takes perindopril 5 mg orally daily and omeprazole 20 mg orally daily. On examination, Gerald does not recognise you and is not oriented to time and place. His tympanic temperature is 37.2°C, heart rate 82/min regular, and blood pressure 135/64 mmHg.
Which investigation is MOST likely to confirm the underlying cause of his presenting symptoms?
A. C-reactive protein
B. Chest X-ray
C. Computed tomography of the head
D. Nuclear bone scan
E. Serum calcium
F. Serum electrophoresis
G. Serum potassium
H. Urine Bence-Jones protein
Correct Answer: E. Serum calcium
Question 14
Anna Meales, aged 38 years, has had a burning rash on her chin over the last month. Initially, she wondered whether it was due to new makeup she used, but she has stopped using all makeup now, and the rash is persisting. She is not keen on taking any tablets for this but is willing to try a cream.
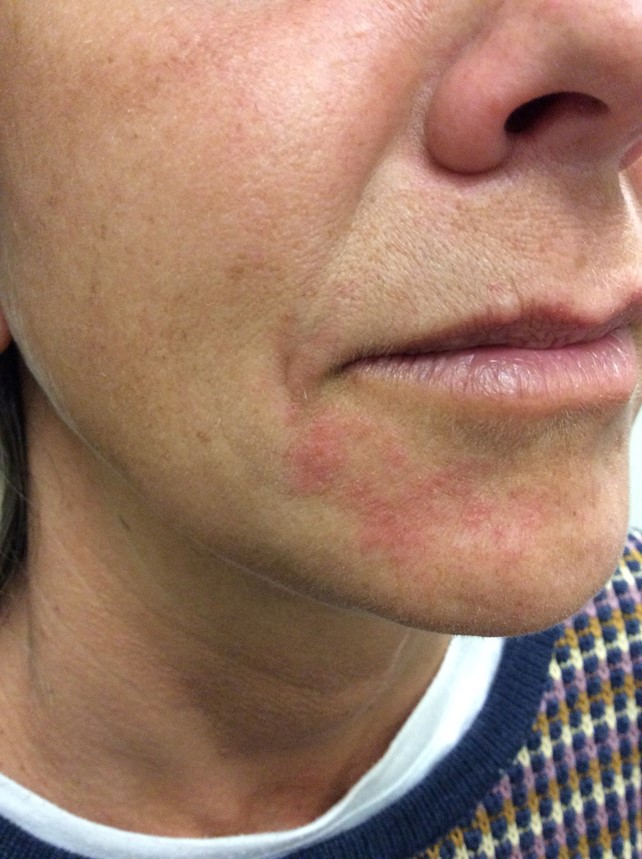
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Benzoyl peroxide 5% cream topically twice daily
B. Brimonidine 0.33% gel topically once daily
C. Hydrocortisone 1% cream topically twice daily
D. Hydrocortisone-clotrimazole 1%/1% cream topically twice daily
E. Metronidazole 0.75% cream topically twice daily
F. Mometasone 0.1% cream topically once daily
G. Mupirocin 2% cream topically twice daily
H. Terbinafine 1% cream topically twice daily
Correct Answer: E. Metronidazole 0.75% cream topically twice daily
Question 15
Theresa Banks, aged 74 years, has been brought in by her daughter, who is concerned about the appearance of Theresa’s toenails. Theresa has had increasing difficulty cutting her nails.
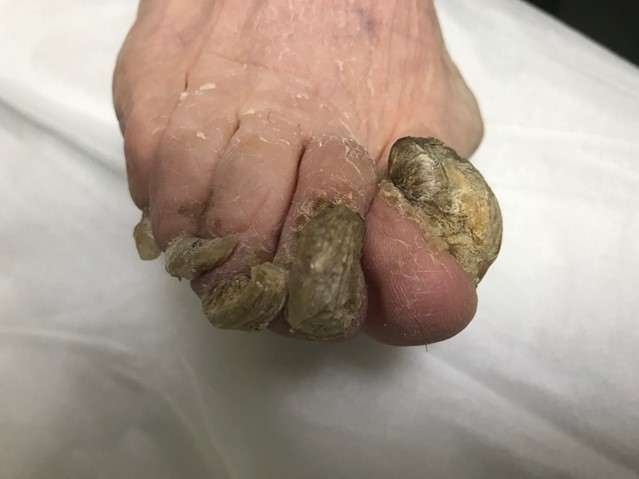
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Chronic paronychia
B. Dermatomycosis
C. Iron deficiency
D. Nail bed squamous cell carcinoma
E. Onychogryphosis
F. Pyogenic granuloma
G. Subungual exostoses
H. Tuberous sclerosis
Correct Answer: E. Onychogryphosis
Question 16
John Jake, aged 30 months, presents with his mother Sarah who is concerned that John has not grown very much since he was age 18 months. John’s measurements today are shown on the growth chart (see image).
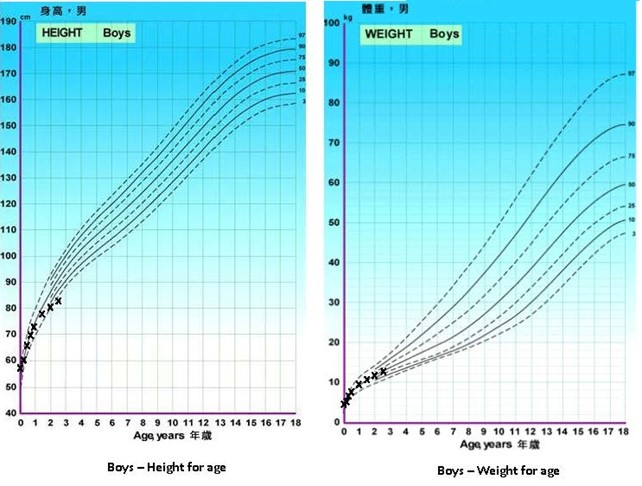
Physical examination reveals a small penis with stretched penile length 2.3 cm (normal range mean 5.1 +/- 0.9 cm). An X-ray of John’s non-dominant hand gives the following results:
Findings: The patient’s chronological age is 30 months. His bone age is most compatible with <18 months.
Impression: Delayed bone age with respect to the age and gender-matched standards.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Constitutional delay
B. Familial short stature
C. Growth hormone deficiency
D. Hypothyroidism
E. Malnutrition
Correct Answer: C. Growth hormone deficiency
Question 17
Domenica Pirotta, aged 54 years, presented 12 months ago with symptoms consistent with gastro-oesophageal reflux. At that time, she started taking pantoprazole 20 mg orally daily and made appropriate lifestyle changes. Her symptoms continued, and she had a gastroscopy two months ago which showed evidence of mild erosive oesophagitis. Her dose of pantoprazole was increased to 20 mg orally twice daily, leading to the complete resolution of her symptoms. Domenica is keen to cease pantoprazole and has reduced the dose on several occasions over the past two months. Unfortunately, each time her symptoms recurred.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Change pantoprazole to esomeprazole 20 mg orally twice daily
B. Continue pantoprazole 20 mg orally twice daily
C. Decrease pantoprazole to 20 mg orally daily and advise her to take a probiotic
D. Decrease pantoprazole to 20 mg orally daily and start domperidone 10 mg orally three times daily
E. Refer her for repeat gastroscopy
Correct Answer: B. Continue pantoprazole 20 mg orally twice daily
Question 18
David Franklin, aged 38 years, reports increasing difficulty performing his job as a courier driver. He feels fatigued and has had increasing lower back stiffness and pain over the past five months, particularly at the start of his early morning shifts. He finds the pain is worse after sitting or lying down but improves when he gets moving again. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 36.8°C, heart rate 72/minute regular, and blood pressure 115/69 mmHg. He has a normal gait and mild tenderness over his right sacroiliac joint. He has a reduced range of motion in forward flexion of the lumbar spine and normal hip flexibility. You arrange X-rays of his lumbar spine and pelvis, both of which are reported as normal.
What is the MOST appropriate investigation to support your provisional diagnosis?
A. Anti-nuclear antibody
B. Anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies
C. Computed tomography lumbosacral spine
D. Human leucocyte antigen B27
E. Iron studies
F. Nerve conduction studies of the lower limbs
G. Radionuclide bone scans
H. Serum B12 level
I. Urine for Bence-Jones protein
Correct Answer: D. Human leucocyte antigen B27
Question 19
Harvey Windsor, aged 13 years, has been unwell for three weeks. He feels lethargic, has not been playing his usual sports, and has a persistent dry cough day and night. He has also had headaches. One week ago, he was prescribed five days of amoxicillin 500 mg orally three times daily, but his symptoms have not improved. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 38.2°C, heart rate 98/min regular, and blood pressure 110/70 mmHg. He has crackles present in both lung fields and mild expiratory wheeze. You arrange appropriate further investigations.
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid 875 mg/125 mg orally twice daily for five days
B. Ciprofloxacin 750 mg orally twice daily for seven days
C. Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for seven days
D. Fluticasone proprionate-salmeterol 100 mcg/50 mcg inhaled twice daily
E. Oseltamivir 75 mg orally twice daily for five days
Correct Answer: C. Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for seven days
Question 20
Steven Jerome, aged 57 years, had a non-ST elevation myocardial infarct two years ago and was started on atenolol 25 mg orally daily, perindopril 4 mg orally daily, rosuvastatin 20 mg orally daily, and aspirin 100 mg orally daily. Since then, he has been more physically active, has strictly followed a Mediterranean-style diet, has given up smoking, and has had no further chest pain. His blood pressure today is 119/72 mmHg, and Steven explains he feels great and would like to reduce or stop his medication. The results of blood tests done prior to his visit today are as follows:
- Fasting glucose: 4.8 mmol/L (Normal range: <3.0 – 5.4)
- Total cholesterol: 5.1 mmol/L (Normal range: < 4.0)
- Triglycerides: 3.6 mmol/L (Normal range: < 2.0)
- High-density lipoprotein (HDL): 1.0 mmol/L (Normal range: > 1.0)
- Low-density lipoprotein: 3.2 mmol/L (Normal range: < 1.8)
- Cholesterolratio: 5.4
What is the MOST appropriate medication change?
A. Add ezetimibe 10 mg orally daily
B. Add fenofibrate 50 mg orally daily
C. Cease atenolol
D. Increase rosuvastatin to 40 mg orally daily
E. Reduce rosuvastatin to 10 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: D. Increase rosuvastatin to 40 mg orally daily
Question 21
Jacinta Perry, a veterinary nurse aged 26 years, has been feeling unwell for four days. She has been experiencing generalised fatigue, low-grade fevers, nausea, and mild headaches. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 38.0°C, blood pressure 125/75 mmHg, and she has enlarged tender right axillary lymph nodes. The remainder of her examination is normal. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Bird fancier’s lung disease
B. Cat scratch disease
C. Infectious mononucleosis
D. Psittacosis
E. Pyogenic lymphadenitis
Correct Answer: B. Cat scratch disease
Question 22
Charles Whitford, aged 76 years, has had loss of hearing and a “pulsing” sound in his left ear for the past two days. He has been using olive oil to try to remove presumed wax and asks you to syringe the wax out. On examination, his external auditory canal on both sides is clear with no wax. Audiometry is performed.
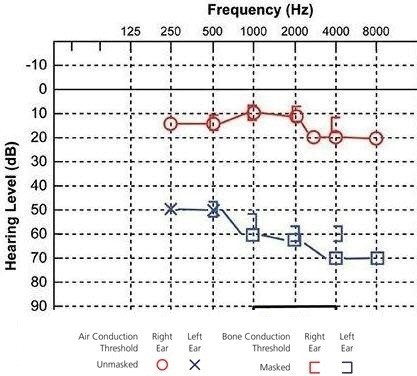
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Amoxicillin 500 mg orally three times daily for seven days
B. Betahistine 24 mg orally twice daily
C. Dexamethasone-framycetin-gramicidin 0.05%/0.5%/0.005% three drops topically to left ear three times daily for five days
D. Prednisolone 50 mg orally daily for 10 days
E. Referral for hearing aids
F. Referral to ear, nose, and throat surgeon for insertion of grommets
G. Valaciclovir 1 g orally three times daily for seven days
H. Xylometazoline 0.1% one spray into each nostril three times daily
Correct Answer: D. Prednisolone 50 mg orally daily for 10 days
Question 23
Billie Pasket, aged 6 years, has had an itchy bottom for the last two weeks. Her father has noticed Billie scratching her anus but has not noticed any change in her bowel habit or diet. Billie often wakes in the night with her symptoms. On examination, her anus appears normal.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Cephalexin 12.5 mg/kg (max 500 mg) orally four times daily for 10 days
B. Clotrimazole 1% cream applied to the area at night for two weeks
C. Mebendazole 100 mg orally stat
D. Send anal swab for microscopy and culture
E. Terbinafine 62.5 mg orally daily for four weeks
Correct Answer: C. Mebendazole 100 mg orally stat
Question 24
Glenn Andrews, aged 22 years, has pain and swelling over his left patella, which has been worsening over the past week. He works as a carpet-layer. Glenn has been resting his knee and has applied ice and a bandage to it, which he feels has improved the swelling. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 37.1°C, heart rate 77/min regular, blood pressure 110/72 mmHg, and body mass index 24 kg/m². There is tender superficial swelling over the left patella and it is warm to touch. He can extend his knee fully and can flex to 90 degrees.
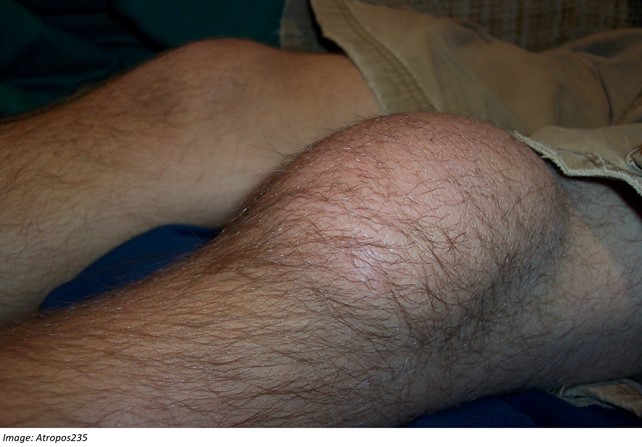
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Colchicine 1 mg orally initially, then 500 mcg one hour later
B. Diagnostic knee joint aspiration
C. Diclofenac 50 mg orally three times daily for five days
D. Dicloxacillin 500 mg orally four times daily for five days
E. Local corticosteroid injection
Correct Answer: C. Diclofenac 50 mg orally three times daily for five days
Question 25
Trudy Armitage, aged 52 years, had an irritated left eye upon waking this morning. She spent most of yesterday afternoon in the garden. She does not use glasses or contact lenses. On examination, her visual acuity is 6/6 in the right eye and 6/9 in the left eye. After fluorescein staining, her eye appears as shown. The rest of her eye examination is normal with no foreign body visible.
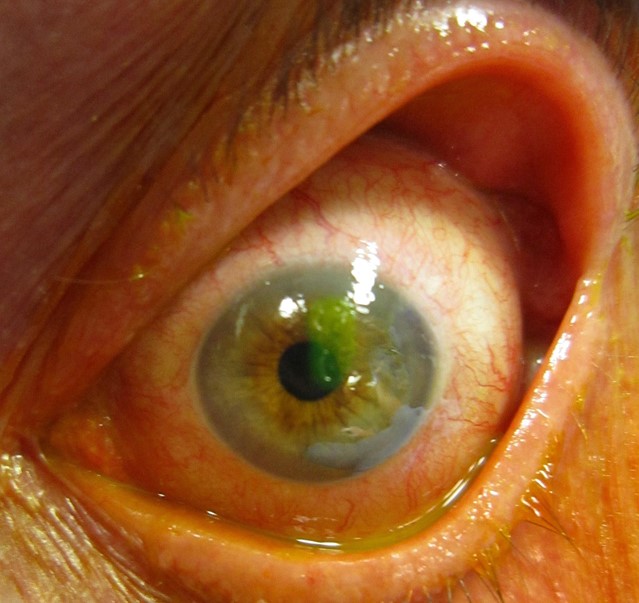
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise lubricating drops as frequently as required until irritation resolves
B. Chloramphenicol 0.5% eye drops four times daily and review in 24 hours
C. Instil tetracaine 0.5% eye drops, apply patch and review in 24 hours
D. Prednisolone 0.5% eye drops topically twice daily for seven days
E. Urgent referral to ophthalmologist today for debridement
Correct Answer: B. Chloramphenicol 0.5% eye drops four times daily and review in 24 hours
Question 26
Anthony Pine, aged 30 years, has had painful urination for two weeks. His male partner, Greg, has not had any symptoms. Anthony’s previous sexual partners have not had any symptoms. Initial investigation results are as follows:
Specimen: First-pass urine
- Chlamydia trachomatis nucleic acid amplification: Negative
- Neisseria gonorrhoea nucleic acid amplification: Negative
- Culture: No significant growth after 48 hours incubation
Urinalysis
- Collection: Mid-stream urine
| Test | Result | Normal Range |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | Negative | – |
| Glucose | Negative | – |
| Ketones | Negative | – |
| Phase contrast microscopy | ||
| Leucocytes | 200* x 10^6/L | < 10 |
| Erythrocytes | < 10 x 10^6/L | < 10 |
| Epithelial | < 10 x 10^6/L | – |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Azithromycin 1 g orally stat followed by metronidazole 400 mg orally twice daily for seven days
B. Ceftriaxone 500 mg in 2 mL of 1% lignocaine intramuscularly stat plus azithromycin 1 g orally as a single dose
C. First pass urine for mycoplasma genitalium nucleic acid amplification testing
D. Trimethoprim 300 mg orally daily for 14 days
E. Urethral swab for human papillomavirus polymerase chain reaction testing
Correct Answer: C. First pass urine for mycoplasma genitalium nucleic acid amplification testing
Question 27
Jerry Wright, aged 50 years, arrives at your rural emergency department in an agitated state, holding his hand to his face. He tells you that he developed a severe stabbing headache behind his right eye 30 minutes ago. His right eye is red and watering. He says his vision is normal. He had a similar episode at around the same time yesterday and the day before. Six weeks ago, he had an episode of this pain that woke him from sleep. A magnetic resonance imaging scan of his brain at that time revealed no structural abnormalities.
The practice nurse has begun to administer high-flow oxygen.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Ceftriaxone 2 g intravenous injection
B. Indomethacin 100 mg rectal suppository
C. Oxycodone 5 mg orally
D. Sumatriptan 6 mg subcutaneous injection
E. Tramadol 50 mg intramuscular injection
Correct Answer: D. Sumatriptan 6 mg subcutaneous injection
Question 28
Charlotte Reid, aged 73 years, has had four months of diarrhoea. She has watery bowel motions, feels bloated and full, and has had a large amount of flatus. Her past medical history includes hypertension, hypothyroidism, and bilateral hip osteoarthritis. Her medications include irbesartan 300 mg orally daily, thyroxine 100 mcg orally daily, diclofenac 50 mg orally twice daily, paracetamol 665 mg two tablets orally three times daily, and glucosamine sulfate 1500 mg orally daily. She recently had a colonoscopy, which was reported as macroscopically normal; however, the biopsy demonstrated evidence of lymphocytic colitis.
Which medication is MOST likely contributing to her symptoms?
A. Diclofenac
B. Glucosamine
C. Irbesartan
D. Paracetamol
E. Thyroxine
Correct Answer: A. Diclofenac
Question 29
Tahliah Filbert, aged 40 years, is unable to fully extend her finger. Yesterday, while trying to make the bed, she slipped and hit her right middle finger against the bedroom wall. On examination, her finger is only minimally tender to palpation, but she is unable to extend the distal interphalangeal joint (see image). You arrange an X-ray, which is reported as normal.
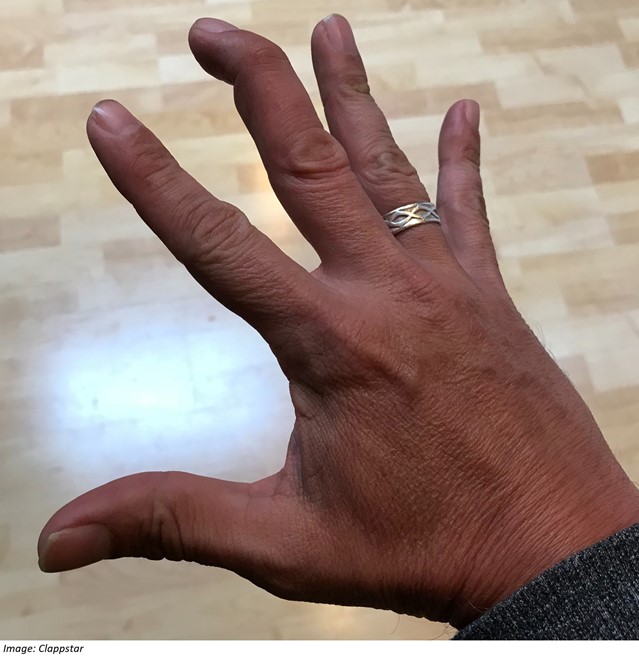
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Buddy taping it to the fourth finger for two to three weeks
B. Extension splint for six to eight weeks
C. Flexion splint for six weeks
D. Referral to a hand therapist for finger stretching exercises
E. Urgent referral to a specialist hand surgeon with a view to operative repair
Correct Answer: B. Extension splint for six to eight weeks
Question 30
Jack Cruise, aged 22 years, is brought to your rural emergency department by his sister. Jack has difficulty breathing. His sister states he began gasping for air while chopping wood about an hour ago. Jack indicates it hurts to take a deep breath. On examination, Jack is pale, his tympanic temperature is 37.2°C, heart rate 135/min regular, blood pressure 100/52 mmHg, and respiratory rate 28/min. There is prominence of his jugular veins, hyperresonance to percussion, and absent breath sounds over the left lung field.
His body mass index is 21 kg/m2.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Arrange urgent chest X-ray
B. Electrocardiogram
C. Perform urgent needle thoracostomy
D. Salbutamol 100 mcg 12 actuations inhaled via metered-dose inhaler and spacer
E. Urgent arterial blood gas analysis
Correct Answer: C. Perform urgent needle thoracostomy
Question 31
Annette Davies, aged 55 years, has had 12 hours of worsening severe central abdominal pain. The abdominal pain eases for approximately 15 minutes every hour but then worsens again. Annette had diarrhoea this morning, and she feels ‘bloated’. She has been well other than recently needing to see a massage therapist for an intermittent ache in her right groin. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 37.2°C, heart rate 95/min regular, and blood pressure 150/95 mmHg. Abdominal examination reveals generalised tenderness with increased bowel sounds. She has no guarding or rebound tenderness. Her right inguinal crease is very tender.
Coughing worsens the discomfort in her abdomen.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Acute appendicitis
B. Acute epiploic appendagitis
C. Diverticulitis
D. Incarcerated femoral hernia
E. Intussusception
F. Mesenteric artery embolus
G. Ovarian cyst rupture
H. Ovarian torsion
I. Perforated appendix
J. Perforated Meckel’s diverticulum
K. Ruptured femoral aneurysm
L. Strangulated inguinal hernia
Correct Answer: L. Strangulated inguinal hernia
Question 32
Debbie Johnstone, aged 57 years, is accompanied by her husband Tony. Debbie says she is having trouble sleeping. Six weeks ago, Debbie narrowly escaped a large fire in the kitchen of the restaurant she manages. Two kitchen staff are still receiving treatment for severe burns. Debbie is having difficulty sleeping because she cannot stop thinking about the fire. She wakes up during the night distressed by nightmares. Tony says she has seemed very irritable and ‘jumpy’ since the incident. Debbie has not returned to work despite the restaurant reopening a week ago. She has done trauma-focused cognitive behavioural therapy with a psychologist but it is not improving. She would like to know what else she can try.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Amitriptyline 50 mg orally nocte
B. Dialectical behavioural therapy
C. Duloxetine 30 mg orally daily
D. Encourage Debbie to return to work
E. Eye movement desensitisation and reprocessing therapy
F. Psychological debriefing
G. Silexan 80 mg orally at night
H. Temazepam 10 mg orally at night
Correct Answer: E. Eye movement desensitisation and reprocessing therapy
Question 33
Fiona Fox, aged 50 years, has had a sore, stiff left shoulder for the past four months. The pain is dull and aching and involves her entire shoulder. It is often worse at night. Over the past few weeks, she has found that the pain has been improving, but the stiffness seems to be worsening. She expresses frustration at being unable to do anything with her left shoulder. She has not had an injury to the shoulder in the past. She has type 2 diabetes, which has been well controlled with diet and exercise, but you note her most recent HbA1c performed yesterday is 8.1%* (normal range < 6.0%).
Which examination finding would MOST support your provisional diagnosis?
A. Both active and passive ranges of motion of the glenohumeral joint are reduced
B. Diminished biceps reflex
C. Painful arc on abduction between 45 to 135 degrees
D. Positive apprehension test
E. Tenderness over acromioclavicular joint
Correct Answer: A. Both active and passive ranges of motion of the glenohumeral joint are reduced
Question 34
Joan Somerville, aged 54 years, has had increasing facial redness, stinging, and burning (see image). Joan has always been prone to ‘blushing’ and wears heavy makeup to cover her skin as she is self-conscious about her appearance. She tries to avoid sun exposure and wears a moisturising sun cream under her makeup daily. She takes no regular medications and does not drink any alcohol.
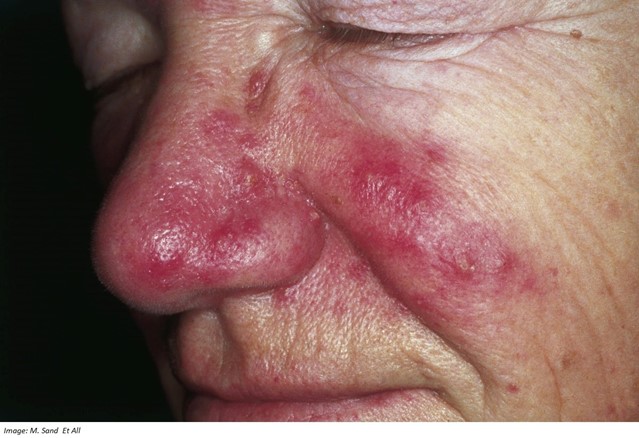
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Cephalexin 500 mg orally four times daily for five to seven days
B. Diclofenac 3% gel applied topically twice daily
C. Doxycycline 50 mg orally daily for up to eight weeks
D. Hydrocortisone 1% cream topically twice daily
E. Isotretinoin 20 mg orally daily for up to six months
F. Mupirocin 2% ointment topically three times daily
G. Nicotinamide 500 mg orally twice daily
H. Spironolactone 50 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: C. Doxycycline 50 mg orally daily for up to eight weeks
Question 35
Felicity Parsons, aged 28 years, has returned for results of tests ordered last week to investigate a neck lump. The results are as follows:
Thyroid stimulating hormone: 1.10 mIU/L (normal range 0.35 – 5.50)
Thyroid ultrasound: In the left lobe, there is a 12 mm solid hypoechoic well-defined nodule with a small area of microcalcification.
The thyroid is otherwise normal, as are the regional lymph nodes.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Carbimazole 5 mg orally twice daily
B. Computed tomography scan of the neck
C. Fine needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid nodule
D. Iodine supplement 150 mcg orally daily
E. Radioactive iodine-131 ablation
F. Radionuclide thyroid scan
G. Refer for surgical excision biopsy of thyroid nodule
H. Serum thyroglobulin
I. Serum thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)
J. Thyroxine 100 mcg orally daily
Correct Answer: C. Fine needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid nodule
Question 36
Angela Brookes, aged 26 years, is brought to your rural hospital by her boyfriend James after she was found walking the streets naked at 1 am. Angela appears to be frightened and is talking very rapidly, pacing the room. She is oriented to person, place, and time but cannot explain why she was naked. James reports that for the past three weeks, Angela has been very irritable and has not been sleeping much. He says that she has been convinced that she has special healing abilities, which has been creating discord in her work as a local physiotherapist. She has been waking most days at about 4 am and working on a research project, as well as fervently cleaning their house. James and Angela both deny any illicit drug use.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Bipolar I disorder
B. Bipolar II disorder
C. Borderline personality disorder
D. Delusional disorder
E. Schizophrenia
Correct Answer: A. Bipolar I disorder
Question 37
Robert Rae, aged 45 years, has developed a very itchy rash on his right foot over the last week. He spent two weeks in Thailand last month on a surfing holiday but cannot remember scratching it on the coral. The itch has been keeping him awake at night, and Robert has been feeling more tired than usual. On examination, the rash appears as shown (see image).
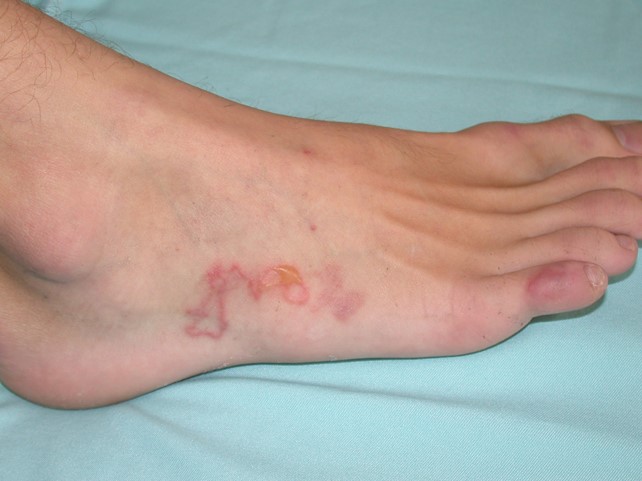
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Cutaneous larva migrans
B. Erythema multiforme
C. Infected coral cut
D. Scabies
E. Sea-bathers eruption
Correct Answer: A. Cutaneous larva migrans
Question 38
Mary Chan, aged 56 years, returns for results of blood tests that you ordered last week. Mary had a fasting blood sugar level of 7.2* mmol/L (normal range 3.0 – 5.4) two years ago. Since that time, she has worked overseas, begun a regular exercise program, and consulted a dietician, leading to a loss of 5 kg of weight. Her HbA1c ordered last week is 7.4%* (normal range <6%).
On examination, Mary’s blood pressure is 120/66 mmHg. Her body mass index is 28 kg/m2.
What is the MOST appropriate immediate management?
A. Arrange oral glucose tolerance test
B. Continue with dietary and exercise modifications and review in three months
C. Gliclazide modified release 30 mg orally daily
D. Metformin slow-release 500 mg orally daily
E. Review Mary in six months following repeat HbA1c
Correct Answer: D. Metformin slow-release 500 mg orally daily
Question 39
James Bradshaw, aged 38 years, would like help to abstain from alcohol. He normally drinks 20 standard drinks per day but has just come out of a drug and alcohol detoxification program and has not consumed any alcohol for two weeks. He is concerned he may start drinking again and would like medication to help him remain abstinent from alcohol. His only current medication is methadone 80 mg orally daily for opiate addiction that is currently under control.
What is the MOST appropriate pharmacological management?
A. Acamprosate 666 mg orally three times daily
B. Diazepam 5 mg orally three times daily
C. Disulfiram 250 mg orally daily
D. Increase methadone to 100 mg orally daily
E. Naltrexone 50 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: A. Acamprosate 666 mg orally three times daily
Question 40
Jared Greenfield, aged 17 years, has had an itchy blocked left ear for the last three days. He is training for the upcoming state water-polo championships. Otoscopy reveals an erythematous external auditory canal with copious white-grey discharge. His tympanic membrane is not visible.
You perform dry aural toilet and advise him to keep the ear dry.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Collect swab for microscopy and culture and review in two days
B. Dicloxacillin 500 mg orally four times daily for seven days
C. Flumethasone-clioquinol 0.02%/1% ear drops three drops instilled into the affected ear twice daily for seven days
D. Referral for urgent audiometry
E. Saline irrigation daily until symptoms abate
Correct Answer: C. Flumethasone-clioquinol 0.02%/1% ear drops three drops instilled into the affected ear twice daily for seven days
Question 41
Sally Johnson, aged 23 years, has had six months of generalised abdominal discomfort, bloating, and diarrhoea. Sometimes she feels like she cannot completely empty her bowels. She experiences abdominal pain at least three days per week which is relieved by defecation. She does not have any significant family history. Her clinical examination is unremarkable.
Blood tests performed one month ago showed normal full blood examination, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, iron studies, and negative coeliac serology. Stool microscopy and culture were also normal.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in investigation?
A. Abdominal ultrasound scan
B. CA-125 blood test
C. Double contrast barium enema
D. Faecal calprotectin test
E. Hydrogen breath test
F. Referral for colonoscopy
G. Referral for sigmoidoscopy
H. Thyroid function test
I. Urea breath test
Correct Answer: D. Faecal calprotectin test
Question 42
Ian Peters, aged 45 years, has been brought to your rural practice by his coworker because he started feeling ‘dizzy’ about an hour ago, vomited twice, and has had difficulty walking in a straight line. His right ear feels ‘fuzzy’ and he cannot hear well. Ian has had several similar episodes over the past five months. The practice nurse has performed an audiogram (see image).
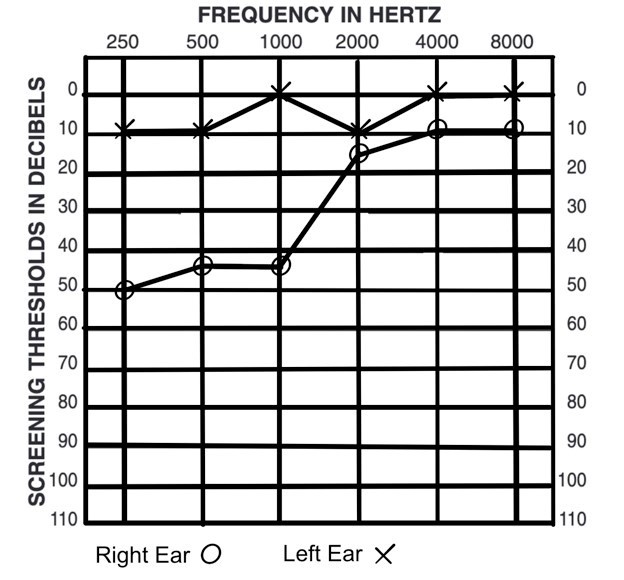
You prescribe appropriate acute symptomatic treatment.
Ian asks how he can reduce the frequency of these episodes.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Amitriptyline 10 mg orally nocte
B. Diazepam 5 mg orally three times daily
C. Metoclopramide 10 mg orally three times daily
D. Prednisone 1 mg/kg (up to 75 mg) orally daily for five days
E. Provide instruction regarding the Epley manoeuvre
F. Refer to ear nose and throat surgeon for placement of grommets
G. Restrict salt intake to no more than 3 g daily and avoid caffeine
H. Sumatriptan 20 mg intranasally at first sign of symptoms
Correct Answer: G. Restrict salt intake to no more than 3 g daily and avoid caffeine
Question 43
John Andrias, aged 46 years, has had worsening symptoms of low mood and of waking early in the morning for the past few months. He recently lost the motivation to go to work. He has had five sessions of cognitive behavioural therapy and has been on escitalopram 20 mg orally daily for 10 weeks with no improvement in his symptoms. He would like to change his medication.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Add melatonin 2 mg orally nocte
B. Add temazepam 10 mg orally nocte
C. Advise he continues with his current medication for a minimum of twelve weeks
D. Change to amitriptyline 25 mg orally nocte
E. Change to lithium 200 mg orally three times daily
F. Change to moclobemide 300 mg orally daily
G. Change to pregabalin 75 mg orally twice daily
H. Change to quetiapine 50 mg orally at night
I. Change to sertraline 50 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: I. Change to sertraline 50 mg orally daily
Question 44
John Gerard, aged 68 years, has had increasing shortness of breath on exertion over the last few months. He has stopped going to his usual aqua aerobics class as he is finding it too difficult. He ceased smoking at the age of 45 years and has a 25-pack year history. He is currently taking tiotropium 18 mcg inhaled once daily and salbutamol 100 mcg two actuations as required. Spirometry is as follows:
| Test | Result | Predicted | % Predicted |
|---|---|---|---|
| FEV1 (Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second) | 1.8 L | 3.0 L | 60% |
| FVC (Forced Vital Capacity) | 3.5 L | 4.0 L | 87.5% |
| FEV1/FVC Ratio | 51% | – | – |
What is the MOST appropriate additional pharmacological management?
A. Aclidinium-formoterol 340 mcg/12 mcg inhaled twice daily
B. Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for 14 days
C. Fluticasone propionate 250 mcg inhaled twice daily
D. Indacaterol 150 mcg inhaled once daily
E. Ipratropium 21 mcg two actuations via metered dose inhaler when required
F. Montelukast 10 mg once daily
G. Nedocromil 4 mg inhaled four times daily
H. Prednisolone 50 mg orally daily for seven days
Correct Answer: D. Indacaterol 150 mcg inhaled once daily
Question 45
Kayla Bethaniel, aged 20 months, has seemed unwell for the last couple of weeks with an occasional runny nose. Her mother, Tracey, has noticed that Kayla has prominent lumps in her neck. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded. Kayla is up to date with her immunisations. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 37.4 °C, heart rate 86/min regular, and she has bilateral slightly tender posterior cervical lymph nodes each less than 1 cm in diameter. The overlying skin is normal.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Amoxicillin-clavulanate 22.5 mg/3.2 mg/kg (up to 875 mg/125 mg) orally twice daily for five days
B. Full blood count
C. Mumps serology
D. Return for review if symptoms worsen
E. Ultrasound of her neck
Correct Answer: D. Return for review if symptoms worsen
Question 46
Mary Tinsbury, aged 72 years, recently moved to your area and presents for renewal of her prescriptions. She has a health summary from her previous doctor outlining her medical history including heart failure, hypertension, and hyperlipidaemia. Her current medications are aspirin 100 mg orally daily, rosuvastatin 10 mg orally daily, metoprolol 25 mg orally twice daily, and spironolactone 25 mg orally daily. Mary states her heart failure has been stable for several years and that she can walk approximately 100 metres on flat ground before becoming short of breath.
On examination, her heart rate is 60/min regular and blood pressure 130/85 mmHg. Her jugular venous pressure is not visibly elevated, her chest is clear, and she has no peripheral oedema.
Her last echocardiogram was 12 months ago and demonstrated an ejection fraction of 35% with no valvular disease.
You arrange fasting blood tests which reveal normal urea, electrolytes, and creatinine. Her cholesterol results are as follows:
| Test | Result | Desirable Range (High Risk) |
|---|---|---|
| Total cholesterol | 3.2 mmol/L | < 4.0 mmol/L |
| Low-density lipoprotein | 1.1 mmol/L | < 2.0 mmol/L |
| High-density lipoprotein | 1.2 mmol/L | > 0.9 mmol/L |
| Triglycerides | 1.2 mmol/L | < 2.0 mmol/L |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Cease rosuvastatin
B. Change aspirin to apixaban 5 mg orally twice daily
C. Change rosuvastatin to atorvastatin 20 mg orally daily
D. Commence frusemide 20 mg orally daily
E. Initiate lisinopril 2.5 mg orally daily
F. Order repeat echocardiogram
G. Reduce metoprolol to 12.5 mg orally twice daily
H. Refer for consideration of implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
Correct Answer: E. Initiate lisinopril 2.5 mg orally daily
Question 47
David Lau, aged 4 years, is brought to see you by his mother, Daisy. She explains David has been unwell for the past six weeks. He initially had a cold but has an ongoing cough that is worse in the morning but occurs both day and night. David is fully immunised. He developed a rash after amoxicillin at age 2 years. On examination, his temperature is 36.9 °C and he has a wet cough. His chest is clear to auscultation. His growth is tracking along the 50th centile. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
You arrange a chest X-ray, and this is reported as normal.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Cefuroxime 15 mg/kg (up to 500 mg) twice daily for two weeks
B. Computed tomography scan of chest
C. Erythromycin 20 mg/kg (up to 800 mg) orally four times daily for 10 days
D. Fluticasone propionate 50 mcg inhaled twice daily via spacer
E. Pertussis serology
F. Reassurance that no specific treatment is required today and review in two weeks
G. Refer to respiratory physician for bronchoscopy
H. Salbutamol 100 mcg inhaler two inhalations via spacer four hourly as needed
Correct Answer: A. Cefuroxime 15 mg/kg (up to 500 mg) twice daily for two weeks
Question 48
Cliff Bankard, aged 74 years, has noticed swelling in his nipple regions recently. He takes ramipril for hypertension, metformin for type 2 diabetes, and finasteride for prostatism. He drinks two to three standard drinks of alcohol a day and does not smoke. On examination, his heart rate is 80/min regular, blood pressure 130/82 mmHg, and body mass index 27 kg/m2. Breast examination reveals symmetrical breast fullness bilaterally. On palpation behind each areola, there is a 1 cm in diameter palpable firm, tender, mobile, and rubbery-feeling ridge. There are no other breast masses.
What is the MOST likely underlying cause of this symptom?
A. Bilateral breast carcinoma
B. Chronic liver disease
C. Chronic renal disease
D. Hyperthyroidism
E. Long-term use of metformin
F. Long-term use of finasteride
G. Long-term use of ramipril
H. Prolactinoma
Correct Answer: F. Long-term use of finasteride
Question 49
Brian Henderson, aged 42 years, has had gradually worsening symptoms of fatigue, generalised weakness, nausea, anorexia, and weight loss over the last year. He has also noticed a dark colouring within his axillae bilaterally. On examination, his blood pressure is 95/50 mmHg and his random blood sugar level is 3 mmol/L. Investigations are completed and results are as follows:
| Test | Result | Normal Range |
|---|---|---|
| Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) | 19* pmol/L | < 10 pmol/L |
| Sodium | 130* mmol/L | 135 – 145 mmol/L |
| Potassium | 5.4* mmol/L | 3.5 – 5.2 mmol/L |
| Chloride | 103 mmol/L | 95 – 110 mmol/L |
| Bicarbonate | 25 mmol/L | 22 – 32 mmol/L |
| Urea | 3.7 mmol/L | 2.5 – 8.0 mmol/L |
| Creatinine | 72 umol/L | 45 – 90 umol/L |
| Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) | 99 mL/min/1.73 m² | > 90 mL/min/1.73 m² |
Which finding on investigation would MOST likely confirm the provisional diagnosis?
A. Anti-nuclear antibody positive
B. Creatinine kinase titre greater than five times normal range
C. Elevated anti-citrullinated protein antibody
D. High mean corpuscular volume
E. High thyroid stimulating hormone
F. Low early morning cortisol
G. Low ferritin
H. Low vitamin B12
Correct Answer: F. Low early morning cortisol
Question 50
Denise Holt, aged 42 years, asks for advice regarding breast cancer screening. Denise’s mother died of breast cancer at age 57 years, two years after she was given the initial diagnosis. Denise’s cousin died at age 52 years of lymphoma, and her brother has had early prostate cancer at age 47 years. Denise’s sister had a large loop excision of the transformation zone procedure two years ago for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 3 change.
What is the MOST appropriate breast screening method to advise?
A. Breast self-examination once per month
B. Magnetic resonance imaging of the breasts every two years starting now
C. Mammogram and bilateral breast ultrasound every year starting now
D. Mammogram every two years from age 50 years
E. Mammogram every year starting now
