Question 1
Bianca Di Lizio, aged 74 years, has had sore shoulders for the past two weeks. It is affecting her ability to do her normal activities, including washing her hair, getting dressed and even pulling up the blankets in bed. She has noticed that, in the morning, her neck and shoulders
feel stiff, and it takes her a few hours to warm up. She has a history of osteoarthritis in both knees for which she takes paracetamol 665 mg two tablets orally three times daily. Her clinical examination is consistent with your suspected diagnosis.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Antinuclear antibody
B. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
C. Ibuprofen 400 mg orally three times daily as required
D. Magnetic resonance imaging cervical spine
E. Methotrexate 5 mg orally weekly with 5 mg folic acid orally on a different day
F. Oxycodone 5 mg orally four times daily as required
G. Referral to physiotherapy for stretching and strengthening exercises
H. X-ray both shoulders
Correct Answer: B. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Question 2
Naomi Gilchrist, aged 24 months, is brought in by her parents, as she has been unwell for the past 24 hours. During this time, they report she is not eating as much as usual, she is drinking less, and is being unusually quiet. They have been giving her regular fluids and paracetamol, as
required. On examination, she appears alert and interactive. Her temperature is 37.9°C, respiratory rate is 35/min, heart rate is 145/min, oxygen saturation is 97% on room air and blood pressure is 90/50 mmHg. Her tympanic membranes and pharynx are erythematous. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Amoxicillin 15 mg/kg (max 500 mg) orally three times daily for five days
B. Arrange urgent review in paediatric outpatient department
C. Continue symptomatic management
D. Nasopharyngeal swab for influenza polymerase chain reaction
E. Transfer to emergency department
Correct Answer: C. Continue symptomatic management
Question 3
Malcolm Davies, aged 68 years, presents for a diabetes review. Malcolm has type 2 diabetes, had an angioplasty after a myocardial infarction five years ago and has heart failure with a stable left-ventricular ejection fraction of 42% on an echocardiogram performed two months earlier. His medications include aspirin 100 mg orally daily, metformin extended release 2 g orally daily, bisoprolol 10 mg orally daily, ramipril 10 mg orally daily and rosuvastatin 20 mg orally daily. Despite his best efforts managing his diet and lifestyle, his body mass index remains at 32 kg/m2 and his glycated haemoglobin has increased from 7.2% three months earlier to 8.7% (target range: < 7%) yesterday.
What is the MOST appropriate additional pharmacological management?
A. Dapagliflozin 10 mg orally daily
B. Exenatide 5 mcg subcutaneously twice daily
C. Gliclazide extended release 30 mg orally daily
Insulin glargine 10 units subcutaneously daily
Sitagliptin 100 mg orally once daily
Correct Answer: A. Dapagliflozin 10 mg orally daily
Question 4
Emma Timms, aged 32 years, is 28 weeks pregnant. This is her first pregnancy. Over the past three weeks, she has experienced increasing pain bilaterally in her gluteal regions that also radiates to both of her hips. Often the pain becomes so severe that she has difficulty walking. The pain starts when she gets out of bed and is worse when walking and going up or down steps. Examination findings confirm your suspected diagnosis.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Bilateral anteroposterior hip X-rays
B. Computed tomography-guided cortisone injection into the sacroiliac joints
C. Diclofenac 25 mg orally three times daily
D. Refer to hospital for urgent cardiotocography assessment
E. Strengthening exercises and use of a lumbopelvic belt
F. Strict bed rest for two weeks
G. Ultrasound bilateral gluteal and hip muscles
H. Urgent obstetric ultrasound
Correct Answer: E. Strengthening exercises and use of a lumbopelvic belt
Question 5
Max Wright, aged 48 years, requests a ‘heart checkup’, as his brother-in-law recently died unexpectedly of a heart attack. Max smoked socially as a teenager for a few years but has not smoked since 20 years of age. He has two standard drinks of alcohol per day. On examination, his blood pressure is 152/98 mmHg and his body mass index is 28 kg/m2. You note his blood pressure readings at his last two visits in the past six weeks were 142/85 mmHg and 149/95mmHg. Results of blood tests are as follows:
| Lipid studies | Result | Normal range (fasting) |
| Total cholesterol | 5.2 mmol/L | < 5.6 |
| High density lipoprotein cholesterol | 1.8 mmol/L | > 1.0 |
| Low density lipoprotein cholesterol | 3.2* mmol/L | < 2.5 |
| Triglyceride | 1.4 mmol/L | < 1.5 |
| Glycated haemoglobin | 5.4% | < 6 |
You calculate his total cardiovascular risk as 3% and discuss lifestyle changes.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Computed tomography coronary angiogram
B. Computed tomography coronary calcium score
C. Perindopril 5 mg orally daily
D. Review in three months
E. Rosuvastatin 5 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: D. Review in three months
Question 6
Annie Stinson, aged 13 months, is brought in by her mother, Paula, who is concerned about Annie’s recent high fluid intake. Annie has been drinking up to 1 L of water daily for the past two weeks. Her nappies are often drenched, and she requires frequent nappy changes up to eight times per day. Annie was born at full term and is up to date with vaccinations. Annie was seen at your practice with two episodes of acute otitis media and one urinary tract infection, during the past three months. Paula says that Annie has had recurrent severe nappy rashes. Her milestones are appropriate for her age. On examination, Annie looks very irritable. Her weight is on the 15th centile and height is on the 50th centile. Her vital signs are normal, and systemic examination is unremarkable.
What is the MOST appropriate next step to support your provisional diagnosis?
A. Antidiuretic hormone
B. Clean catch urine for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
C. Random blood glucose
D. Serum and urine osmolarity
E. Serum calcium
Correct Answer: C. Random blood glucose
Question 7
Ronald Dudley, aged 75 years, was admitted to a local residential aged care facility three days earlier, as he was not managing living at home alone. He was well on admission, but the staff are concerned about him becoming restless and irritable in the past 24 hours. Ronald takes paracetamol 1 g orally four times daily, as required, for osteoarthritis of his hips and knees. Prior to his admission, Ronald would consume up to six standard drinks of alcohol per day. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 37.9°C, heart rate is 109/min, blood pressure is 130/74 mmHg and respiratory rate is 18/min. He is confused and agitated, and he reports feeling nauseated. He is sweating profusely and has a new, bilateral hand tremor.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Cefalexin 500 mg orally four times daily for five days
B. Chest X-ray
C. Computed tomography scan brain
D. Endone 5 mg orally
E. Glucagon 1 mg intramuscularly
F. Haloperidol 5 mg intramuscularly
G. Mid-stream urine for microscopy culture and sensitivities
I. Risperidone 2 mg orally
J. Temazepam 10 mg orally
K. Transfer to emergency department
Correct Answer: K. Transfer to emergency department
Question 8
Sarah Nguynh, aged 24 years, has arranged a telephone consultation, as her insulin pump has stopped working. She says her blood glucose level is 13 mmol/L and ketone level is 0.2 mmol/L. She was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes at 7 years of age and has used an insulin pump for the past six months. This is the first time she has had a problem with the insulin pump.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise her to administer a correction dose of insulin glargine via subcutaneous injection
B. Advise her to administer a correction dose of insulin lispro via subcutaneous injection
C. Contact the pump manufacturer for advice
D. Recheck blood glucose and ketone levels in two hours
E. Urgent referral to the local hospital emergency department
Correct Answer: B. Advise her to administer a correction dose of insulin lispro via subcutaneous injection
Question 9
Stephen Colles, aged 19 years, has had five days of fever, headache, sore throat, malaise and dry cough. He is tolerating fluids. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 38°C, heart rate is 80/min, blood pressure is 105/70 mmHg and oxygen saturation is 95% on room air. His pharynx is erythematous and there are bibasal crepitations on lung auscultation. You arrange a chest X-ray (see image). COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
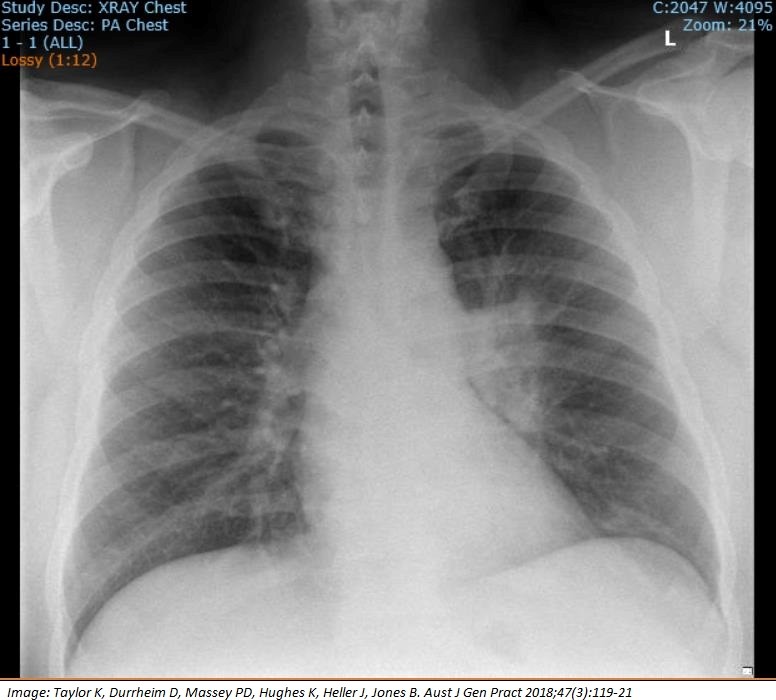
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Amoxicillin 1 g orally three times daily
B. Arrange hospital admission for intravenous antibiotics
C. Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily
D. Oseltamivir 75 mg orally twice daily
E. Sputum microscopy, culture and sensitivities, and review in 48 hours for results
Correct Answer: C. Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily
Question 10
Andrea Bodger, aged 49 years, has a painful left ear. One week earlier, she had a bilateral ear syringe for wax impaction. A few days after the ear syringe, she developed pain in her left ear. The pain has progressively worsened since then. She has also noticed reduced hearing and a blocked sensation in the left ear. On examination her tympanic temperature is 36.8°C, the left ear canal is inflamed and swollen, and it is not possible to visualise the tympanic membrane.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Dexamethasone–framycetin–gramicidin 0.05%/0.5%/0.005% ear drops three drops topically three times daily for three days
B. Dicloxacillin 500 mg orally four times daily for five days
C. Fluconazole 150 mg orally stat
D. Flumetasone–clioquinol 0.02%/1% ear drops three drops topically twice daily for seven days
E. Syringe ear with warm water to remove any debris
Correct Answer: D. Flumetasone–clioquinol 0.02%/1% ear drops three drops topically twice daily for seven days
Question 11
Sally Armstrong, aged 38 years, has had worsening shortness of breath on exertion and an increasing cough. She has experienced malaise and has unintentionally lost 6 kg over the past six weeks. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 36.8°C, heart rate is 99/min, blood pressure is 134/77 mmHg, respiratory rate is 24/min and oxygen saturation is 95% on room air. Her lungs are clear on auscultation and there is no lymphadenopathy. You arrange investigations, and the results are as follows:
Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme: 41* U/L (normal range: 12–40).
Chest X-ray: micronodular interstitial densities throughout bilateral lung fields with apical fibronodular granulomatous change.
Respiratory function testing: restrictive ventilatory pattern with reduced transfer factor.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Eosinophilic pneumonia
B. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
C. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
D. Sarcoidosis
E. Wegener’s granulomatosis
Correct Answer: D. Sarcoidosis
Question 12
Kate Green, aged 36 years, attends your practice for a routine antenatal check–up. This is her first pregnancy and she is currently 20 weeks’ gestation. She has had frontal headaches for the past two weeks. On examination, her blood pressure is 115/72 mmHg, neurological examination is normal and urinalysis is unremarkable. The fetal heart rate is 140/min. While checking her blood pressure, you notice the following lesion on her forearm (see image).
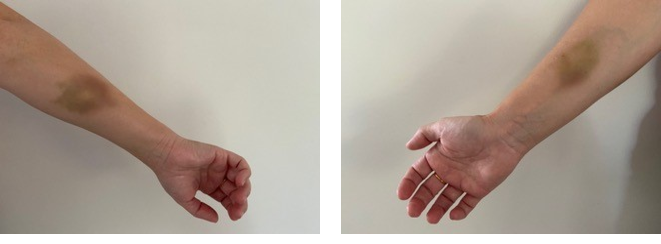
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Arrange urgent obstetric review
B. Enquire about smoking history
C. Full blood count
D. Liver function tests
E. Reassurance that no further management is needed
F. Screen for domestic violence
G. Ultrasound right forearm
H. Urgent international normalised ratio
Correct Answer: F. Screen for domestic violence
Question 13
Marcus Lee, aged 25 years, is a transgender man who presents to discuss options for contraception. He has casual male sexual partners and has receptive vaginal and anal intercourse. His regular medications are testosterone undecanoate 1000mg intramuscular injection every 12 weeks and tenofovir disoproxil–emtricitabine 300 mg/200 mg orally daily for human immunodeficiency virus pre-exposure prophylaxis. He has been amenorrhoeic since commencing testosterone therapy for gender transition four years earlier.
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Advise him to avoid vaginal intercourse
B. Encourage him to consider hysterectomy and oophorectomy
C. Levonorgestrel–ethinylestradiol 150 mcg/30 mcg orally daily
D. Offer subdermal etonogestrel 68 mg implant
E. Reassure him that he does not require contraception
Correct Answer: D. Offer subdermal etonogestrel 68 mg implant
Question 14
Aaron Cook aged 21 years, an Aboriginal man, has had several episodes of wet cough over the past 12 months. He was seen by several different general practitioners during this time and was treated with a course of amoxicillin and later, a course of clarithromycin. After each treatment, his cough initially improved for a few weeks, but then worsened again. On examination, chest auscultation reveals bilateral crepitations and wheeze, which is heard loudest in the lower zones. A chest X-ray taken one month earlier when unwell revealed slightly increased lung markings within both lower zones. In between episodes of cough, he had spirometry completed, with results shown below:
| Test | Predicted value | Actual (prebronchodilator) value | % Predicted (prebronchodilator) | Actual (postbronchodilator) value | % Change (postbronchodilator) |
| Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) (L) | 4.63 | 3.32 | 71 | 3.45 | 4 |
| Forced vital capacity (FVC) (L) | 5.35 | 5.2 | 97 | 5.40 | 4 |
| FEV1/FVC (%) | 85 | 63 | 74 | 63 | 0 |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Allergen-specific immunoglobulin E
B. Azithromycin 500 mg orally daily for three days
C. Bronchoscopy with lung biopsy
D. Budesonide–formoterol 200 mcg/6 mcg inhaled twice daily
E. Fluticasone 250 mcg inhaled twice daily
F. High-resolution computed tomography scan chest
G. Salbutamol 100 mcg inhaler two puffs every four hours as required
H. Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme
I. Sputum microscopy for acid-fast bacilli
Correct Answer: F. High-resolution computed tomography scan chest
Question 15
Olive Baker, aged 2 days, is brought in by her mother, Katrina, who is concerned about Olive’s risk of contracting chicken pox. Olive’s brother, Jacob, was diagnosed with chicken pox last week and this was confirmed with varicella polymerase chain reaction testing of a swab of his rash. Katrina had negative varicella serology during her pregnancy and today has developed a vesicular rash on her torso. Physical examination of Olive is normal.
What is the MOST appropriate management to recommend for Olive?
A. Aciclovir 20 mg/kg (max 800 mg) orally five times daily for seven days
B. Arrange admission to hospital for administration of zoster immunoglobulin
C. Prednisolone 1 mg/kg (max 50 mg) orally daily for three days
D. Reassurance that Olive is not at risk of contracting varicella infection and no treatment is required
E. Recommend varicella vaccination today
Correct Answer: B. Arrange admission to hospital for administration of zoster immunoglobulin
Question 16
Vivian Trent, aged 35 years, had palpitations while at the gym the night before. She recently started a new fitness program and has noticed weight loss and increased sweating (not just when exercising) and has felt very tired. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 36.8°C, heart rate is 125/min, blood pressure is 145/80 mmHg and her body mass index is 19 kg/m2. Her palms feel warm and moist and she has a fine tremor at rest. The remainder of her examination is unremarkable.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Anxiety
B. Electrolyte imbalance
C. Hyperthyroidism
D. Iron deficiency anaemia
E. Panic attack
F. Pheochromocytoma
G. Stimulant medication use
H. Vigorous exercise
Correct Answer: C. Hyperthyroidism
Question 17
Tony Balboa, aged 45 years, has requested an urgent appointment due to a one-hour history of severe headache, flushed face and feeling unwell. Tony is a long-term C4 quadriplegic. On examination, his face appears red and is covered in perspiration, and you note widespread piloerection over his torso and limbs. His tympanic temperature is 36.8°C, heart rate is 50/min and blood pressure is 190/120 mmHg. You note cloudy urine in his urinary catheter bag.
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Aspirin 300 mg orally
B. Glyceryl trinitrate spray 400 mcg sublingually
C. Initiate perindopril 5 mg orally and review tomorrow
D. Morphine 5 mg subcutaneously
E. Recline wheelchair to lie patient down flat
Correct Answer: B. Glyceryl trinitrate spray 400 mcg sublingually
Question 18
Imogen Newall, aged 21 years, is worried about germs. She is fearful of contracting a virus and constantly washes her hands. Lately, she has not wanted to leave the house due to her fears and has missed a week of university this semester. She frequently argues with her mother about how dishes are washed, as she does not feel that they are clean enough. She often asks to be taken to the doctor for examination and investigation, despite having no symptoms of infection. For the past 12 months, Imogen has seen a psychologist and has been engaging in cognitive behavioural therapy. Despite this, her symptoms have worsened and she would like to trial a medication.
What is the MOST appropriate pharmacological management?
A. Amitriptyline 25 mg orally at night
B. Clomipramine 50 mg orally at night
C. Diazepam 5 mg orally three times daily as required
D. Duloxetine 60 mg orally once daily
E. Escitalopram 10 mg orally once daily
F. Mirtazapine 15 mg orally at night
G. Olanzapine 5 mg orally at night
H. Quetiapine 50 mg orally at night
Correct Answer: E. Escitalopram 10 mg orally once daily
Question 19
Steven Rice, aged 56 years, returns for results of recent blood tests arranged after he presented for a check-up. Steven has hypertension treated with telmisartan 40 mg orally daily and hypercholesterolaemia treated with rosuvastatin 10 mg orally in the morning. On examination, his blood pressure is 125/75 mmHg and his body mass index is 34 kg/m2.
His full blood count is normal. Further results are as follows:
| Test | Result | Normal range | |
| Total cholesterol | 6.3* mmol/L | < 5.5 | |
| High-density lipoprotein | 0.8 mmol/L | > 1.0 | |
| Low-density lipoprotein | 5.5* mmol/L | < 2.5 | |
| Triglycerides | 1.8 mmol/L | < 2.0 | |
| Liver function tests | Result | Normal Range | |
| Total protein | 63 g/L | 60 – 82 | |
| Albumin | 35 g/L | 35 – 50 | |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 120 ?mol/L | 30 – 120 | |
| Bilirubin | 10 U/L | < 25 | |
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase | 59* U/L | < 51 | |
| Aspartate aminotransferase | 36 U/L | < 41 | |
| Alanine aminotransferase | 28 U/L | < 41 | |
| Test | Result | Normal range | |
| Fasting blood glucose | 5.4 mmol/L | 3.6 – 5.4 | |
| Serum iron | 14 umol/L | 5 – 30 | |
| Transferrin | 2.2 g/L | 2.0 – 3.2 | |
| Transferrin saturation | 25% | 10 – 45 | |
| Ferritin | 420* ng/ml | 30 – 320 | |
| Erythrocyte sedimentation rate | 5 mm/hr | 2 – 14 | |
| C-reactive protein | 2 mg/L | < 5 | |
What is the MOST appropriate next step to further investigate the abnormal test results?
A. Computed tomography scan chest and abdomen
B. Echocardiogram
C. Glycated haemoglobin
D. HFE gene mutation
E. Ultrasound liver
Correct Answer: E. Ultrasound liver
Question 20
Ann Carter, aged 64 years, has localised back pain, which has woken her from sleep most nights over the past two weeks. She reports night sweats and recurrent easy bruising over the past month. She has not noticed any weight loss. On examination, some bruising on her forearms is notable. Her vital signs are normal. She has full range of motion of her cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine, but experiences some pain with these movements.
Which investigation is MOST appropriate to confirm your provisional diagnosis?
A. Alkaline phosphatase
B. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
C. Human leukocyte antigen B27 genotype
D. Protein electrophoresis
E. Serum corrected calcium
Correct Answer: D. Protein electrophoresis
Question 21
Jake Baker, aged 24 years, presents to your rural emergency department with a severe right sided headache. The headache is above the right eye and radiates to his forehead and to the back of his head. He also has a stuffy nose on the right side and watering of the right eye. He tells you that he has experienced these headaches over the past few years. They typically occur in the early hours of the morning. They occur up to three times per day and last from 15 minutes to two hours. The headaches usually occur for a few weeks at a time and then settle. They tend to be brought on by alcohol. Physical examination is consistent with your provisional diagnosis.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Aspirin 900 mg orally stat
B. Computed tomography scan sinuses
C. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
D. Full blood count
E. Lumbar puncture
F. Magnetic resonance imaging brain
G. Metoclopramide 10 mg intramuscularly stat
H. Sumatriptan 6 mg subcutaneously stat
I. X-ray skull
Correct Answer: H. Sumatriptan 6 mg subcutaneously stat
Question 22
Aahna Khatri, aged 41 years, had her third child six months ago and would like to discuss options for contraception. Her baby is exclusively formula fed, and she is unsure if she would like any more children. She has recently been diagnosed with trigeminal neuralgia that is controlled with phenytoin 300 mg orally daily. On examination, her blood pressure is 135/90 mmHg and her body mass index is 36 kg/m2.
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Ethinyloestradiol–levonorgestrel 50 mcg/125 mcg orally once daily
B. Etonogestrel 68 mg implant subdermally
C. Etonogestrel–ethinyloestradiol 11.7 mg/2.7 mg ring intravaginally every three weeks
D. Fertility awareness-based methods
E. Levonorgestrel 52 mg intrauterine device
Correct Answer: E. Levonorgestrel 52 mg intrauterine device
Question 23
Peter Jones, aged 28 years, has been feeling very low in mood since his twin brother, Michael, died suddenly eight months earlier while trekking in South America. Michael’s autopsy was normal. Their grandfather, who was known to be a strong swimmer, also died mysteriously by drowning at 33 years of age. Peter has been waking early in the morning, having trouble sleeping and has lost much of his motivation. He has had occasional thoughts of suicide but is aware that his family have suffered enough and has no intention of killing himself. Peter has been smoking five cigarettes per day and the occasional marijuana joint. He has been seeing a psychologist for some time and she has advised him to see you for review.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Arrange admission to mental health facility
B. Electrocardiogram
C. Escitalopram 10 mg orally daily
D. Iron studies
E. Refer to drug and alcohol services
F. Referral for eye movement desensitisation and reprocessing therapy
G. Urine albumin:creatinine ratio
I. Venlafaxine 75 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: B. Electrocardiogram
Question 24
Sarah Sandring, aged 36 years, is becoming increasingly frustrated by daily, moderate vaginal bleeding for the past month. She had a levonorgestrel 52 mg intrauterine device inserted three months ago, when her youngest child, Thomas, was three months old. Thomas is exclusively bottle fed. Her cervical screening is up to date. On examination, her blood pressure is 123/75 mmHg and the intrauterine device string is visible. A urine pregnancy test is negative.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise to use condoms until the bleeding stops
B. Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for seven days
C. Mefenamic acid 500 mg orally three times daily for five days
D. Norethisterone 5 mg orally three times daily for 21 days
E. Remove the levonorgestrel intrauterine device
Correct Answer: C. Mefenamic acid 500 mg orally three times daily for five days
Question 25
Graeme Wyatt, aged 42 years, presents to your rural practice in southern Victoria with a painless, non-healing wound on his left knee (see image). He states that he first noticed a lump that became an ulcer, and over the past six weeks, the ulcer has been getting larger. He saw another general practitioner one week ago and was prescribed flucloxacillin 500 mg orally four times daily for five days; however, there has been no improvement. On examination the lesion measures 5 cm × 3 cm.
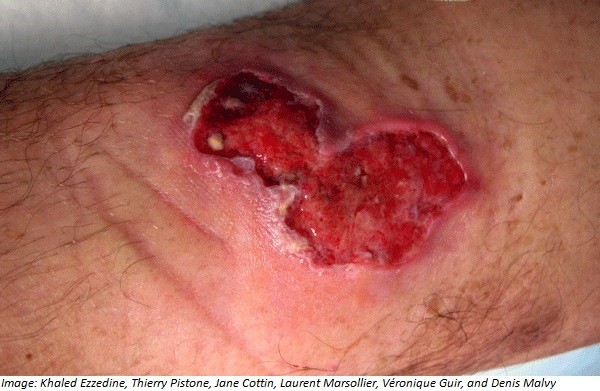
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Amelanotic melanoma
B. Basal cell carcinoma
C. Buruli ulcer
D. Dermatitis herpetiformis
E. Group A streptococcus infection
F. Merkel cell carcinoma
G. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection
H. Porphyria cutanea tarda
I. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection
J. Squamous cell carcinoma
Correct Answer: C. Buruli ulcer
Question 26
Arthur Falkland, aged 40 years, is a gas plumber who installs under-floor heating ducts. He has experienced three months of intermittent ‘pins and needles’ in the fourth and fifth fingers of his right hand. His symptoms are worse at work, especially with prolonged elbow flexion. Examination of his cervical spine, right elbow and right hand is normal.
What is the MOST appropriate initial management?
A. Amitriptyline 10 mg orally at night
B. Magnetic resonance imaging cervical spine
C. Padded right elbow extension splint worn at night for six weeks
D. Referral to surgeon for consideration of right ulnar nerve release
E. Ultrasound right elbow
Correct Answer: C. Padded right elbow extension splint worn at night for six weeks
Question 27
Sandra Peters, aged 68 years, returns to discuss her recent 24-hour blood pressure monitor report. The mean blood pressure was 165/105 mmHg. Her current medications are lercanidipine 20 mg orally daily and perindopril 10 mg orally daily. Sandra has asthma and takes budesonide–eformoterol 400 mcg/12 mcg inhaled twice daily and salbutamol 100 mcg 2–4 inhalations as required. One month earlier, she had an episode of calcium phosphate kidney stones and is awaiting formal urological follow up at the local hospital. Investigations for secondary causes of hypertension are normal.
What is the MOST appropriate pharmacological management?
A. Add candesartan 4 mg orally daily
B. Add hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg orally daily
C. Add metoprolol 25 mg orally twice daily
D. Add spironolactone 12.5 mg orally daily
E. Cease perindopril and initiate frusemide 20 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: B. Add hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg orally daily
Question 28
Anton Johns, aged 45 years, presents to your rural clinic with pain, redness, warmth and swelling of his left foot. He cut his foot on rocks while fishing in the ocean five days earlier. He attended the local emergency department yesterday, and the lacerations on his foot were cleaned and dressed. He was given a tetanus booster and a single dose of intravenous antibiotics. He had an argument with a patient with whom he was sharing a room, left hospital before further treatment was given and refuses to return. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 37.4°C and blood pressure is 128/72 mmHg. He has tenderness and redness surrounding the wounds on his foot. You arrange to review him tomorrow.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Dicloxacillin 500 mg orally four times daily
B. Duplex venous ultrasound left lower limb
C. Flucloxacillin 500 mg orally four times daily plus doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily
D. Mupirocin 2% ointment topically three times daily for seven days
E. X-ray left foot
Correct Answer: C. Flucloxacillin 500 mg orally four times daily plus doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily
Question 29
Peter Baker, aged 18 months, is brought in by his mother, Sharon, as he has had a fever and has been off his food for the past two days. On examination, he is alert and interactive. His tympanic temperature is 37.9°C, heart rate is 130/min and respiratory rate is 35/min. The rest of his examination is unremarkable.
His parents have a urine specimen they collected overnight with an adhesive urinary collection bag. The urine dipstick sample is positive for leucocytes and nitrites. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Arrange transfer to emergency department
B. Cefalexin 33 mg/kg (max 500 mg) orally twice daily for five days
C. Collect a second adhesive urinary collection within the clinic for dipstick testing today
D. Instruct his parents to collect a clean-catch specimen for repeat dipstick testing today
E. Send the urine sample for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
Correct Answer: D. Instruct his parents to collect a clean-catch specimen for repeat dipstick testing today
Question 30
Kerryn Gravell, aged 52 years, returns for blood test results you arranged to investigate swelling of her toes and brittle nails. She uses methylprednisolone aceponate 0.1% cream topically for plaque psoriasis and takes ramipril 5 mg orally daily for hypertension. On examination, there is diffuse swelling of the proximal interphalangeal joints of her left second and third toes. You notice her nails are brittle and crumbly. C-reactive protein is 9* mg/L (normal range: 0-6) and rheumatoid factor is 8 IU/L (normal range: < 30). You discuss these results, the likely diagnosis and associated comorbidities that need to be considered.
What is the MOST appropriate next investigation?
A. Bone densitometry
B. Chest X-ray
C. Fasting lipids
D. Iron studies
E. Stress echocardiography
Correct Answer: C. Fasting lipids
Question 31
A carer at the local supported care facility calls you to urgently see Sarah Luscombe, aged 64 years, regarding an escalation in Sarah’s behaviour over the past three days. Sarah has bipolar disorder. Two months earlier, she ceased citalopram with a goal to eventually use only complementary therapies. She continues to take lithium 250 mg orally twice daily and zolpidem 10 mg orally at night, as well as vitamin supplements prescribed by her naturopath. During your visit today, Sarah informs you that she refuses to see her psychiatrist again. She is argumentative and has rambling thoughts and is demanding you cease her lithium, as she is convinced she does not have bipolar. You try to reason with her, but Sarah yells abusively at you, pushes you out the door and then slams the door in your face. Collaborative history from her daughter includes escalation of text messages, with her daughter receiving over 400 messages from Sarah in the past few days.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Arrange for Sarah’s medical care to be transferred to a new general practitioner
B. Cessation of all vitamin supplements
C. Facilitate involuntary psychiatric admission
D. Increase lithium to 500 mg orally twice daily
E. Recommence citalopram 20 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: C. Facilitate involuntary psychiatric admission
Question 32
Olga Petrova, aged 22 years, has had episodes of dizziness every week for the past three months. Each episode lasts several hours and starts with nausea, followed by a feeling that the room is spinning. She then develops a pounding headache on the left side of her head and sometimes vomits. She says that during each episode, turning her head makes the dizziness worse, and the only thing that seems to relieve the symptoms is sleep. The episodes are quite debilitating and leave her unable to work. During one episode, she attended the emergency department. A magnetic resonance imaging scan of her brain was normal. On examination, while symptom free, her heart rate is 76/min, blood pressure is 120/75 mmHg and neurological examination is normal. Dix-Hallpike manoeuvre is negative.
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Audiometry
B. Betahistine 8 mg orally three times daily
C. Epley manoeuvre
D. Hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg orally daily
E. Low sodium diet
F. Prednisolone 50 mg orally daily for five days then taper over 15 days
G. Prochlorperazine 5 mg orally three times per day for 1 month
H. Propranolol 20 mg orally at night
I. Repeat magnetic resonance imaging brain
Correct Answer: H. Propranolol 20 mg orally at night
Question 33
Steve Wilkie, aged 36 years, has an ongoing issue with ear wax accumulation. He regularly cleans his ears with a cotton bud. While performing this treatment the night before, he developed sudden pain in his left ear. On examination, otoscopy of his left ear shows his tympanic membrane as demonstrated in the image below (see image). The Weber test lateralises to the left ear and the Rinne test reveals bone conduction is greater than air conduction in his left ear.
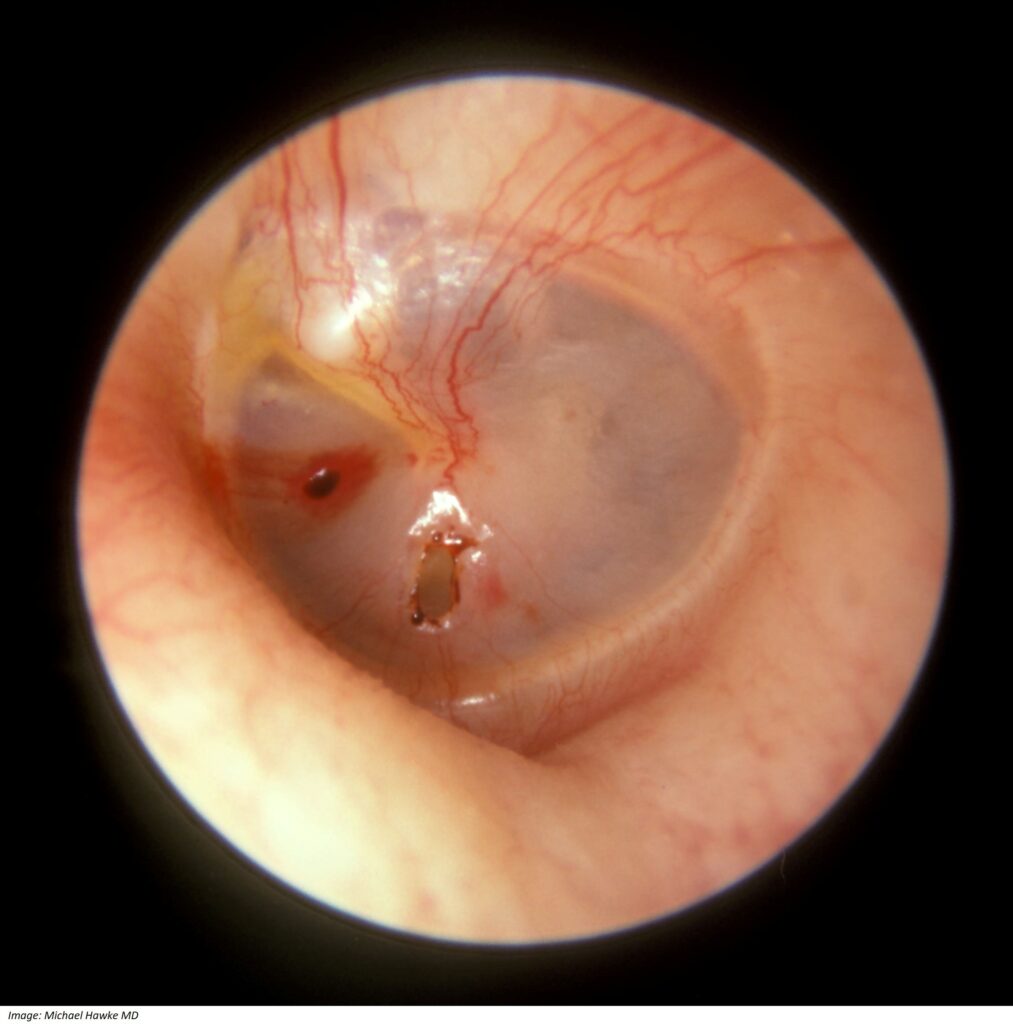
What is the MOST appropriate immediate management?
A. Advise him to keep the ear dry
B. Amoxicillin–clavulanic acid 875 mg/125 mg orally twice daily for five days
C. Arrange audiometry
D. Ciprofloxacin 0.3% ear drops five drops topically into the left ear twice daily
E. Flumetasone pivalate–clioquinol 0.02%/1% ear drops three drops topically into the left ear twice daily for five days
F. Perform saline flush of ear canal
G. Refer for hearing aid
H. Urgent review by ear, nose and throat surgeon
Correct Answer: A. Advise him to keep the ear dry
Question 34
Emma Richards, aged 33 years, has been recalled to discuss blood test results. She presented last week reporting a four-week history of fatigue, difficulty concentrating and 2 kg of unintentional weight loss. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 36.1°C, heart rate is 88/min and blood pressure is 125/84 mmHg. Palpation of her thyroid gland reveals a smooth, normal-sized thyroid gland. The rest of her examination is unremarkable.
Full blood examination, kidney and liver function and ferritin are within normal limits. Serum human chorionic gonadotropin is negative. The remainder of her results are shown below:
| Test | Result | Normal range |
| Thyroid-stimulating hormone | < 0.05* mU/L | 0.4 – 4.0 |
| Free T4 | 38* pmol/L | 9.0 – 25.0 |
| Thyroid peroxidase antibodies | 42* IU/mL | < 35 |
| Thyroglobulin antibodies | 31* IU/mL | < 20 |
| Anti-thyroid stimulating hormone receptor antibodies | 2.02* IU/L | < 1.75 |
What is the MOST appropriate investigation to support your provisional diagnosis?
A. Computed tomography scan thyroid and neck
B. Magnetic resonance imaging thyroid gland
C. Thyroid scintigraphy (isotope scan)
D. Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of the thyroid gland
E. Ultrasound thyroid gland
Correct Answer: C. Thyroid scintigraphy (isotope scan)
Question 35
Candice Kingston, aged 49 years, has had two days of weakness in her right foot. One week earlier, she presented to the local emergency department with sudden onset of severe right calf pain. Right lower leg X-ray, calf ultrasound and lower leg Doppler ultrasound were all normal. She was discharged with analgesia and advised to follow up with her general practitioner if she did not improve. On examination, she has an antalgic gait, right foot plantar flexion power 4/5, absent ankle jerk and decreased sensation to the sole of her right foot.
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Central spinal canal stenosis
B. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy
C. Motor neurone disease
D. Multiple sclerosis
E. Right Achilles tendon rupture
F. Right gastrocnemius tear
G. Right L4/5 foraminal stenosis
H. Right-sided L5-S1 disc prolapse
I. Right tarsal tunnel syndrome
Correct Answer: H. Right-sided L5-S1 disc prolapse
Question 36
Lea Stewart, aged 24 years, has had a painful rash on her feet and lower legs for the past three days (see image). Lea has been otherwise well. She commenced medroxyprogesterone acetate 150 mg intramuscular injection for contraception four weeks earlier and takes naproxen 250 mg orally three times daily as required for management of primary dysmenorrhoea. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 37.0°C, blood pressure is 110/78 mmHg and body mass index is 35 kg/m2. Initial investigations, including full blood count, renal and liver function and C-reactive protein, are within normal limits.
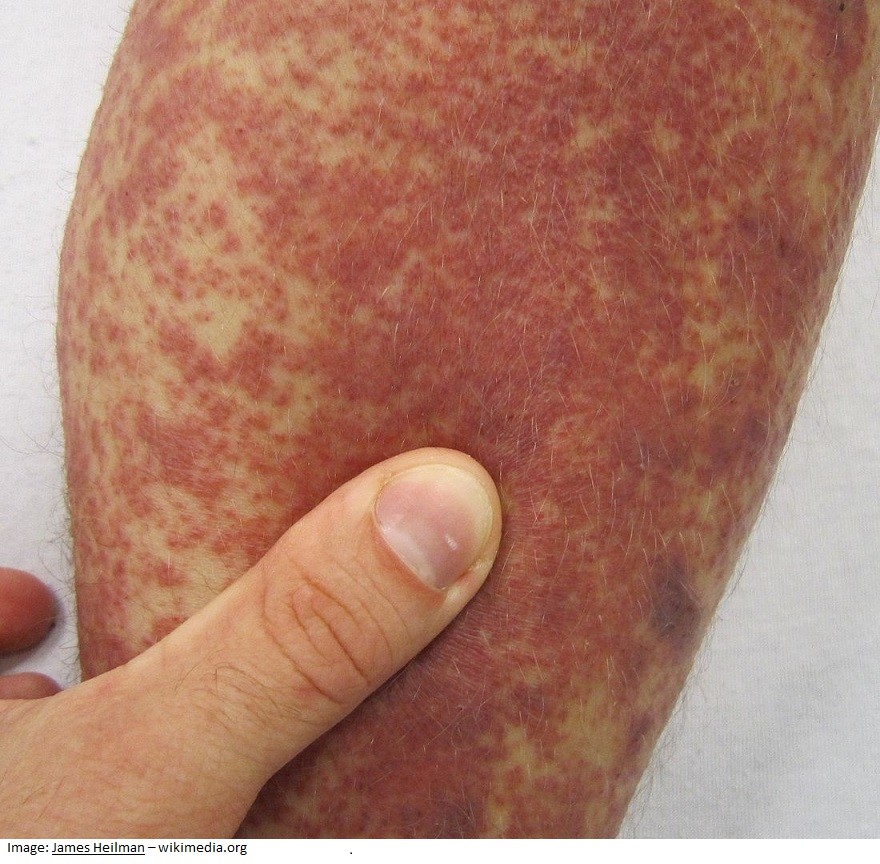
What is the MOST appropriate provisional diagnosis?
A. Cryoglobulinaemia
B. Factor VII deficiency
C. Giant cell arteritis
D. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
E. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis
F. Urticaria
G. Venous eczema
H. Von Willebrand disease
Correct Answer: E. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis
Question 37
Angela Giuliani, aged 55 years, presents with 10 days of intermittent, severe right-sided facial pain. She describes episodes of severe stabbing pain from her right upper lip to her right eye, lasting about one minute and occurring several times per day. The pain often occurs when she is eating or cleaning her teeth. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 36.7°C, heart rate is 72/min and blood pressure is 128/73 mmHg. Physical examination is unremarkable.
What is the MOST appropriate management?
A. Amitriptyline 10 mg orally at night
B. Amoxicillin 500 mg orally three times per day for five days
C. Carbamazepine 100 mg orally twice per day
D. Famciclovir 250 mg orally three times per day for five days
E. Indomethacin 25 mg orally three times per day
F. Oxygen 100% via Hudson mask for 15 minutes
G. Prednisolone 50 mg orally daily for seven days, then taper over three weeks
H. Refer for fitting of an intraoral occlusal night splint
I. Sumatriptan 20 mg via nasal spray at onset of pain
J. Verapamil extended release 180 mg orally daily
Correct Answer: C. Carbamazepine 100 mg orally twice per day
Question 38
Tim Grant, aged 56 years, presents to your rural emergency department with five days of increasing central chest pain. The pain is an intermittent dull ache worsened by inspiration. The pain is improved by sitting forward and is worse at night when he is lying down. He is taking ibuprofen 400 mg orally three times daily, which helps relieve the pain a little. He had a mechanical aortic valve replacement and aortic root replacement three months earlier. All follow-up checks have been normal. He takes warfarin 10 mg orally daily and his international normalised ratio was in the normal range two days earlier. A stat troponin and chest X-ray taken today are both unremarkable.
Blood tests reveal a white cell count of 11.7* ×109/L (normal range: 4.0–11.0) and his C reactive protein is 129* mg/L (normal range: < 3).
An electrocardiogram is performed (see image).
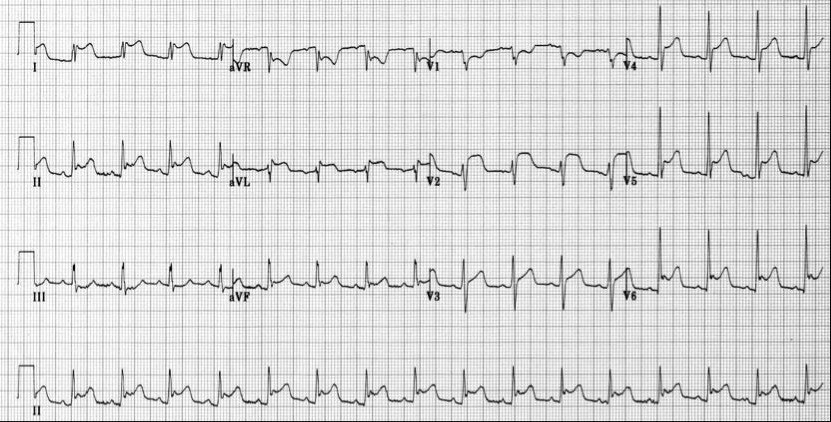
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Alteplase infusion 10 mg intravenous bolus, followed by 90 mg over two hours
B. Apixaban 10 mg orally twice daily
C. Aspirin 300 mg orally stat
D. Ceftriaxone 1 g intravenously twice daily
E. Clindamycin 300 mg orally three times daily
F. Colchicine 500 mcg orally twice daily
G. Enoxaparin 1 mg/kg subcutaneously twice daily
H. Glyceryl trinitrate 10 mcg/min by intravenous infusion
I. Morphine sulfate 2 mg intravenously stat
J. Ticagrelor 180 mg orally for the first dose, then 90 mg twice daily
K. Urgent transfer to tertiary centre for percutaneous coronary intervention
Correct Answer: F. Colchicine 500 mcg orally twice daily
Question 39
Bernice Donato, aged 27 years, presents with an itchy rash on her left arm (see image). It has been worsening over the past three weeks, despite changing her body wash and trying to wash more often.
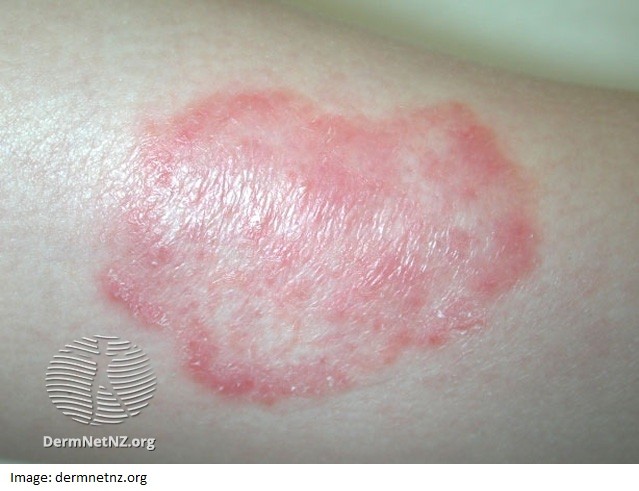
What is the MOST appropriate initial treatment?
A. Doxycycline 100 mg orally daily for seven days
B. Fluconazole 150 mg orally once per week for six weeks
C. Mometasone furoate 0.1% topically twice daily until resolution of rash
D. Mupirocin 2% cream topically three times daily for 10 days
E. Terbinafine 1% cream topically twice daily for 7–14 days
Correct Answer: E. Terbinafine 1% cream topically twice daily for 7–14 days
Question 40
Alex Anderson, aged 2 months, is brought in by his mother, Amanda, who is distressed and exhausted because Alex has ‘colic’. Alex was born at term and his birth weight was 3540 g. He is currently on the 50th centile for weight. He is fully breastfed and is up to date with his immunisations. Alex has been difficult to settle since he was born, but his crying has been getting more intense in the past couple of weeks. There is no pattern to his crying and he can cry for hours at a time. He often draws his legs up as if he is in pain. Breastfeeding is the only thing that settles him, and he feeds every 2–3 hours. His motions are often slightly green and watery. He has a wet nappy every time he feeds. Physical examination is unremarkable. Amanda’s Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale score is normal.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Alternate breastfeeds with feeds of lactose-free formula
B. Assist Amanda to establish a pattern to feeding, settling and sleep
C. Eliminate cow’s milk from Amanda’s diet for two weeks
D. Faeces microscopy, culture and sensitivities
E. Omeprazole 5 mg orally daily for four weeks
Correct Answer: B. Assist Amanda to establish a pattern to feeding, settling and sleep
Question 41
Sally Moore, aged 30 years, presents at 34 weeks’ gestation with concern regarding reduced frequency of fetal movements during the past six hours. On examination, her heart rate is 82/min and blood pressure is 108/72 mmHg. Symphysis-fundal height measurement is 35 cm and fetal heart rate is 148/min.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Fasting blood glucose level
B. Reassure Sally and review at next antenatal visit
C. Recommend use of kick-chart: Less than 10 movements in a two-hour active period requires review
D. Ultrasound scan for fetal growth and wellbeing
E. Urgent referral to obstetric unit for cardiotocography
Correct Answer: E. Urgent referral to obstetric unit for cardiotocography
Question 42
Ronald McCann, aged 67 years, attends your rural practice for review of his type 2 diabetes. His blood tests performed last week reveal glycated haemoglobin of 9.6*% (target range: < 7). He has a history of ischaemic heart disease. His current medications include metformin extended release 2 g orally daily, gliclazide 120 mg orally daily, atorvastatin 40 mg orally daily, lisinopril 10 mg orally daily, amlodipine 5 mg orally daily, aspirin 100 mg orally daily and metoprolol 25 mg orally twice daily. On examination, his heart rate is 72/min, blood pressure is 128/74 mmHg and body mass index is 32 kg/m2.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Antiglutamic acid decarboxylase antibody titre
B. Change gliclazide to glibenclamide 2.5 mg orally twice daily
C. Continue current medications and repeat glycated haemoglobin in three months
D. Dulaglutide 1.5 mg subcutaneously once per week
E. Insulin glargine 100 units/mL 0.2 units/kg (up to 30 units) subcutaneously daily
Correct Answer: D. Dulaglutide 1.5 mg subcutaneously once per week
Question 43
Izaac Bates, aged 6 weeks, is brought in for his first routine immunisations. You perform an appropriate examination and note that his left testis is palpable in the inguinal canal. It is of normal size and can be brought down into the scrotum without tension. His right testis is normally located.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Arrange scrotal ultrasound
B. Explain that the testicle could be surgically placed in scrotum, but fertility will be permanently reduced
C. Organise review at three months of age
D. Reassure that this is normal and no further follow up is required
E. Urgent referral to a paediatric surgeon for consideration of orchidopexy
Correct Answer: C. Organise review at three months of age
Question 44
Hilda Holmwood, aged 42 years, presents two weeks after a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. She has been unwell for three days with a fever and intermittent pain in her right upper abdomen. On examination, her tympanic temperature is 38.6°C, heart rate is 96/min, blood pressure is 126/82 mmHg and respiratory rate is 34/min. There is right upper quadrant tenderness on abdominal palpation.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Amoxicillin 500 mg orally three times daily
B. Arrange transfer to emergency department
C. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography
D. Perform blood cultures
E. Ultrasound scan upper abdomen
Correct Answer: B. Arrange transfer to emergency department
Question 45
Renee Sampson, aged 28 years, presents to you for her routine cervical screening test. Her regular male partner is currently receiving treatment for Mycoplasma genitalium urethritis, and Renee asks if she should also be tested. She does not have any urogenital symptoms.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Advise to return for review if she develops symptoms of Mycoplasma genitalium infection
B. Azithromycin 1 g orally on the first day, then 500 mg orally daily for three days
C. Doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily for seven days
D. High vaginal swab polymerase chain reaction for Mycoplasma genitalium
E. Perform co-test
Correct Answer: D. High vaginal swab polymerase chain reaction for Mycoplasma genitalium
Question 46
Magdelena Sadowski, aged 36 years, returns for blood test results. She commenced agomelatine 25 mg orally at night four weeks earlier for management of major depression. Two years earlier, she had an episode of major depression treated with citalopram. During treatment, she experienced a significant loss of libido and wants to minimise the risk of this occurring again. She sees a psychologist regularly for cognitive behavioural therapy. Her liver function test results are shown below. On examination, her heart rate is 65/min, blood pressure is 120/75 mmHg and body mass index is 20 kg/m2.
| Test | Result | Normal range |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 400* U/L | 30 – 115 |
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase | 135* U/L | 0 – 45 |
| Alanine aminotransferase | 150* U/L | 0 – 45 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase | 120* U/L | 0 – 41 |
| Total bilirubin | 32* umol/L | 2 – 20 |
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Change agomelatine to duloxetine 60 mg orally daily
B. Change agomelatine to mirtazapine 15 mg orally at night
C. Change agomelatine to paroxetine 10 mg orally daily
D. Change agomelatine to sertraline 50 mg orally daily
E. Change agomelatine to venlafaxine 75 mg orally daily
F. Continue current treatment and repeat liver function tests in three weeks
G. Increase agomelatine to 50 mg orally at night
H. Recommend taking agomelatine with food
Correct Answer: B. Change agomelatine to mirtazapine 15 mg orally at night
Question 47
Sam Phillips, aged 23 years, injured his left ankle while playing basketball one hour earlier. He jumped to catch the ball and then landed awkwardly, rolling his left ankle. He was unable to continue playing the game but has been able to walk slowly. Twelve months earlier, he sprained his left ankle, but made a full recovery with physiotherapy. On examination, he has an antalgic gait. There is significant swelling and bruising of his left ankle and foot. On palpation,there is tenderness over the tip of the lateral malleolus.
What is the MOST appropriate indication for an ankle X-ray for this patient?
A. An X-ray is not indicated in this patient
B. Antalgic gait
C. Point tenderness over the tip of the lateral malleolus
D. Previous sprain in the same ankle
E. Significant swelling and bruising
Correct Answer: Point tenderness over the tip of the lateral malleolus
Question 48
Sasha McPherson, aged 18 years, presents with her mother, Stephanie, for review following an intentional drug overdose at home one week earlier. Sasha consumed ten 500 mg paracetamol tablets and five 200 mg ibuprofen tablets after her boyfriend broke up with her via a text message because she was too ‘clingy’. She was managed at the local hospital prior to being discharged two days ago. Two years earlier, she took three of her mother’s temazepam tablets following a physical fight with a friend at school. Sasha denies any current suicidal thoughts or intent to self-harm. She states she has felt ’empty’ and ‘worthless’ since her parents’ divorce three years earlier.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Amitriptyline 50 mg orally at night
B. Cognitive processing therapy
C. Dialectical behavioural therapy
D. Diazepam 5 mg orally three times daily, as required
E. Escitalopram 20 mg orally in the morning
F. Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing
G. Prolonged-exposure therapy
H. Quetiapine 50 mg orally at night
I. Sleep–wake cycle management
J. Slow-breathing exercises
K. Venlafaxine 75 mg orally in the morning
Correct Answer: C. Dialectical behavioural therapy
Question 49
Ahmed Hassan, aged 35 years, a Syrian refugee, has been experiencing recurrent epigastric discomfort after meals for the past two weeks. He presented with the same symptoms eight weeks earlier and was prescribed esomeprazole 20 mg orally daily for four weeks. His symptoms had settled during treatment. On examination, his tympanic temperature is 36.8°C, heart rate is 72/min and blood pressure is 122/78 mmHg. His abdomen is soft on palpation with mild epigastric tenderness.
What is the MOST appropriate next step?
A. Barium swallow
B. Helicobactor pylori serology
C. Pantoprazole 40 mg orally daily
D. Ultrasound abdomen
E. Urea breath test
Correct Answer: E. Urea breath test
Question 50
Phoebe Bridge, aged 32 years, has been experiencing pain in her right wrist for the past few months. She has recently taken on a big project in her work as a landscaper and is concerned that the pain is limiting her ability to work. She has tried ibuprofen 400 mg orally three times daily and splinting her wrist. She finds it difficult to use her gardening tools with the splint in place, and therefore, can only use it at night. On examination, there is tenderness to palpation over the radial styloid. Ulnar deviation of the wrist and extension of the thumb against resistance are both very painful.
What is the MOST appropriate next step in management?
A. Corticosteroid injection into the location of pain
B. Magnetic resonance imaging right wrist
C. Prednisolone 30 mg orally daily for five days
D. Referral to an orthopaedic surgeon
E. X-ray right wrist
