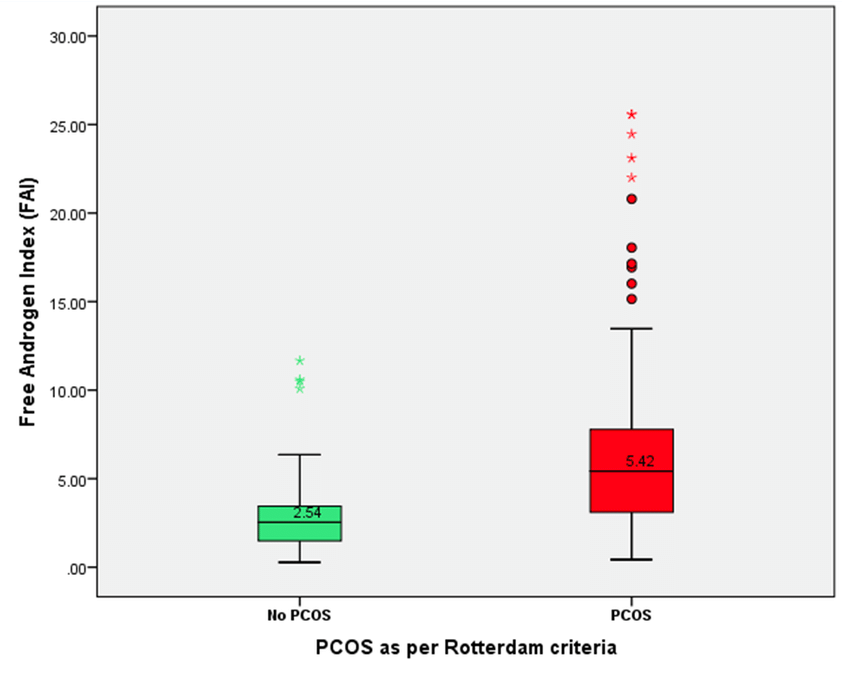
The Free Androgen Index (FAI) is a calculated value used to estimate the amount of bioavailable testosterone in the bloodstream. It’s determined by taking the total testosterone level and dividing it by the sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) level, and then multiplying by 100 to get a percentage.
The Free Androgen Index is useful in several clinical situations:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Women with PCOS often have elevated levels of androgens, which can contribute to symptoms such as hirsutism (excessive hair growth), acne, and menstrual irregularities. FAI can be used as one of the diagnostic markers to assess the androgenic status of these patients.
- Hypogonadism in Men: Hypogonadism refers to the underproduction of testosterone by the testes. While total testosterone is commonly assessed, FAI can provide additional insight into how much testosterone is available to tissues.
- Conditions affecting SHBG Levels: SHBG levels can be influenced by various factors such as certain medications, liver disease, hyperthyroidism, and obesity. In such conditions, while the total testosterone might appear normal, the FAI can offer a clearer picture of bioavailable testosterone.
- Assessment of Androgen Status in Women: Besides PCOS, there are other conditions where assessing androgen status in women is vital, such as congenital adrenal hyperplasia or androgen-secreting tumors. FAI can be a tool to evaluate the androgen excess in such situations.
- Testosterone Therapy Monitoring: In individuals receiving testosterone therapy, the FAI can be used alongside other parameters to monitor treatment efficacy and adjust dosing.
- Post-Menopausal Androgen Status: After menopause, the ovarian production of estrogens decreases, but the ovaries continue to produce androgens. FAI can be used to assess the androgenic status in post-menopausal women, especially if symptoms of androgen excess or deficiency are present.
However, it’s essential to understand that while FAI provides useful information, it is a calculated value and not a direct measurement. Other direct measurements, such as free testosterone assays, can also be used, although each method has its advantages and limitations.