Case 1: Joel Ford
Joel Ford, aged 26 years, reports a five-day history of increasing mucopurulent rectal discharge associated with constipation and mild anal discomfort during defecation. He feels fatigued, hot and cold and has generalised body aches. He has no other focal symptoms.
Joel has no significant past medical history, takes no regular medications and has no known allergies. He does not smoke, has two standard drinks of alcohol three nights per week and does not use recreational drugs. He has had unprotected receptive anal sexual intercourse with two male partners in the past two weeks. He has no significant family medical history.
On examination, Joel looks well. His temperature is 36.6 °C, blood pressure is 121/79 mmHg, heart rate is 75/min regular, respiratory rate is 14/min and body mass index is 23 kg/m2. His abdomen is soft and non-tender and there are no palpable inguinal lymph nodes. Digital rectal examination is painful and reveals mucopurulent discharge, but no other focal features. The remainder of his examination is normal.
Question 1
What are the most likely underlying causes of Joel’s presentation? Write three (3) specific causes.
- …
- …
- …
Question 2
What initial investigations would help to confirm the most likely diagnosis? Select four (4) investigations from the following list.
- Anorectal swab for chlamydia polymerase chain reaction
- Anorectal swab for gonorrhoea polymerase chain reaction
- Anorectal swab for herpes simplex virus polymerase chain reaction
- Anorectal swab for human papilloma virus polymerase chain reaction
- Anorectal swab for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
- Anorectal swab for mycoplasma genitalium polymerase chain reaction
- Anorectal swab for trichomoniasis polymerase chain reaction
- C-reactive protein
- Computed tomography scan of abdomen and pelvis
- Faecal calprotectin
- Faeces for clostridium difficile toxin
- Faeces for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
- Faeces for ova, cysts and parasites
- First pass urine for chlamydia polymerase chain reaction
- First pass urine for trichomoniasis polymerase chain
- First pass urine for mycoplasma genitalium polymerase chain reaction
- Full blood count
- Hepatitis A serology
- Hepatitis B serology
- Hepatitis C serology
- Human immunodeficiency virus serology
- Liver function tests
- Syphilis serology
- Ultrasound scan of abdomen
- Urea and electrolytes
- Urine for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
Question 3
Joel’s investigations confirm the most likely diagnosis, and you commence appropriate pharmacological treatment.
What non-pharmacological management actions are appropriate? Write four (4) specific nonpharmacological management actions.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Case 2: Jessie Carpenter
Jessie Carpenter, aged 32 years, reports a two-month history of a tender area of skin on her left hand. It initially started as a small red patch and has enlarged over the past few months.
Jessie has no significant past medical history, takes no regular medications and has no known allergies. She does not smoke and has two standard drinks of alcohol three nights per week.
On examination, Jessie looks well. Her temperature is 36.9 °C, blood pressure is 118/72 mmHg, heart rate is 72/min regular, respiratory rate is 14/min and body mass index is 22kg/m2. The lesion on her left hand is shown below (see image). The remainder of her examination is normal.
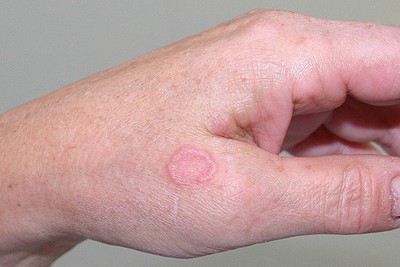
Question 4
What is the single most likely diagnosis? Write one (1) specific diagnosis.
- …
Question 5
What pharmacological management action is appropriate for the most likely diagnosis? Write one (1) specific pharmacological management action, including the drug class and one specific example, route and frequency (dosages not required).
- …
Case 3: Jessica Cooper
Jessica Cooper, aged 28 years, returns for her routine prescriptions and blood results. She has been well recently.
Jessica’s past medical history includes polycystic ovarian syndrome and bipolar 1 disorder, which was diagnosed during an admission six months ago with a first episode of mania. She currently takes lithium carbonate 500 mg orally twice daily and quetiapine modified-release 50
mg orally twice daily. She has no known allergies. She does not smoke and drinks two standard drinks of alcohol four nights per week. She does not use recreational drugs.
On examination, Jessica looks well. Her temperature is 36.8 °C, blood pressure is 120/78 mmHg, heart rate 68/min regular and body mass index is 28 kg/m2. The remainder of her examination is normal.
Jessica’s recent investigation results are as follows:
Urea and electrolytes – Normal Thyroid function tests
| Test | Result | |
| Thyroid stimulating hormone | 5.9* mIU/L | |
| Free T4 | 12.8 pmol/L |
Question 6
What is the single most likely diagnosis? Write one (1) diagnosis.
- …
Question 7
Jessica is concerned about having another episode of mania and asks about strategies to prevent a relapse of her bipolar 1 disorder.
Other than onwards referral, what non-pharmacological advice is appropriate? Write four (4) pieces of non-pharmacological advice.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 8
Jessica returns 12 months later with her partner, Chris. Chris was working away from home for a few days recently. When he returned, Jessica told him that she had not slept at all. She believed that she needed to save the business that she works for from financial ruin. Jessica says that she has been hearing a voice that has been encouraging her to murder her competitors to ensure that her company survives. Chris says Jessica ceased her medications six months ago, as they had decided to have a baby.
What specific management actions are appropriate? Write two (2) specific management actions.
- …
- …
Case 4: Billy Sims
Billy Sims, aged 62 years, is a Torres Strait Islander man who reports a three-day history of a painful and swollen left foot. The pain has been interrupting his sleep at night. There is no history of trauma to his foot.
Billy’s past medical history includes type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension for which he takes metformin modified-release 500 mg orally twice daily, irbesartan 150mg orally daily and hydrochlorothiazide 25mg orally daily. He smokes five cigarettes per day and drinks six standard units of alcohol five nights per week.
On examination, Billy looks well. His temperature is 36.6 °C, blood pressure is 135/95 mmHg, heart rate 85/min regular and body mass index is 32 kg/m2. An image of his feet is shown below (see image). The remainder of his examination is normal.
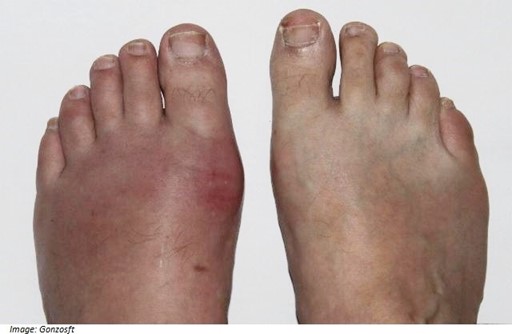
Question 9
What is the single most likely diagnosis? Write one (1) specific diagnosis.
- …
Question 10
You arrange further investigations that confirm the most likely diagnosis.
What immediate pharmacological management actions are appropriate? Write three (3) immediate pharmacological management actions, including the route and frequency. Dosages are not required.
- …
- …
- …
Question 11
Billy returns for review two weeks later. His symptoms have improved following your management.
What non-pharmacological management options are appropriate? Write four (4) nonpharmacological management actions.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Case 5: Shirley Jennings
Shirley Jennings, aged 75 years, presents to your rural clinic complaining of a six-month history of morning cough. She brings up small amounts of white sputum. Shirley has also had difficulty
‘catching her breath’ when carrying her groceries into her house. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
Shirley has a past medical history of hypertension, for which she takes ramipril 5 mg orally daily. She purchased a salbutamol 100 mcg inhaler over-the-counter six weeks ago and has been taking two to three inhalations four times daily as required but has had inadequate symptom relief. She takes no other regular medications and has no known allergies. She has never smoked, however her husband was a heavy smoker and died 12 months ago from lung cancer. She does not drink alcohol. COVID-19 vaccinations are up to date.
On examination, Shirley looks well and is not short of breath at rest. Her temperature is 36.7 °C, blood pressure is 127/84 mmHg, heart rate is 78/min regular, respiratory rate is 14/min, oxygen saturation is 96% on room air and body mass index is 22 kg/m2. Examination of her chest reveals mild scattered expiratory wheeze in both lung fields. The remainder of her examination is normal.
You perform spirometry with results as follows:
| Parameter | Units | Predicted | Pre | % Predicted | Post | % Predicted | % Change |
| Forced vital capacity (FVC) | L | 2.89 | 2.46 | 85.1 | 2.81 | 97.3 | 14.3 |
| Forced expiratory volume 1 (FEV1) | L | 2.16 | 1.59 | 73.6 | 1.72 | 79.8 | 8.5 |
| FEV1:FVC | % | 73.4 | 64.4 | 87.8 | 61.2 | 83.4 | -5.1 |
Question 12
What pharmacological management options are appropriate? Write four (4) pharmacological management options (including a class and appropriate example, dosing is not required).
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 13
Shirley returns four weeks later. She reports three days of fever, increasing breathlessness and increasing frequency of her cough. Her sputum has become thick and discoloured.
What additional specific features on examination would indicate that Shirley requires admission to hospital? Write four (4) specific examination features.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 14
Shirley is managed appropriately and makes a full recovery.
Shirley returns to see you for an urgent appointment two weeks later. She has had nausea, vomiting, a headache and pain in her right eye for the past four hours. She says the vision in her right eye is very hazy.
On examination, Shirley looks well though uncomfortable. Her temperature is 36.9 °C, blood pressure is 131/89 mmHg, heart rate 76/min regular, respiratory rate is 14/min and oxygen saturation is 96% on room air. Examination of her eyes (see image) reveals that her visual acuity is 6/6 in her left eye and 6/18 in her right eye.
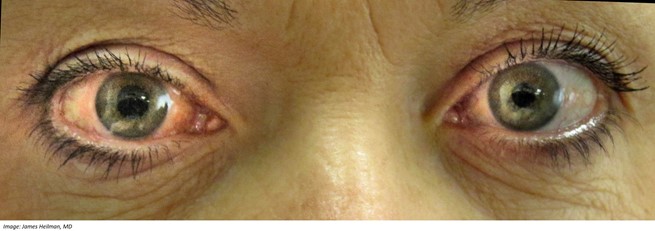
What immediate management actions are appropriate? Write four (4) immediate management actions (dosing is not required).
- …
- …
- …
- …
Case 6: Charlie Newsom
Question 15
Charlie Newsom, aged 4 years, is an Aboriginal boy who is brought in to your remote clinic by his mother, Dana. Charlie has been unwell since last night with fevers and a sore left ear. He has had no other focal symptoms. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
Charlie has no significant past medical history, takes no regular medications and has no known allergies. His immunisations are up to date. He is growing on the 50th centile and is meeting appropriate developmental milestones.
On examination, Charlie is cooperative and interactive. His temperature is 38.2 °C, heart rate 95/min regular and respiratory rate is 20/min. You note the following appearance on otoscopic examination of his left ear (see image). The remainder of his examination is normal.
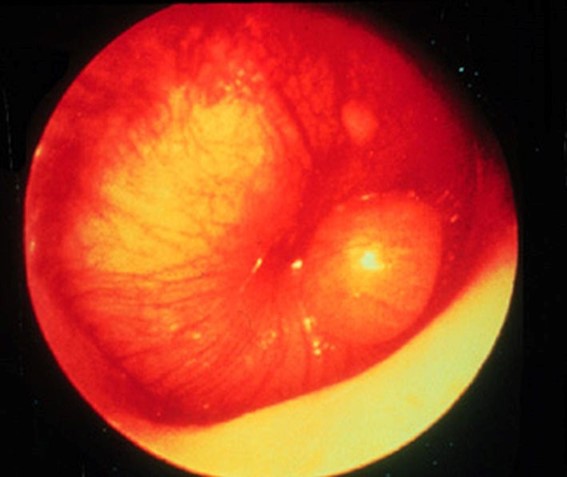
Question 16
What pharmacological management actions are appropriate? Write two (2) pharmacological management actions, including the route and frequency of the medication, dosages are not required.
- …
- …
Question 17
Charlie returns six weeks later with persistent purulent discharge from his left ear.
On examination, Charlie looks well. His temperature is 36.6 °C, heart rate 90/min regular and respiratory rate is 20 b/min. You note the following appearance on otoscopic examination on his left ear (see image). The remainder of his examination is normal.
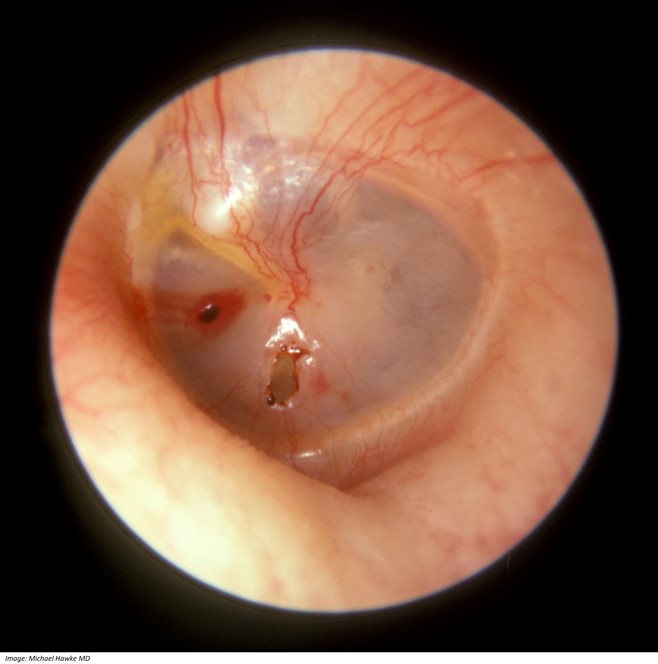
What immediate management actions are appropriate? Write four (4) specific immediate management actions. If your answer includes medications, include route and frequency, dosages are not required.
- …
- …
- …
- …
Case 7: Dora Naeger
Question 18
Dora Naeger, aged 53 years, is an Aboriginal woman who presents to your remote Cape York clinic with a six-week history of cough. She is coughing up copious amounts of cream-coloured sputum, which is intermittently streaked with blood. She has felt extremely tired and has lost 6 kg in the last six weeks. She has had no other focal symptoms. At the start of her illness she was prescribed amoxicillin 1000 mg orally three times a day for seven days and doxycycline 100 mg twice a day for five days by another doctor, without improvement. COVID-19 has been definitively excluded.
Dora has a past medical history of type 2 diabetes mellitus for which she takes metformin modified- release 500 mg orally twice daily. She has no known allergies. She smokes 40 cigarettes per day and drinks 10 standard drinks of alcohol most nights. She lives in a local hostel.
On examination, Dora looks well but thin. Her temperature is 36.7 °C, blood pressure is 129/84 mmHg, heart rate 82/min regular, respiratory rate is 14/min, oxygen saturation is 98% on room air and body mass index is 19 kg/m2. Examination of her chest reveals bronchial breath sounds in her left upper lobe. The remainder of her examination is normal.
You arrange an X-ray of her chest (see image).
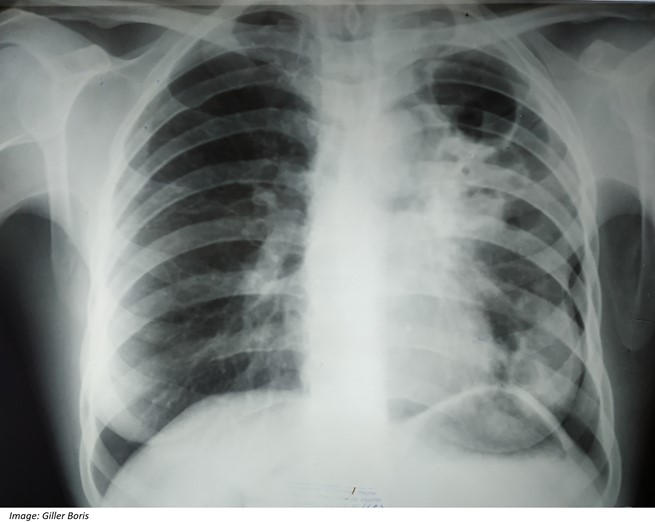
What are the most likely differential diagnoses? Write three (3) specific differential diagnoses.
- …
- …
- …
Question 19
What initial investigations are appropriate? Select three (3) investigations from the following list.
- Aspergillus serology
- Blood cultures
- Bronchoscopy
- C-reactive protein
- Chlamydia pneumoniae serology
- Echocardiogram
- Electrocardiogram
- Fasting blood glucose
- Fasting lipids
- Full blood count
- Glycosylated haemoglobin
- High resolution computed tomography scan of chest
- Human immunodeficiency virus serology
- Interferon-gamma release assay for Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Legionella antigen
- Liver function tests
- Mantoux test
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae serology
- Nasopharyngeal swab for Bordetella pertussis polymerase chain reaction
- Nasopharyngeal swab for respiratory virus polymerase chain reaction
- Serum folate
- Spirometry
- Sputum for acid-fast bacilli microscopy
- Sputum for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
- Sputum for mycobacterium polymerase chain reaction and culture
- Urea and electrolytes
- Urine albumin:creatinine ratio
- Urine for legionella pneumophila antigen
- Urine for streptococcal antigen
- Vitamin B12
Case 8: Cherie Hine
Cherie Hine, aged 25 years, presents to your rural clinic with abdominal pain. She says that over the last few months she has had upper abdominal pain after meals approximately once or twice a week but the pain has always settled within an hour. Today the pain is more severe and has been present since last night. She has been vomiting and she feels ‘awful’.
Cherie has no significant past medical history, takes no regular medications and has no known drug allergies. She does not smoke and drinks four standard drinks of alcohol two nights per week.
On examination, Cherie looks unwell and has scleral icterus. Her temperature is 38.7 °C, blood pressure is 102/58 mmHg, heart rate 126/min regular, respiratory rate is 26/min, oxygen saturation is 98% on room air and body mass index is 28 kg/m2. Her abdomen is soft but very tender in the epigastrium and right upper quadrant.
The nearest hospital is 500 km away.
Question 20
What initial investigations are appropriate? Select six (6) investigations from the following list.
- Anti-gliadin antibodies
- Beta human chorionic gonadotrophin
- Blood cultures
- C-reactive protein
- Calcium studies
- Computed tomography cholangiogram
- Computed tomography scan of abdomen
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- Faecal calprotectin
- Faecal occult blood test
- Faeces for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
- Full blood count
- Hepatitis A serology
- Hepatitis B serology
- Hepatitis C serology
- Iron studies
- Lipase
- Liver function tests
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography
- Random blood glucose level
- Serum calcium
- Thyroid function tests
- Tissue transglutaminase antibodies
- Ultrasound scan of abdomen
- Ultrasound scan of pelvis
- Urea and electrolytes
- Urease breath test
- Urine for microscopy, culture and sensitivities
- Venous blood gas
Question 21
Cherie’s investigations confirm the most likely diagnosis.
What immediate management actions are appropriate? Write five (5) specific management actions (dosing is not required).
- …
- …
- …
- …
- …
Question 22
Cherie is managed with an appropriate surgical procedure.
Cherie returns to see you one week after discharge. She has been feeling unwell over the last few days with fevers and increasing abdominal pain. She has noticed redness of the skin around her abdominal wounds.
On examination, Cherie looks well but tired. Her temperature is 37.3 °C, blood pressure is
118/78 mmHg, heart rate 75/min regular, respiratory rate is 14/min and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Her abdomen is soft but generally tender. The remainder of her examination is normal.
What are the most likely diagnoses? Write four (4) diagnoses.
- …
- …
- …
- …
