Atrial fibrillation (AF) and atrial flutter (AFl) are two common types of supraventricular tachycardia characterized by rapid and irregular heartbeats. Here’s a detailed overview of their diagnosis, differential diagnosis, and management:
Diagnosis
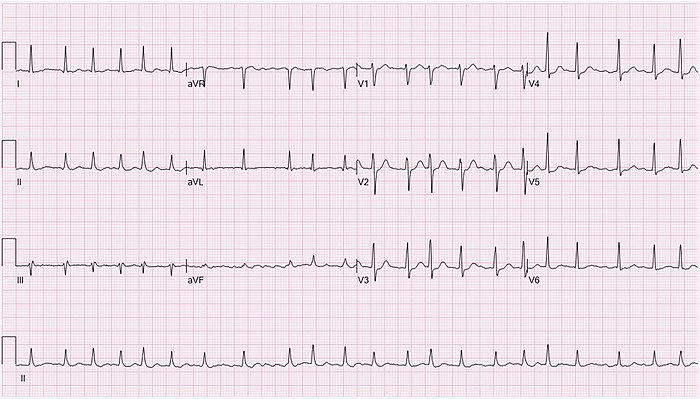
Atrial Fibrillation
- Clinical Presentation: Palpitations, fatigue, dyspnea, chest pain, dizziness, or it may be asymptomatic.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Characterized by irregular R-R intervals and absence of distinct P waves.
- Holter Monitor: For intermittent AF, a 24-hour (or longer) ECG may capture episodes.
- Echocardiography: To assess structural heart disease, ventricular function, and atrial size.
- Laboratory Tests: TFT, FBC, UEC to rule out thyroid disease, anemia, and electrolyte imbalances.
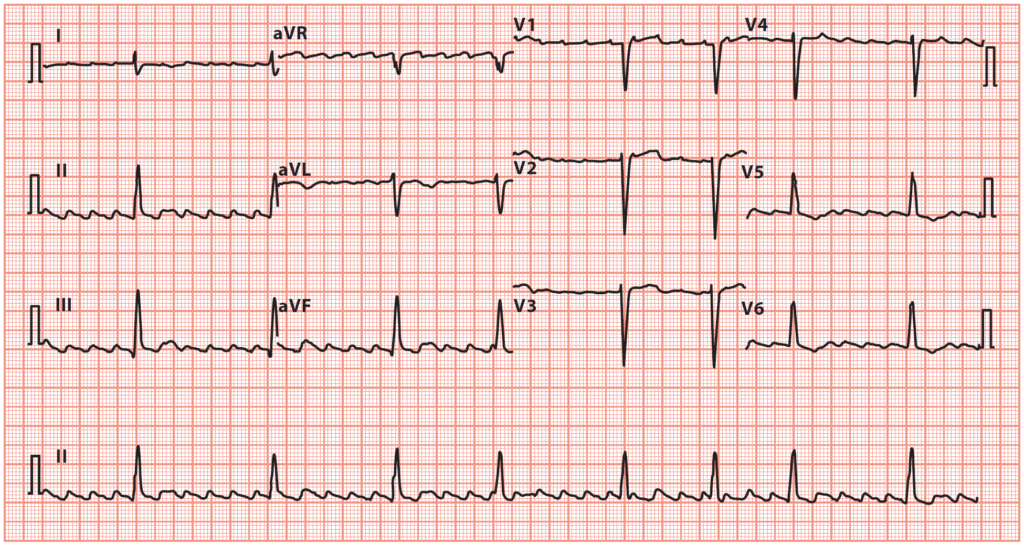
Atrial Flutter
- Clinical Presentation: Similar to AF, but often with more regular palpitations.
- ECG: Shows characteristic “sawtooth” flutter waves, especially in leads II, III, and aVF.
- Echocardiography: To assess the heart structure and function.
- Electrophysiology Study (EPS): Sometimes used for definitive diagnosis and therapeutic ablation.
- Laboratory Tests: TFTs, FBC, UEC to rule out thyroid disease, anemia, and electrolyte imbalances.
Differential Diagnosis
- Adenosine: This can be used to block AV nodal conduction which can make defining the underlying problem easier, and in some cases convert the patient back to sinus rhythm
- Sinus Tachycardia with Sinus Arrhythmia: Regular rhythm with normal P wave preceding each QRS complex.
- Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT): Irregular rhythm but with multiple distinct P wave morphologies.
- Other Supraventricular Tachycardias: Such as AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) or AV reentrant tachycardia (AVRT).
- Ventricular Tachycardia: Differentiated by QRS complex width and morphology.
Management
Atrial Fibrillation
- Rate Control
- Acute
- Metoprolol 2.5-5mg IV, repeat every 5 minutes up to 3 doses
- Digoxin and Amiodarone as additional
- Chronic
- Atenolol 25-100mg oral OD
- Metoprolol 25-100mg oral BD
- Diltiazem MR 180-360 oral OD if BB contraindicated
- Acute
- Rhythm Control:
- Electrical cardioversion in selected patients.
- If AF < 48 hours can be done emergently
- If AF > 48 hours we need 3/52 of anticoagulation
- Pharmacological cardioversion
- Flecanide or Amiodarone IV
- Chronic
- Sotalol 40-160mg oral BD
- Flecanide or Amiodarone oral
- Electrical cardioversion in selected patients.
- Stroke Prevention:
- Anticoagulation based on risk assessment using CHA2DS2-VASc score.
- Options include
- warfarin
- direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) like rivaroxaban, apixaban, or dabigatran.
- Apixaban 5mg oral BD
- Lifestyle Modification: Addressing underlying causes such as
- hypertension
- obesity, and
- alcohol use.
Atrial Flutter
- Rate Control: Similar to AF with beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers.
- Rhythm Control:
- Catheter ablation is more effective in AFl compared to AF.
- DC Cardioversion can also be used, and is often used earlier
- Stroke Prevention: Similar to AF, based on risk assessment.
- Considerations for Ablation: Catheter ablation is often considered as a first-line treatment for AFl due to its high success rate.
General Considerations
- Lifestyle and Risk Factor Management
- Control of Comorbidities: Hypertension, diabetes, and heart failure.
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight management, smoking cessation, and limiting alcohol intake.
- Long-Term Monitoring
- Stroke Risk: Regular reassessment of the need for anticoagulation.
- Heart Failure: Monitor for signs of deterioration.
- Recurrence of Arrhythmia: Especially in those with intermittent episodes.
