The recommended activities are often more intensive for ATSI people due to the higher prevalence of certain health issues in these populations. The recommendations focus on a holistic approach to care that takes into account the social, emotional, cultural, and physical aspects of health.
- General Health Assessment: An annual health assessment (MBS Item 715) is recommended for all ATSI people. This includes a comprehensive assessment of physical, psychological, and social well-being, as well as risk factor assessment for common conditions.
- Cardiovascular Risk Assessment: Due to higher rates of cardiovascular disease among ATSI populations, cardiovascular risk assessments are recommended from age 18 years (compared to 45 years for non-ATSI).
- Diabetes Screening: Type 2 diabetes is more common in ATSI populations. For ATSI, we proceed directly to Fasting BSL and HbA1c from age 18 years (compared to 45 for the non-ATSI).
- Note that we do not use AUSDRISK.
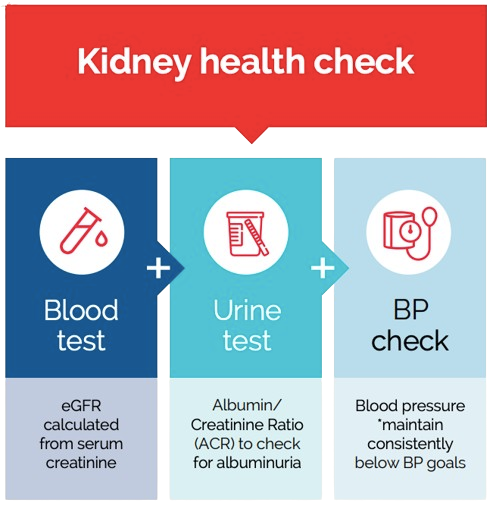
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Kidney health check annually from age 18 years
- BP (Blood pressure)
- ACR (Albumin-to-creatinine ratio)
- If positive, repeat x 2 over the next 3 months.
- eGFR (estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate)
- Chronic Respiratory Conditions: Clinical assessment for symptoms of chronic respiratory conditions, such as COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease), especially in smokers or ex-smokers.
- Liver Disease: Consider screening for hepatitis B and C in individuals who are at risk.
- Eye Health: Given the higher prevalence of certain eye diseases, regular eye checks are recommended for ATSI people.
- Hearing Health: Regular hearing assessments are also suggested, especially in children, due to the higher prevalence of ear disease.
- Mental Health: Given the higher rates of psychological distress, regular mental health screening and culturally appropriate care are recommended.
- Lifestyle Factors: Assessments related to SNAP-O.
- Immunisation: ATSI people should follow the standard immunisation schedule, but they also qualify for additional vaccines due to higher risk:
- BCG @ birth
- Meningococcal B @ 2, 4, 12 months (+6 months for at-risk)
- Extra pneumococcal 13V @ 6/12
- Extra pneumococcal 23V @ 4 years and @ 9 years
- Annual influenza vaccination (unlike 5-65 break for non-ATSI)
- Hepatitis A @ 18/12 and @ 4 years
- The 13V pneumococcal vaccine @ 50 years of age (unlike @ 70 for non-ATSI) followed up with 23V pneumococcal vaccine @ 51 years and @ 56 years.
- Shingrix early @50 (2 doses 2-6 months apart)