Aldara (imiquimod) and Efudix (5FU – fluorouracil) are topical medications commonly used to treat skin cancer, precancerous lesions and some types of warts.
- Aldara (imiquimod) works by stimulating the immune system to attack abnormal skin cells. It’s primarily used for:
- Actinic keratosis is rough, scaly patches on the skin caused by excessive sun exposure, typically on the face, ears, and back of the hands.
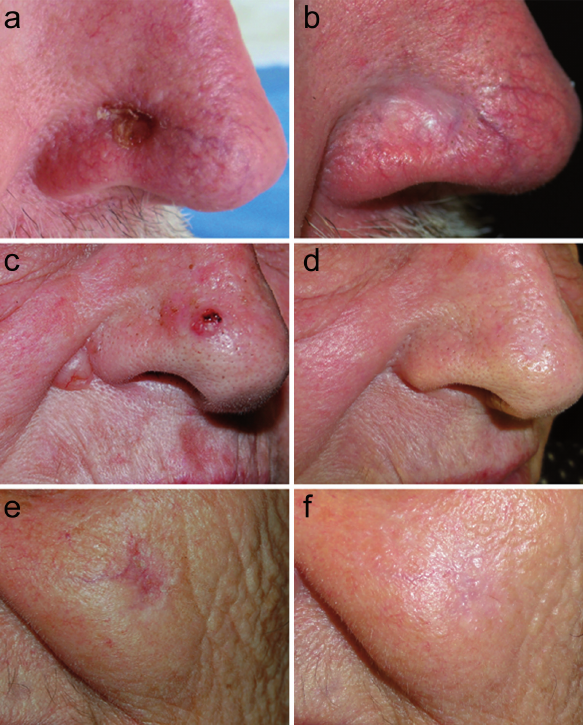
- Superficial basal cell carcinoma, when surgery wouldn’t be an appropriate treatment.
- External genital and perianal warts.
- Aldara is applied directly to the skin in the affected area.
- It encourages the body to produce interferon and other chemicals that boost the immune response against abnormal cells.
- Efudix (fluorouracil), on the other hand, is a form of chemotherapy drug that works by inhibiting rapidly dividing cancerous or precancerous cells. It’s used to treat:
- Actinic keratosis.
- Superficial basal cell carcinoma.
- Other conditions where abnormal cell growth occurs, such as Bowen’s disease.
- Efudix is also applied topically and works by disrupting DNA synthesis in the cells, leading to cell death, particularly in fast-dividing cells like cancerous cells.
- Side Effects: Both medications can cause local skin reactions, including redness, irritation, swelling, and in some cases, pain or itching at the application site.
- These reactions are typically a sign that the medication is working.
- However, systemic absorption and more serious side effects are rare but possible.
Usage Tips:
- Only apply these medications to the affected areas as prescribed.
- Protect the treated areas from sunlight, as both medications can make your skin more sensitive to the sun.
- Always wash your hands before and after applying these treatments.
The application frequency and duration for Aldara (imiquimod) and Efudix (fluorouracil) can varies depending on the condition being treated and the specific instructions from the treating doctor. Here’s a general guideline for each:
Aldara (Imiquimod)
- Actinic Keratosis: Typically applied 2 to 3 times per week for about 16 weeks. The cream is usually applied before bedtime and left on the skin for approximately 8 hours.
- Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma: Commonly applied 5 times per week for a full 6 weeks. Similar to its use for actinic keratosis, it should be applied before bedtime and washed off after 8 hours.
- External Genital Warts: Applied 3 times per week until the warts are cleared, which can take up to 16 weeks. The cream should be left on the skin for 6 to 10 hours before washing it off.
Efudix (Fluorouracil)
- Actinic Keratosis: Generally applied once-twice daily for 2 to 4 weeks. The treatment period may vary based on the response of the lesions.
- Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma: Applied twice daily for 6 weeks, or as directed by a healthcare provider. Continuous evaluation of the treatment area is necessary to adjust the duration if needed.
- Other Conditions (like Bowen’s disease): The application schedule can be similar, but the duration might be adjusted based on the severity of the lesions and the treatment response.
Important Considerations:
- The area should be clean and dry before application.
- Users should follow the specific instructions provided regarding application times, duration, and care of the treated area.
- During the treatment period, it’s crucial to monitor for severe skin reactions and communicate with a doctor if the reaction seems excessive or unusually painful.
These treatments are potent and effective when used correctly, but due to the potential for serious skin reactions and the need for precise application, following medical guidance is essential.
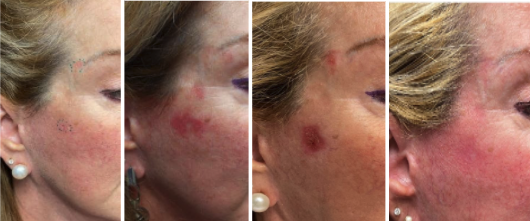
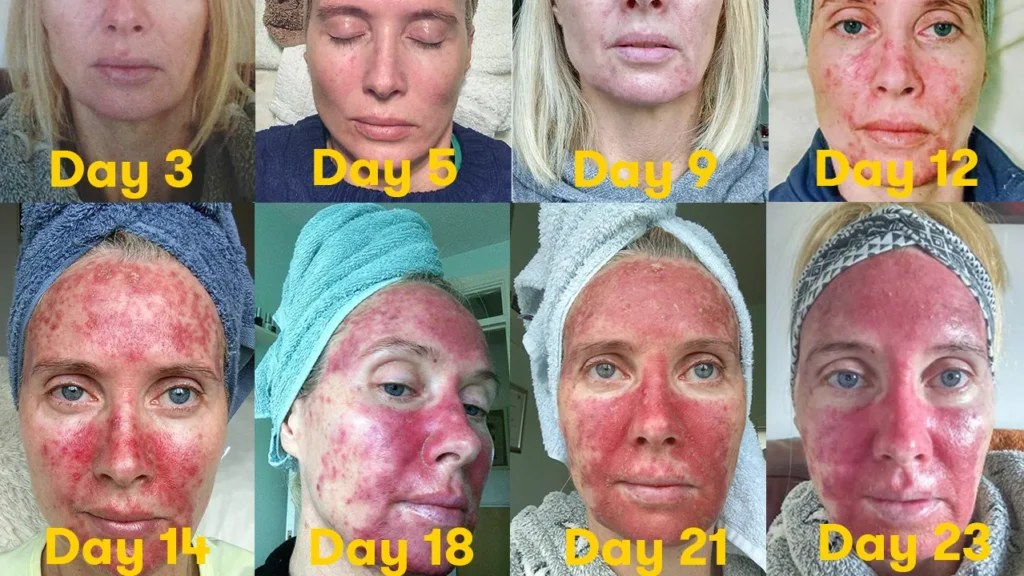
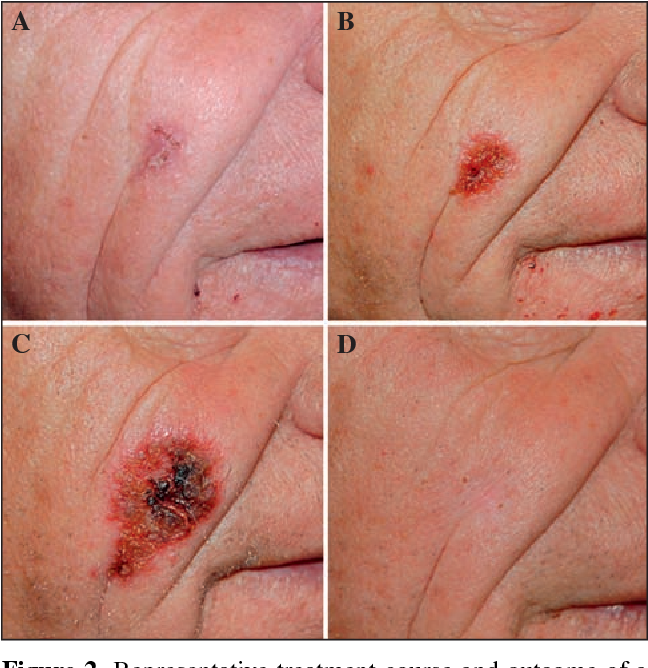
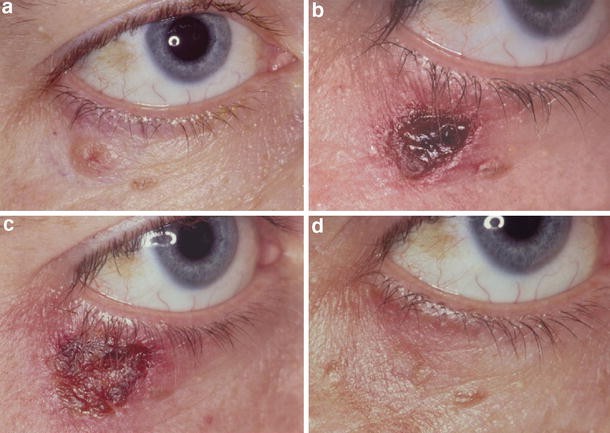
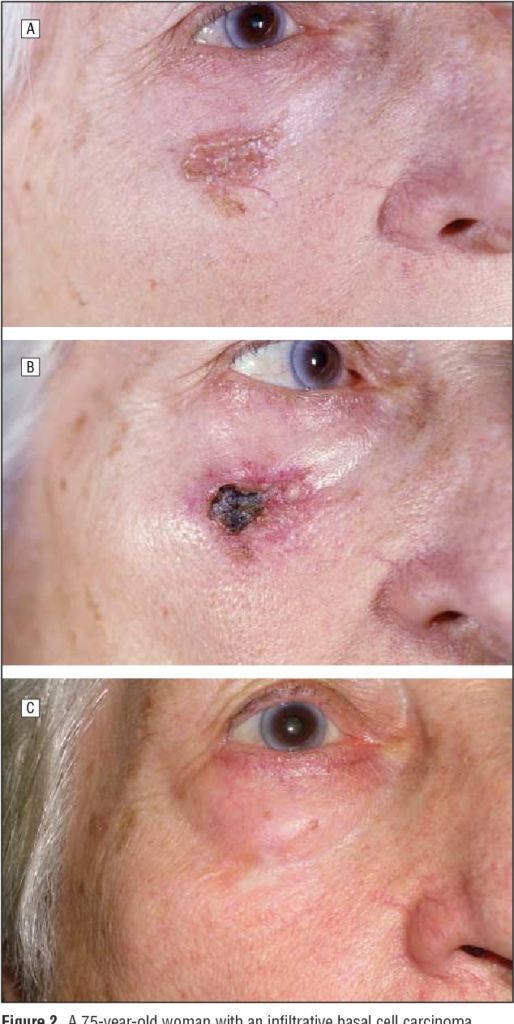
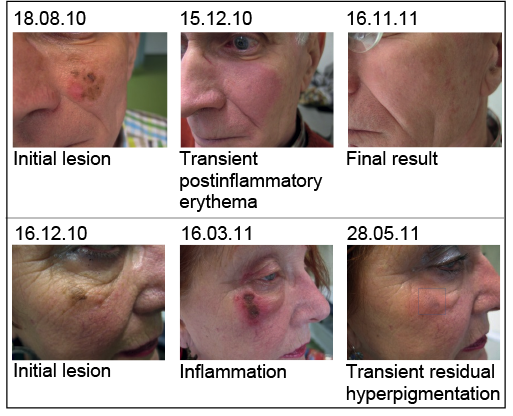
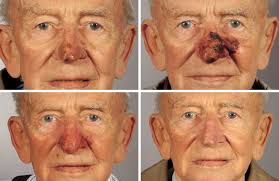
What to expect before – during – after treatment
The response to these topical treatments can vary from nothing (indicating treatment failure) to quite florid. The duration of treatment is often guided by how quickly the skin reacts. For example, for some patients using 5FU, a reaction occurs within a week, and another week of keeping the skin red and angry is typically sufficient. The average treatment time of 21 days may be extended out to 4 weeks in patients who react slowly. After treatment finishes it takes another 3 weeks for the skin to settle. If you think about how long it takes to recover from a bad sunburn you will get an idea about this.